![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
123 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
What is the propinquity effect |
The more we see other people the more likely we are to think positively about and interact with them -concept of functional distance by Fedtinger |
|
|
|
Why does the propinquity effect work |
Familiarity or mere exposure effect -liking increases the more exposure we have to someone -feelings can be anything but negative |
|
|
|
Online relationshipships |
-people are more comfortable revealing their "true" self -success depends if the relationship continues offline -moslty used by introverts |
|
|
|
What is the social compensation effect |
-sites are used by introverts and those poorer social skills who have trouble forming relationships in person |
|
|
|
Similarity |
We are attracted to people who are simular to us especially in attitudes and values -stronger in mutual friendships -includes attachment style, leisure and recreational activities
|
|
|
|
What is the opposite of similarity |
Complementarity -attracted to people who are opposite to us |
|
|
|
Evidence of similarity |
-may be bidirectional but this perception may be illusory |
|
|
|
Complementarity relationships |
Are short lived and less strong -reflects admiration, inttigue, and curiosity Rather than liking |
|
|
|
What is reciprocal liking |
Liking someone who also likes us -only have influence is you have self esteem -self verification effects -one of the prime determinants of interpersonal attraction |
|
|
|
The effects of physical attractiveness on liking |
Physical attractiveness influences liking -emphazized more by men -true for all -happens at the implicit (first impressions) and explicit level |
|
|
|
What are the 3 facial factors that explain attractiveness |
1) preference for population average (Spatial difference of the face compared to the population spatial average face)
2) preference for bilateral symmetry (Both sides of face should be similar)
3) sexual dimorphism (Female face conveys female traits and vis versa) |
|
|
|
Why are these people found attractive |
1) signal reproductive success by indicating mate quality and viability of the offspring 2) indicate presence of good genes (low contagion and high diseases resistance) 3) mates are likely to live long enough to ensure the reproductive success of any child |
|
|
|
Culture and attractiveness |
Firm cross cultural agreement on human facial attractiveness -attractive people get preferential treatment (beautiful is good)
|
|
|
|
How do close relationships differ from good friends and intimate relationships |
1) spend more time together 2) spend time together in a wider range of activities 3) exclude other people 4) partners provide emotional support 5) high degree of self disclosure |
|
|
|
What are the two distinctions in Hatfield and Walster theory of love |
Passionate love Companionate love |
|
|
|
What is passionate love |
The feeling of intense longing accompanied by heightened physiological arousal (lust) we feel for another person |

|
|
|
What is companionate love |
Feelings of intimacy and affection we feel for another person with whom are lives are intertwined |

|
|
|
What is the VTA area |
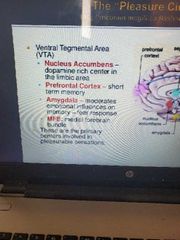
The pleasure circuit |
|
|
|
Passionate love in Western individualistic cultures |
Not in collectivist cultures -passionate love is culturally specific
|
|
|
|
What is the Romantic myth |
There is someone out there for you
This person will be -be the right person for you -will resolve and fulfill all your romantic longings -make your life complete |
|
|
|
Gender and love |

|

|
|
|
What is companionate love |
-Has passion and intensity -reciprocal liking, respect and common interests -caring and high levels of self disclosure |
|
|
|
What is self disclosure |
Belief that lives are intertwined or interdependent |
|
|
|
What is the sociobiological approach (evolutionary explanation) |
-derived from evolutionary biology -reproducation is much more costly for females than males -dating and mating are behaviors that reflect a competition for desirable mates -mating strategies |
|
|
|
Female competition |
Based on females belief that -males seek fertile partners -compete on attributes that signal frrility like health, attractiveness and youth |
|
|
|
Male competition |
Based on the beliefs -females seek males who can provide for them and their children -compete with eachother on dimensions that imply protection and support (economic and career opportunities) -women are choosier than males |
|
|
|
What does Bowlby argue about infants |
Infants devolop internal working models about the nature of relationships from interactions with primary caregivers -remian throughout life and form expectations about the nature of future interpersonal relationships -develop relationship schemas |
|
|
|
What are the 2 kinds of internal working models |
Working models of others Working models of the self |
|
|
|
What are Ainsworth 3 types of attachment styles |
Secure attachment Avoidant attachment Anxious ambivalent attachment |
|
|
|
Adult Attachment Interview idea |
Parents recollections of their parents responsiveness predicted the attachment style of these adults with their own children -socialized into future generations |
|
|
|
What did Bartholomew and horowitz conclude |
2 types of avoidant attachment -4 adult attachments |
|
|
|
What are the 4 adult attachments |

