![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
72 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
if heat is applied, microbes are _________.
|
killed |
|
|
|
if cold temperatures are used, microbial growth is _____________.
|
inhibited |
|
|
|
what are the 5 optimal growth ranges
|
psychrotrophic mesophilic thermophilic hyperthermophilic |
|
|
|
0 - 20 centigrade
|
psychrophilic |
|
|
|
20-30 centigrade |
psychrotrophic
|
|
|
|
25-40 centigrade |
mesophilic |

|
|
|
45-65 centigrade |
|

|
|
|
>80 centigrade
|
hyperthermophilic |
|
|
|
Overall ______________ are more heat resistant than most other forms of life. |
bacteria |

|
|
|
factors affecting heat sensitivity of organisms |
cell density moisture content pH medium composition |
|
|
|
denatures enzymes, dehydrates microbes and kills by oxidation effects |
dry heat |
|
|
|
standard application temperature and time for dry heat is
|
170 centigrade for 2 hours |
|
|
|
_______ ______ denatures enzymes more efficiently
|
moist heat |
|
|
|
_______ ________ methods include pasteurization, boiling and autoclaving |
moist heat |
|
|
|
In __________________ temperatures are maintained at 72 centigrade for 15 seconds or 63 centigrade for 30 minutes to kill designated organisms that are pathogenic or cause spoilage.
|
pasteurization |

|
|
|
__________ 100 centigrade for 10 minutes will kill vegetative bacterial cells; however, it doesn't inactivate endospores. |
boiling |
|
|
|
the most effective method of moist heat sterilization is _____________. |
autoclaving |
|
|
|
_______________ is the use of steam under pressure to sterilize things.
|
autoclaving |
|
|
|
increased _____________ raises the boiling point of water and produces steam with a higher temperature.
|
pressure |

|
|
|
standard conditions for ________________ are 15 psi at 121 C for 15 minutes. |
autoclaving |
|
|
|
_________________ is usually sufficient to kill endospores and render materials sterile |
autoclaving |
|
|
|
______________ _________ __________ is the length of time required to kill all bacteria in a liquid culture at a given temperature. |
thermal death time TDT |
|
|
|
____________ _________ __________ is the temperature required to kill all bacteria in a liquid culture in 10 minutes. |
thermal death point TDP |
|
|
|
____________ __________ ___________ is the time, in minutes, in which 90% of a population of bacteriua at a given temperature will be killed. |
decimal reduction time DRT or D value |
|
|
|
explain why fungi and Bacillus sometimes grow better after heat treatment. |
fungi and Bacillus can produce endospores which are heat activatedhou |
|
|
|
the decimal reduction time DRT is the time it takes to kill 90% of cells present. assume that a DRT value for autoclaving a culture is 1.5 minutes. how long would it take to kill all the cells if 10^6 cells were present? What would happen if you stopped the heating process at 9 minutes.
|
there would be only 1 survivor
|
|
|
|
a biological indicator used in autoclaving is a vial containing 10^9 _________________ _______________ cells that is placed in the autoclave with the material to be sterilized. After autoclaving the vial is incubated and examined for growth. why is this species used as opposed to E. coli or Bacillus subtilis?
|
answer: it is hyperthermophilic which means it is only killed at temperatures in excess of 80 C |
|
|
|
give an example of: incineration pasteurization autoclaving |
pasteurization- milk production autoclaving- pressure cooking |
|
|
|
why are old and young bacillus used in the lab comparison of the bactericidal effects of dry heat and moist heat.
|
bacillus species produce endospores which can withstand temperatures in excess of 100 C. |
|
|
|
____________ differs in wavelength and energy. |
radiation |

|
|
|
the __________ wavelengths have more energy.
|
shorter |
|
|
|
x rays and gamma rays are forms of _____________ radiation. Their principal effect is to ionize water into highly reactive ______ _________ (with unpaired electrons) that can break strands of DNA.
|
free radicals |

|
|
|
variable effecting the influence of radiation?
|
age of cells media composition temperature |
|
|
|
Some ______________ wavelengths are essential for biochemical processes.
|
nonionizing |

|
|
|
animal cells synthesize ______ __ in the presence of light around 300nm
|
Vitamin D |

|
|

is absorbed by |
green plants photosynthetic bacteria |
|
|
|
Nonionizing radiation between 15 and 400 nm is called ______________.
|
Ultraviolet |

|
|
|
Wavelengths below _____ nm are absorbed by air and do not reach living organisms.
|
200 nm |
|
|
|
The most lethal wavelengths, sometimes called biocidal, are in the _____ range, 200-290 nm. these wave lengths correspond to the optimal absorption wavelengths of _____.
|
DNA |

