![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
127 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
What are attitude |
The thoughts and evaluation of a person object or idea |
|
|
|
What are the 3 components of attitudes |
ABC 1)Affective 2)Behavioural 3)Cogntive |
|
|
|
What are affectively based attitudes ( where our attitudes come from) |
Based on people's emotions and feelings towards the attitude object |
|
|
|
How are affectivlty based attitudes created (1) |
A) classical conditioning -parining a neutral stimuli (cs) with a positive or negative evaluation (ucs) -creating a psotive or negative evaluation to the cs |
|
|
|
How are affectivlty based attitudes created (2) |
Attitudes are a reflection of our values -attitudes reflect our religious or moral beliefs -attitudes serve to validate these values not correct them |
|
|
|
What are the 3 components of affective based attitudes |
1) result from non rational examinations 2) thry are not based on logic 3) linked to a person's values |
|
|
|
What is a cognitively based attitude |
An attitude based on a person's beliefs about the properties of an attitude object -used to classify the pluses or minuses of an object |
|
|
|
How are cognitively based attitudes created (1) |
Instrumental conditioning -paring a behavior with anticipated reward or avoidance of an embarrassing problem (Acne cleansers) |
|
|
|
How are cognitively based attitudes created (2) |
Observational learning -observing that models obtain rewards increases likelihood that the observer will repeat that behavior |
|
|
|
What are behaviorally based attitudes |
Based on observations of of how one behaves toward an attitude object |
|
|
|
What is self perception theory |
People don't knoe how they feel until thry see how they behave -Explains how behaviorally based attitudes change attitudes |
|
|
|
What are the 2 aspects of self perception theory |
-initial attitude is weak -no other plausible explanation for the behavior |
|
|
|
What are the 2 stated of attitudes |
Explicit level Implicit level |
|
|
|
What is the explicit level |
Attitudes that we consciously endorse and can easily report -rooted in recent experiences |
|
|
|
What is the implicit level |
Attitudes that are involuntary, uncontrollable and unconscious -nearly impossible to change -rooted in childhood experiences |
|
|
|
Do attitudes predict behaviors |
No -laPierre -Wicker |
|
|
|
What is the theory of planned behavior |
best predictor of people's planned behavior is the person intention to do the behavior |
|
|
|
What are the elects if the theory of planned behavior |
A+S+P =intentions 1)attitude towards the behavior
2)subjective norms (belief of hoe other people they care about eill see the behavior)
3)perceived behavioral control (ease the person can perform the behavior) |
|
|
|
What produces effective behavioral change in intervention programs |
Perceived behavioral control -Intervention programs that develop skills not just passive interventions |
|
|
|
What does nit work in effective AIDs reduction |
-messages that create fear -persinal stories or history -communicatiins delivered by lay people (vers knowledgeable people) |
|
|
|
What is the yale attitude change approach |
Studys the conditions where people are more likely to change their attitudes in response to persuasive messages -use a message learning approach |
|
|
|
What is the message learning approach to attitude change |
Learning a new attitude is like learning any other behavior -new attitude has to be learned and rewarded and old have to be forgotten and not rewarded |
|
|
|
What is persuasive communication |
Communication advocating a particular side of an issue |
|
|
|
What is needed for persuasive communication (yale attitude change) |
1) source of the communication 2) the nature of the communication 3) the nature of the audience 4) the nature of the media |
|
|
|
What does the yale attitude change approach focus on |
-who -what -whom -what way |
|
|
|
What are the 2 kinds of effective communicatiors |
-people who are seen as trustworthy (experts)( no ulterior motives) -people who are simular to the audience, attractive and positive reputations |
|
|
|
What are the factors of what is being presented (message factors) |
Nature of the arguments -how many arguments -one side of issue or both -draw a conclusion or not
Fear appeals -get attention -followed by recommendation |
|
|
|
What determines is someone picks one side ot both |
-number of the quality arguments -audience support -auduence refute the arguments |
|
|
|
What are the 3 recipient factors |
1) whatgullible personality 2) intelligence (retention and yielding) 3) self esteem |
|
|
|
What is the process approach to attitude change |
1) we think about what is said, who and how it is said 2) what we think about the message influences our acceptance
|
|
|
|
What are the 2 ways persuasive communication can cause an attitude change in the heuristic systematic model of persuasion |
Systenatic and heuristic processing |
|
|
|
What us systemic processing |
People process and think about the merits and validity of the arguments |
|
|
|
What is heuristic processing |
People use mental shortcuts or persuasion cues to assess the merits and validity if the message (experts are always right) (Lots of arguments to support his position) |
|
|
|
In the elaboration likelihood model what are the 2 ways to persuasive communication can cause attitude change |
1) central route 2) peripheral route |
|
|
|
What is the central route |
When people are motivated and have the ability to pay attention to the arguments in the communication |
|
|
|
What is the peripheral route |
When people do not pay attention to the arguments but are instead swayed by surface characteristics |
|
|
|
When do people use central route or systematic processing |