Secure Preoccupied (anxious) Dismissive Fearful |
|
|
|
What is attachment drift |
Specific to general |
|
|
|
Social exchange theories of how people feel about their relationships depends on.... |
1) perceived rewards and costs present in the relationship
2) the kind of relationship people believe they deserve (comparison level)
3) their chances of having a better relationship with someone else (comparison level for alternatives) |
|
|
|
What determines the comparison level |

Reward/ cost ratio
|
|
|
|
What is equity theory |
People are happiest in relationships in which the rewards and cost that a person experiences and the contributions that are made to relationships are roughly equal to rewards, coasts and contributions of the other person |
|
|
|
Exchange relationships (equity theory) |
Casual relationships governed by the need for a comparable ratio of rewards and costs (equal concerns) -characterizes short term relationships -focuses on fairness |

|
|
|
Communal relationships (equity theory) |
Long term intimate relationships in which the primary concern is not with equity but being responsive to the others needs -focused on responsiveness to partners needs |

|
|
|
Those in a committed relationship are more likely..... to maintain commitment to the relationship |
-rate other attractive people as less attractive -convince themselves that other people arnt attractive -let others know they are taken -more forgiving of mistakes
|
|
|
|
What are positive illusions |
Romantic idealizations for our relationships and partners to maintain the relationship -posstive illusions enhance relationships under a limited set of conditions |
|
|
|
The more we idealize our partner.... |
-The greater our satisfaction with the relationship -more likely the relationship will continue -over time each partner comes to live up to the other person's idealizations |
|
|
|
When do positive illusions enhance relationships |
-postive illusiom at the newlywed stage reported greater feelings marital love |
|
|
|
What is misattribution of arousal |
The process whereby people make mistaken inferences about what is causing them to feel the way they do |
|
|
|
What is secure attachment |
Characterized by trust, lack of concern with abandonment and view that one is worthy and loved |
|
|
|
What is avoidant attachment |
Characterized by a suppression of attachment needs because attempts to be intimate have been rebuffed -difficult to develop intimate relationships |
|
|
|
What is anxious attachment |
Characterized by a concern that others will not reciprocate ones desire for intimacy -higher levels of anxiety |
|
|
|
What is fearful avoidant style |
Close relationshipso are avoided because of mistrust and fears of being hurt |
|
|
|
What is Dismissive avoidant style |
The person is self sufficient and claims not to need close relationships |
|
|
|
What is prosocial behavior or altruism |
Any act performed by another person that has -no explicit benefit for actor -obvious benefits for the recipient (prosocial behavior) -sometimes costs for the actor (altruistic behavior) |
|
|
|
Evolutionary psychology suggests what prosocial behavior occurs because |
Kin selection The norm reciprocity |
|
|
|
What is kin selection |
The idea that behavior that helps a genetic relative is favored by natural selection |
|
|
|
What is norm reciprocity |
When people are unrelated -it is expected that helping others will increase the likelihood that others will help us in the future |
|
|
|
What does social exchange theory argue about prosocial behavior |
Prosocial behavior It is based on our own self interest |
|
|
|
Self interest |
-stems from the desire to maximize our outcomes and minimize our costs - |
|
|
|
What is bystander calculus |
-costs and rewards of helping -costs and rewards of not helping |
|
|
|
What is empathy |
The ability to put ourselves in the place of another person, experiencing events and emotions the way that person experiences them. |
|
|
|
How are empathy and sympathy different |
Empathy differs from sympathy in that in sympathy we express or mirrors another person's distress but we do not experience that distress |
|
|
|
What is empathy altruism hypothesis |
Suggests that if a person feels empathy towards another person, the person will offer help, regardless of what the favor doer has to gain or loose |
|
|
|
Why mood states influence helping |
Feel good do good effect -more likely to help when they are in a good mood
|
|
|
|
Why are you more likely to help when they are in a good mood |
-shift in perspective (look on the bright side) -helping others prolongs our own good mood -increase in self focused attention on norms and values -acts as a go signal expanding our current thoughts and actions |
|
|
|
What us negative state relief hypothesis |
The idea that people help in order to alleviate their own sadness and distress -also known as egoism hypothesis -more likely to help when we feel guilty, sad or distressed |
|
|
|
What is the bystander effect |
The greater the number of bystanders who witness and emergency the less likely any one of then will help -kitty genovese murder |
|
|
|
What us diffusion of responsibility |
Decrease in each bystander's sense of responsibility to help as the number of witnesses to an emergency or crisis increases |
|
|
|
What do Latane and Darley suggest |
People go through 5 decision making steps before they help someone -if bystanders fail to take any one of the 5 steps they won't help |
|
|
|
What are the 5 steps to helping |
1) notice the event 2) interpret the event as an emergency 3) assume responsibility 4) know appropriate form of assistance 5) decide to implement help |
|
|
|
What is and causes pluralistic ignorance |
Assumes nothing is wrong because no one else is worried or doing anything and that leads to diffusion of responsibility -an answer to steps 1-3 causes it |
|
|
|
What is prosocial behavior |
Any act performed with the goal of benefiting another person |
|
|
|
What is altruism |
The desire to help other even if it involves a cost to the helper |
|
|
|
What is altruistic personality |
Aspects of a person's makeup that causes him or her to help others in a wide variety of situations |
|
|
|
Wjat is an in group |
The group with which an individual identifies with and feels a member of |
|
|
|
What is an out group |
A group with which the individual does not identify with |
|
|
|
What is the urban overload hypothesis |
Theory that because people living in cities are constantly being bombarded with stimulation -they keep to themselves to avoid being completely overloaded by it |
|
|
|
What is aggression |
Intentional behavior aimed at causing physical or psychological pain -intent to harm separates aggression from assertiveness and ambition |
|
|
|
What is hostile aggression |
Agression stemming from feelings of anger and aimed at inflicting pain or injury |
|
|
|
What is instrumental aggression |
Aggression as a means to a goal other than causing pain |
|
|
|
Why do evolutionary psychologists believe males are more aggressive |
-females will choose them for their superior genes (aggression= status) -males knowledge of his paternity can be assured -consistent with crime stats |
|
|
|
Alcohol and aggression |
More people drink the more likely they are to behave aggressively -alcohol lowers our threshold for aggressive behavior and reduces our inhibitions so that we are more likely to perform behaviors that we would normally keep in check -our ability to considered the consequences of our actions is reduced |

