![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
44 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Lipid function |
Storing energy: storing fats for available energy Insulation from environment: high heat capacity (absorb heat), mechanical protection (shock absorbers) Water repellent: keeps surface of animal dry, prevents loss of evaporation Buoyancy: increased density for diving, sound in whales |
|
|
Other function of lipids |
Membrane structure Cofactors for enzymes: vitamin K Signaling molecules (converted into hormones and vitamins) Pigment: tomatoes and birds Antioxidant: vitamin E |
|
|
2 classifications |
1. Fatty acids: storage of lipids and membrane lipids 2. Lipids that do not contain fatty acids: cholesterol |
|
|
Fatty acids |
Carboxylic acids with hc chains 4-36 carbons Almost alll have even number of carbons Most natural fatty acids are unbranched |
|
|
Types of fatty acids |

Saturated: no double binds btw C in chain Monounsaturated: single double bond btw C in chain Polyunsaturated: more than one double bond in chain |
|
|
Fatty acid nomenclature |

Systematic name: cis-9-octadecanoic acid Common name: oleic acid Delta numbering system: count carbons (18) from the carbonyl end and the number of double bonds (1). The delta 9 indicates where the double bond is. Omega number system: count C from terminal end (18) and the use omega instead |
|
|
Need to know 12-20, common name and structure |

Back (Definition) |
|
|
Know this |

See pic |
|
|
Omega 3 fatty acids |

Essential nutrients Cannot sythesize them, Use ALA form diet to synthesize Called omega 3 due to double bond on 3 C |
|
|
Solubility and melting point |
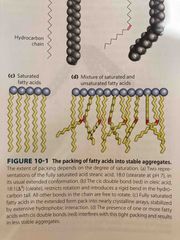
Both Decrease as the chain length increases MP decreases as double bonds increases (they cause less packing) |
|
|
Saturated vs unsaturated |
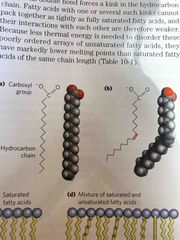
Saturated do not have double bonds Unsaturated have double bonds. Takes less energy to disrupt this structure bc of weak interactions |
|
|
Trans fatty acid |
Dehydrate fatty acid partially to create a lipid to have a larger shelf life This creates a trans double bond Allows for packing more tightly together thus have higher melting point Consuming them causes cardiovascular disease bc they can’t be broken down in the body and create clogged blood vessels |
|
|
Triacylglycerols nonpolar |
Storage lipids Solid called fats, liquid called oils Primary storage of lipids (body fat) Less soluble in water than fatty acids due to esterfication of the carboxylic group (causes polarity of this group to go away) Less dense than water |
|
|
Triacylglycerol structure |

Glycerol with 3 fatty acids chains attached |
|
|
Esterification |

When the OH groups in triglycerides is replaced with alky C chain (carboxylic acid) |
|
|
Fats provide good storage |
AAdvantage over polysaccharides: Carry more energy per C bc they are reduced Carry less water per gram bc nonpolar While glucose is for ST and quick energy needs, fats are for LT (months). Slow delivery and good storage |
|
|
Waxes |
Esters of long chains saturated and unsaturated fatty acids with alcohol Insoluble and high melting point Beeswax is mixture of large number of lipids |
|
|
Variety of functions of waxes |
Storage of fuel (plankton) Protection for hair and skin Waterproofing birds feathers Protection from evaporation in plants Ointments, polishes, lotions |
|
|
Structural lipids |

Contain nonpolar tails and polar heads Usually attached to fatty acids Can have different: backbone, fatty acid, or head group (which determine property of membrane) Know the 4 |
|
|
Glycerophospholipids |

Primary make up of membranes 2 fatty acids form ester linkage with first and second hydroxyl groups of L-glycerol 3 phosphate Phosphate group is charged at pH allowing binding to happen due to higher polarity (notice two Os with - charges) |
|
|
Unsaturated structure |

Unsaturated fatty acids are commonly found connected to C2 of glycerol 3 phosphate |
|
|
Naming |

Based on head group |
|
|
Phosphotudylcholine |

Major component of eukaryotic cell membranes Prokaryotes, including e.coli cannot synthesize it Family of lipids bc fatty acid chains can vary in length |
|
|
Ether lipids: plasmalogen |

Ether linked Common in vertebrae heart tissue Function is not well understood: Resistant to cleavage by lipase May increase membrane rigidity or antioxidant |
|
|
Ether lipids: platelet-activating factor |
Aliphatic ether analog of phosphatidycholine Acetic acid has esterified position C2 First signaling lipid to be identified and stimulates blood platelet development Also plays role in inflammation |
|
|
Sphingolipids |
-The backbone of sphingolipids is not glycerol, It is a long chain amino alcohol -A fatty acid joined to sphingolipid via an amide linkage rather than an eater bond Polar head is connected to sphingosine by a glycosidic or phosph. Linkage Sugar containing glycosphingolipids are found outside plasma membranes |
|
|
Types of sphingolipids |

Pic |
|
|
Sphingomyelin |

Ceramide (sphingosine+amide linked fatty acid) + phospho. Abundant is myelin sheath |
|
|
Glycosphingolipids and blood groups |

Blood groups are determined by group of sugars on head groups Different antigens are saccahiride chains Structure is based on transferase or not. If we don’t have, then O |
|
|
Structural and signaling lipids are degraded in the lysosome |
Most cells degrade their membrane lipids Phospholipids are degraded phospjolases A-D (cleaves a specific bond) Gangliosides are degraded via enzymatic cleavages Failure to degrade results in build up of lysosome |
|
|
Archeal ether lipids |
Not important |
|
|
Summary of fatty acids |

Back (Definition) |
|
|
Sterol and cholesterol |

Sterol: 4 fused rings, OH polar head, various nonpolar side chains |
|
|
Role of sterols |
Cholesterol in most eukaryotic cells membranes. Modulate fluidity, permeability, thicken it. None in bacteria Obtain from food or synthesize in liver Bound to proteins is transported to tissues via blood vessels Cholesterol will bind to LDL so low LDL is important bc will deposit in your arteries |
|
|
Steroid hormones |

Oxidized sterols Lack alkyl chain making the more polar Synthesize from cholesterol in gonads and adrenal glands Carried through blood (attached to carrier proteins) |
|
|
Aldosterone and cortisol |
Regulate sat excretion |
|
|
Biologically active lipids |
Present in much smaller amount Play roles in signaling molecules Eicosanoids and lipid-soluble vitamins (A D E K) A, D are hormone precursors, E,K are oxidation-reduction cofactors |
|
|
Arachidonic acids yield eicosanoids through enzyme oxidation |

Makes prostaglandins: fever and inflammation Thromboxanes: forms blood clots Leukotrienes: smooth muscle contraction in lungs NSAIDS change structure of Arachidonic to prevent formation of prostaglandins and thromboxanes |
|
|
Vitamin D is synthesized from cholesterol |

Mixed with UV light to create cholecalciferol (vitamin D3) Deficiency can lead to rickets (bowed legs) |
|
|
Vitamin A (retinol) |
Derives from beta-carotene Visual pigment (rhodopsin) Precursor for other hormones involved in signaling Rice was made golden to express proteins that make beta carotene |
|
|
Vitamins E and K |
Repeating isoprene units E acts as an antioxidant K is involved in blood clotting cofactor |
|
|
Polyketides |
Diverse family of compounds synthesized similar to fatty acids biosynthesis |
|
|
8 major categories of bio lipids |

Pic |
|
|
Chart you need |

Pic |