-motivated -interest -ability to pay attention |
|
|
|
When do people use peripheral route or heuristic processing |

-bored -tired -cant concentrate |
|
|
|
What type of advertising is best for cognitive based attitudes |
Using rational arguments and personal relevance |
|
|
|
What type of adver is best for affectivlty based attitudes |
Using enotion |
|
|
|
What is cognitive dissonance (motivational arousal) |
Feeling of discomfort or tension from the realization that one's behavior isn't consistent with one's attitudes or that one hold two conflicting attitudes -when we do something stupid -motivated to reduce the tension -stopped by changing or justifying the behavior (consonance) |
|
|
|
When is dissonance maximized |
-When choices we make contrary to our moral code -When behaviors violate our own self standards or self guides |
|
|
|
What is post decision dissonance |
Dissonance is inevitably aroused after a person makes a decision -more permanent decision the greater dissonance -ruduced by enhancing the attractiveness of the chosen alternative and and devaluating rejected alternatives |
|
|
|
What is the justification of effort |
The tendency for individuals to increase their liking for something they have worked hard to attain (Self justification effects) |
|
|
|
What is counter attitudinal advocacy |
The process that happens when a person states an opinion or attitude thar runs counter to their private belief -when cant find external justification u find internal justification |
|
|
|
What did Festunger and carlsmith do |
Gave participants $20 or $1 to lie to a fellow student -role of incentives for advocacy - insufficient external justification led people to change their attitudes to make themselves feel like they told the truth |
|
|
|
Look at |

|
|
|
|
What is the rationalization trap |
Dissonance reduction by self justifications that lead to a chain of stupid or immoral actions |
|
|
|
What is self affirmation theory |
People reduce the impact of a dissonance arousing threat to their self concept by..
-focusing and affirming their competence on a other dimensions unrelated to the threat -temporarily getting a self esteem boost -reminding people of their moral values |
|
|
|
What is social influence |
Changing in behavior from the real or imaged influence of other people |
|
|
|
What are the 3 kinds of social influence |
1) conformity 2) compliance 3) obedience |
|
|
|
What is conformity |
A change in behavour due to the real or imaged influence of others that bring out behavior in line with social norms |
|
|
|
What is compliance |
Influence directed by one person towards another to change the other person's behavior -changed behavior due to a direct request from another person |
|
|
|
What is obedience |
Direct ordering of someone to do something -person who orders is perceived to have a power advantage over the other -authority figure |
|
|
|
Social influence in everyday life |
-affects us without our awareness ot knowledge -can lead to negative behaviour like eating disorders |
|
|
|
What are the 2 main reasin for conforming |
1) informational social influence 2) normative social influence |
|
|
|
What is informational social influence |
Conforming because we believe that others interpretations are more correct to help use choose the right course of action -when a task is important and we want to be accurate we conform to the other people behavior (Need to know whats right) (Used when a situation is ambiguous or in crisis situation or experts) Ex. Sherif study |
|
|
|
What are the 2 kinds informational social influence |
Private acceptance Public acceptance |
|
|
|
What is private acceptance |
Conforming to other peoples behavior out or belief that what thry are doing or saying is right |
|
|
|
What is public acceptance |
Conforming to other peopoe behaviour publicly without believing in what they are doing or saying -go along to get along -higer amount of conformity at this level |
|
|
|
What is mass psychogenic influence |
When simular physical symptoms where there is no known physical of medical cause in a group of people -When informational social influence goes really wrong |
|
|
|
What is normative social influence |
Conformity to the attitudes and behaviors of other people when we want to -be liked and accepted -remain a group member -gain advantages of group membership -aviod ridicule, punishment or rejection |
|
|
|
What are social norms |
Implicet or explicit rules a group has for the acceptable values, beliefs and behaviours of group members |
|
|
|
What are reference groups |
Conform to norms of a group when tge group is important to use and we want the members to like and accept us -high cost to losing these people |
|
|
|
What were the asch line judgment studies |
-lines -66% conformed to the group by giving the wrong answer at least once -1/3 conformed on all trials -shows that we conform even when the group isn't important to us -affraid to look foolish or be alone in front of strangers -normative social influence |
|
|
|
What did Berns find |
In fmri study -non conformity activated the amygdala area sensitive to negative emotions -caudate nucleus brain area responsive to social behavior |
|
|
|
When does conformity drop |
1) cohesion is low 2) group larger than 4 3) social support for the deviant is present 4) participants respond in private |
|
|
|
What is social impact theory |
Predicts that the likelihood of conforming to social influence depends on ☆-stength (how important the group is to u) ☆
☆-immediacy (how close the group is to u in space and time during influence attempt) ☆
-number (how many people are in the group) |