|
|
|
What is frustration |
The perception that you are being prevented from obtaining a goal -goal blocking if it is unpleasant leads to aggression |
|
|
|
What is frustration aggression theory |
Theory that frustration will increase the probability of an aggressive response -an aggressive act can be traced back to a frustrating event |
|
|
|
Chances that frustration will lead to aggression are increased when..... |
1) you are close to reaching your goal and are prevented from doing so 2) frustration is unexpected 3) goal blocking is seen as arbitrary 4) frustration source seen as illegitimate |
|
|
|
When does frustration not lead to aggression |
1) if the power or strength of the person causing the frustration is considerable 2) if the person causing the frustration can retaliate and is likely to do so 3) if frustration is understandable, legitimate and unintentional |
|
|
|
What is relative deprivation |
The perception that you have less than you deserve, less than what you have been led to expect, or less than what people simular to you have |
|
|
|
Know |

|
|
|
|
What are our sources of aggression |
1) ditect provocation 2) social exclusion 3) presence of aggressive objects |
|
|
|
Violent video games |

|

|
|
|
Violent video games conclusion |
Evidence strongly suggests that exposure to violent video games is up causal risk factor for increased aggressive behaviour, aggressive cognition, and aggressive effect and decreased empathy and prosocial behaviour |
|
|
|
What does the exposure to erotica cause |
-increase in physical arousal -an increase or decrease of current emotional state depends on the type of erotic material (Sexual arousal and aggression cause increases) |
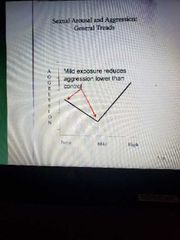
|
|
|
What can xxx rated movies cause |
-degrade women -mix sex and violence where females are victims -people may want to do what thry see in movies -may result in an increase of aggression |
|
|
|
What are the effects of prolonged exposure to pornigraphy |
-see rape as not a serious offense -express less sympathy toward rape victims -greater acceptance of rape myths -more tolerant to bizarre forms of pornography |
|
|
|
Know |
In these movies it is often the violent portrayals not the sexual content that contributes to the negative effects |
|
|
|
The numbing effect of media violence |

