![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
19 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Metabolism of glycogen and starch |
Glycogen and starch at insoluble due to their high molecular weight and often form granules in cells Granules have enzymes that synthesize and degrade polymers Glycogen and amylopectin have one reducing end with many non reducing ends (where enzymatic processing occurs) |
|
|
Cellulose is a linear Homopolysaccharide of glucose |

Formed by beta->4 linked chains with hydrogens bonds and additional H bonds Creates a tough and water soluble structure Most abundant in nature Ie: cotton |
|
|
Cellulose metabolism |
Water insoluble and do not have enzyme to hydrolyze beta1-4 linkage (in certain animals) Some fungi bacteria termites secrete cellulase which breaks it down. Cows can bc have bacteria that do it Use for future in fermentation of biomass into biofuels |
|
|
Chitin (may not be on exam) |
Linear homopolysaccharide of N-acetylgucosamine Beta 1-4 linked chains |
|
|
Phi and psi can rotate bonds and form different bond angles |
Not just linear, also helix or 3D |
|
|
Agar and agarose |
Branched heteropolysaccharide composed of agarose Component of cell wall in some seaweeds Used in electrophoresis to separate DNA and can grow bacteria |
|
|
Glycosaminoglycans |
Linear polymers of repeating disaccharide Be able to identify them on basis of nitrogen containing group: N-acetyl-glucosamine or N-acetyl-galactosamine Hydrated molecule that forms proteins in matrix, connective tissue, and lubricants for joints |
|
|
4 Types of glycosaminoglycans |
Hyaluronate, chondroitin 4 sulfate, keratan sulfate, heparin Made up of amino and sulfate groups that create negative charge |
|
|
Heparin and heparan sulfate |
Heparin is linear polymers Heparan sulfate is like heparin polysaccharide but attached to protein Highest negative charge Prevents blood clotting, activated antithrombin Binding to cells regulates formation of blood vessels (signaling molecule) Can also bind to viruses |
|
|
Understand this page including type units and roles |
Back (Definition) |
|
|
Glycoconjugates : glycoproteins |
Carb attached to AA via anomeric C (attached at ser, thr, and asn). Can be O linked or N linked 1/2 of mammals proteins are glycoproteins Play role protein-protein recognition Viral proteins are heavily glycosylated which helps avoid immune system attacks |
|
|
Glycoconjugates: glycolipids |
Lipids with covalent bond obligosaccharide Parts of plant/animal cell membrane; help determine blood groups In gram negative bacteria: these cover pep layer |
|
|
Glycoconjugates: proteoglycans |
Sulfate groups attached to large rod shaped protein in cell membrane 2 classes: syndecans-single transmembrane domain and glypicans- anchored to lipid membrane Interact with a variety of receptors from neighboring cells, regulate cell growth |
|
|
Heparin sulfate can facilitate protein interactions (4 of them) |
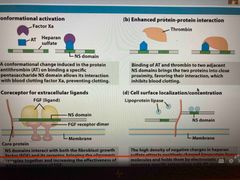
Conformational activation: with antithrombin (AT) prevents blood clotting Enhances protein-protein interactions: increases interaction by binding thrombin and AT which inhibits blood clotting Coreceptor for extracellular ligands: can increase concentration Cell surface localization/concentration: negative charge can attract positive charge of other molecules like lipase |
|
|
Structure of proteoglycans |

Linked to different core proteins Links via anomeric carbon Our tissues have many different core proteins (ie aggrecan) |
|
|
Aggrecan (proteoglycans) |
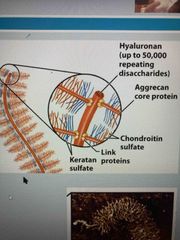
Forms aggregates that hold a lot of water and provide lubrication Covers joints |
|
|
Extracellular matrix |
Strength, elasticity, barrier Contains: Proteoglycan aggregates, collagen fibers, elastin Barrier for tumor cells but some tumor cells have enzyme that breaks down matrix |
|
|
Cells with ECM |

Integral membrane proteins: syndecans, integrins, Link cytoskeleton to ECM and transmit signals to regulate: growth, movement, apoptosis, healing |
|
|
Oligosaccharides and recognition |

Recognizing viruses and bacteria |