|
|
|
How can we resist inappropriate normative social influence |
-beacoming aware of social norms -finding an ally -gathering idiosyncrasy credits (credits gained over time by conforming to norms of a group in the past) |
|
|
|
What do groups do to bring a deviant person back in line with the group |
-increase communication to the person to create conformity pressure -cold shoulder response -group reaction if cant bring back in line |
|
|
|
What is minority influence |
When a minority of a group influences the behavior or beliefs of the majority -internalization of new norms and behavior -present new info that makes members reconsider |
|
|
|
Look at |

|
|
|
|
What does compliance involve |
Elaborate and planned construction of reality to increase the likelihood of agreement |
|
|
|
What are the 5 kinds of planned construction |
1) ingratiation 2) foot in the door 3) door in the face 4) TNA effect 5) low balling |
|
|
|
What is ingratiation |
Getting people to like you so they will do you favors -making the person feel good about themselves -use self presentational ploys -self depreciation and self disclosure |
|
|
|
What are self presentational ploys |
??? -a brief though of 1-2 secind when asking for a favor (touch gives a dominance view) |
|
|
|
What is the foot in the door technique |
Get people to comply with a large request -start with a small request -then present a large request Works because to shifts in self perception (u do favors, are nice and reasonable so by saying no u question such assumptions about yourself) |
|
|
|
What is the door in the face technique |
-large request that u wont expect -present a smaller request that is more reasonable to u r more likely to agree Uses reciprocity norm and self perception as u see yourself as reasonable, fair and open to negotiation |
|
|
|
What is the reciprocity norm |
Is someone does something nice for use we are more likely to reciprocate by doing something nice for them |
|
|
|
What us the TNA effect |
Thats not all effect -example of reciprocity norm |
|
|
|
What are low balling techniques |
Works by -getting a constomer to agree to purchase a product at a low price then raising the price -still make the purchase even at new price |
|
|
|
Why does low balling work |
1) change in self perception (already agreed to lower) 2) post dissonance reduction (pleasure u would have lost if you didn't buy it)
|
|
|
|
What is obedience to legitimate authority |
Under stong social pressure we will conform to the authority even when it means doing something immoral (milgrams shock study) |
|
|
|
Milligrams study |
-the power of informational social influence (clear signs of authority) -self justification or entrapment (already did a few shocks so they felt the pressure to continue |
|
|
|
What is entrapment |
The process where individuals escalate commitment to a course of action to justify investment of time money or effort |
|
|
|
What is a group |
Collection of 3 of or more people who interact with eachother and are interdependent |
|
|
|
What is a dyad |
Two person group |
|
|
|
What us interdependent mean |
1) meets the needs of group members 2) group goals and personal needs necessitate that people rely on one another |
|
|
|
What are the 2 properties that all groups have |
1) structural properties 2) psychological properties |
|
|
|
What are the 4 kinds of structural properties |
1) roles (expectations and duties of members) 2) status (social positions of members) 3) norms (rules governing groups behaviour) 4) cohesiveness (sum of all pressures causing people to stay in a group) |
|
|
|
What are some psychological properties of groups |
1) shared reality (common beliefs) 2) uniformity of opinion (group consensus) 3) perceived interdependence -Contrsuction of shared reality has been called a fundental feature of group processes |
|
|
|
What does interdependce refer to |
-perceived reciprocal role relationships between members -common fate -change in the state of any subpart changes the state of other subparts |
|
|
|
What basic human needs are met by forming relationships (groups) |
1) need to belong us an innate need 2) social identity (identify who they are and who thry will become) 3) motivated people to be involved in social change |
|
|
|
What happens when others act as an audience or co actors |
-improves perfoe on simple tasks (social facilitation) -poor persinmace on new or difficult tasks (social inhibition) |
|
|
|
What are the 3 theories that suggest that arousal underlies social facilitation |
1) drive theory of social facilitation 2) impession management concerns 3) distraction conflict theory |
|
|
|
What does drive theory of social facilitation state |
Presence of others is arousing |