|
|
|
|
What is catharsis |
The notion that blowing off steam by... -performing an aggressive act -watching others engage in aggressive behaviors (Relieves built up aggressive energy and reduces the likelihood of further aggressive behavior) |
|
|
|
Results of many studies do not support the catharsis hypothesis |
-peoppe often behave more aggressively after being given the opportunity to vent their anger -watching competitive or aggressive games tends to increase aggression -even more so if angered or aroused |
|
|
|
What is social learning theory |
Theory that we learn social behavior by observing others and imitating them |
|
|
|
What is prejudice |
A hostile or negative attitude. |
|
|
|
What are the 3 components of prejudices |
1) an affective or emotional component (emotion liked with the attitude) 2) cognitive component ( the thoughts that make the attitude) 3) behavioral component (ones actions) |
|
|
|
What is a stereotype |
A generalization about a group of people in winch identical characteristics are assigned to virtually all members of the group -cognitive component |
|
|
|
What is discrimination |
Unjustified negative or harmful action towards a member of a group simply because they were a member of that group -behavioural component |
|
|
|
What are the groups explained by social identity theory |
People are seen as belonging either to.... Our group (in group) Or different group (out group) |
|
|
|
What is in group bias |
The tendency in all humans to evaluate in group members more positively than out group members |
|
|
|
Why do we show in group bias |
-belonging to a group for social identity -having social identity contributes to self esteem -the level we identify with our group the more we are likely to discrimination against the out group |
|
|
|
What is out group homogeneity |
The perception that out group members are more similar to each other than they really are |
|
|
|
What is in group heterogeneity |
The perception that in group members are unique and special and very different from each other |
|
|
|
When are stereotypes activated to increase prejudice |
-when we hear someone else make a narrative remark about a group -when we observe a negative action by one of the group members -stereotypes are just barely suppressed |
|
|
|
What is Divine's two step model that explains how stereotypical beliefs influence cognitive processing |
1) automatic process (stereotypes are automatically triggered) 2) controlled process ( decide whether or not to accept the stereotype) |
|
|
|
What factors influence the automatic activation of stereotypes |
-motivation to control prejudice -the need to feel good about ourselves (self enhancement and impression management concerns) |
|
|
|
What is meta stereotypes |
A person's belief regarding the stereotype that out group members hold about their own group -prejudice also depends on this |
|
|
|
Know |

|
|
|
|
What is ultimate attribution error |

Our tendency to make dispositional attributions about an entire group of people |
|
|
|
What is realistic conflict theory |
Limited resources lead to conflict among groups and results in increased prejudice and discrimination -sherifs study of conflict in a boys camp |
|
|
|
What is mutual interdependence |
Situation in which two or more groups need each other and must depend on each other to accomplish a goal that is important to both groups -prejudice is reduced by common goals |
|
|
|
Know |

|
|
|
|
What is injunctification |
Motivated tendency to see the status quo as the most desirable State of Affairs -people may conclude that social norms are the way things are supposed to be to justify their beliefs |
|
|
|
What us modern prejudice |
Tendecy where people become careful, outwardly acting unprejudiced inwardly maintaining their prejudiced views -no outward hate but increased social distance and values based rejection |
|
|
|
What 3 dimensions folliw people who are more likely to hold negative attributes towards out groups |
-right wing authoritarianism -religious fundamentalism -social dominance orientation |
|
|
|
What is right wing authoritarianism |
-high degree of submission to authority figures -aggression towards groups that are seen as legitimate targets by authority figures -high degree of conformity to rules established by authority figures -mesured by F scale |
|
|
|
What is religious fundamentalism |
- belive in the absolute and literal truth of ones religious beliefs -their religion is right and that forced of evil are threatening to undermine the truth -not to be confused eith being religious |
|
|
|
What is social dominance orientation |
-beilivr that groups of people are inherently unequal -beilive it is acceptable for some groups to benefit more than others and for some groups to receive poorer treatment than others -adoption of legitimizing myths |
|
|
|
What is a stereotype threat |
The apprehension experienced by members of a minority group that they might behave in a manner that confirms an existing cultural stereotype |
|
|
|
Solutions for stereotype threat |

|
|
|
|
Know |

|
|
|
|
What is the jigsaw classroom |
Is a classroom setting designed to reduce prejudice and to raise the self esteem of children by...... -placing them in small desegregated groups -making each child dependent on the other children in the group to learn the course material and do well in the class |
|
|
|
What is the extended contact hypothesis |
The mere knowledge that a member of One's Own group has a close relationship with a member of another group can reduce some one's prejudices towards that group |
|