|
|
|
What does impession management concerns state |
Presence of others makes up apprehensive about being evaluated (evaluation apprehension) |
|
|
|
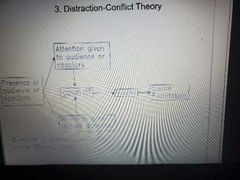
What does distraction conflict theory state |
Presencd of others distracts us from the task at hand |
|
|
|
What are impression management concerns |
The presence of other people causes us to become alert and vigilant and concerned about our performance |
|
|
|
Where does arousal stem from |
-anticipating the evaluation if co-actor audience -public challenge to reputation -efforts to show competency |
|
|
|
What is social loafing |
When people are working or performing in the presence of others and individual performance cannot be evaluated -do worse on simple tasks and better on complex -become relaxed and improves performance -free rider effect -more in men in individualist cultures |
|
|
|
What is the shift toward polarization |
Groups make riskier and more conservative judgments than individuals working alone -know as the risky shift |
|
|
|
This shift is due to what |
1) attention to group values 2) attention to change process |
|
|
|
What is group think |
Thinking where mailing group cohesion is more important than the facts -reflectd motivational and information processing errors - results from how groups construe an issue |
|
|
|
Motivational process error underlying group think |

|
|
|
|
Processing error underlying group think |

|
|
|
|
How to eliminate group think effects |
1) every group member plays a role of critical evaluation (stop mind guard) 2) use of minimal groups 3) use outside evaluators 4) increase time between reading a decision and acting on it |
|
|
|
What is deindividuation |
A state of reduced self evaluation and reduced evaluation apprehension causing anti normative behavior -lose ourselves in a crowd |

|
|
|
When is group decision making better than individual |
1) group members are motivated to search for a solution that is best for the whole group 2) group relies on knowledge and expert persons to guide the decision |
|
|
|
What is group process loss |
Any aspect of group interaction that inhibits good problem solving |
|
|
|
When does process loss happen |

|
|
|
|
What is transactive memory |
Used to describe the contribution to problem solving from the memory of many people |
|
|
|
What is the great person theory |
Ceritan key personality traits make a person a good leader regardless of the situation tgr leader faces -more intelligent -extrovertrd -driven by power -socially skilled -adaptive (Weak relationship between these traits and leadership effectiveness) |
|
|
|
What is the transactional leader style |
Set clear short term goals and reward people who meet them -good job of making sure the needs of the group are met |
|
|
|
What us the transformational leader style |
Inspire followers to focuse on common long term goals -think creatively about needs, inspire, -not liked to personality traits |
|
|
|
What are the 2 leaders in contingency theory leadership |
Task oriented Relationship oriented (Orientation interacts with the am8ut of control the leader has over the group) |
|
|
|
What is a task oriented leader |
Concerned with getting the job done than with feeling and relationships between workers -when situational control is high |
|
|
|
What us relationship oriented leaders |
Concerned with the feelings and relationships between workers -perform best when situational control is moderate |
|
|
|
When us there high situational control |
-leader has excellent relationships with subordinates -leadership is unquestioned and known -work to be done is clearly structured and well defined |
|
|
|
When is there low situational control |
-relarionship with subordinates is poor -work us not well defined -leader is questioned |
|
|
|
What is the elaboration likelihood model |
States there is 2 ways thar persuasive communication can cause an attitude change -central route -peripheral route |
|
|
|
What is fear arousing communication |
A persuasive message that attempts to change attitudes by arousing fear |
|
|
|
What are subliminal messages |
Word or pictures that are not consciously perceived but influence attitudes and behaviors |
|
|
|
What is attitude inoculation |
Process of making people immune to changes of their attitudes by exposing them to small doesed of opposite arguments |
|
|
|
What is contagion |
Rapid transmission of emotions or behavior through a crowd |
|
|
|
What is scoail facilitation |
Tendency for people to do better on simple tasks than complex tasks when they are aroused and in the presence of others |
|
|
|
What is social dilemma |
Conflict in which the most beneficial actions of an individual will be harmful to most others |
|