|
|
|
______ wavelengths (290-320 nm) can also cause damage to _____.
|
DNA |

|
|
|
______ wavelengths (320-400 nm) are not as readily absorbed and are therefore less active on living organisms.
|
UVA |
|
|
|
UV WAVELENGTHS 290-320 nm = 200-290 nm = wavelengths < 200 nm = |
UVB UVC UV absorbed by air but not living things |
|
|
|
Wavelengths: -biocidal= -DNA absorbing= -cause some damage to DNA= |
UVB UVA |
|
|
|
Ultraviolet light induces __________ _________ in DNA, which result in mutation. mutations in critical genes may result in the death of the cell unless the damage is repaired. |
thymine dimers |
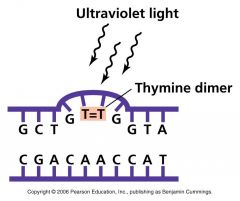
|
|
|
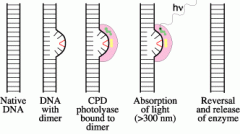
When thymine dimers are exposed to visible light, _____________ are activated; these enzymes split the dimers, restoring the ______ to its undamaged state.
|
photolyases
|
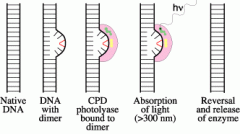
|
|
|
the process of thymine dimers being repaired by photolyases is called ________ __________ or photoreactivation.
|
light repair
|
|
|
|
Another repair mechanism, called ______ ________, is independent of light. Dimers are removed by endonuclease, _____ ___________ replaces the nucleotides, and _____ __________ seals the sugar-phosphate backbone.
|
DNA polymerase DNA ligase |
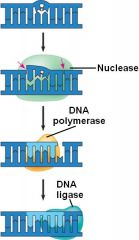
|
|
|
As a sterilizing agent, ultraviolet radiation is limited by its poor _________________ ability.
|
penetrating |
|
|
|
____________ _____________ is used to sterilize some heat-labile solutioons, to decontaminate hospital operating rooms and food processing areas and to disinfect ____________. |
ultraviolet radiation wastewater. |

|
|
|
If the Bacillus had sporulated before exposure to radiation, would that affect the results of of the bacteria vs UV light experiment?
|
endospores are only killed by autoclaving so the Bacillus would have regrown. |
|
|
|
Wide varieties of chemicals called ______________ agents are available for controlling the growth of microbes.
|
antimicrobial |
|
|
|
_____________ are chemical agents used on inanimate objects to lower the level of microbes on their surfaces; ____________ are chemicals used on living tissue to decrease the number of microbes.
|
Disinfectants antiseptics |
|
|
|
Chemicals that result in bacterial death are called ____________ agents. those causing temporary inhibition of growth are ______________ agents.
|
bacteriostatic |
|
|
|
additional variables to consider in selecting an antimicrobial agent include:
|
pH, solubility, _________, organic material present, and ______.
|
$ cost |
|
|
the important criteria when evaluating antimicrobial agents are:
|
length of contact cidal or static |
|
|
|
the standard method for measuring the effectiveness of a chemical agent is the _________ __________ ____________ _________'_ ____-_________ _____. Also known as the use dilution test. |
American official analytical chemist's use-dilution test. |
|
|
|
the three strains of bacteria us in the American official analytical chemist's use-dilution test. are:
|
Salmonella enterica Staphylococcus aureus Pseudomonas aeruginosa |
|
|
|
in 1940 Selman A. Waksman isolated the antibiotic ______________, produced by an actinomycete. This antibiotic was effective against many bacteria that penicillin did not affect.
|
streptomycin |
|
|
|
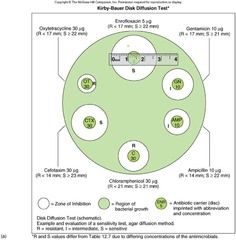
To minimize the variance between laboratories, the standardized ________-_______ _____ for agar diffusion methods is performed in many clinical laboratories with strict quality controls this test uses ________-_________ _____. the agar allows the antimicrobial agent of diffuse freely.
|
Kirby-Bauer test Mueller-Hinton agar |
|
|
|
the standardized Kirby-Bauer test for agar diffusion methods is performed in many clinical laboratories with strict quality controls this test uses ________-_________ _____. the agar allows the antimicrobial agent of diffuse freely.
|
Mueller-Hinton agar
|

|
|
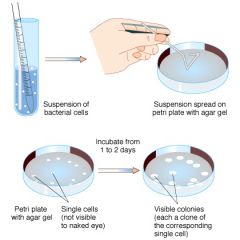
|
2.) When the MIC is determine, inhibition zones can be correlated with MICs. 3.)Then, inhibition zones can be correlated to a standard table to use the disk diffusion method to determine susceptibility. |
|
|
|
the measure (millimeters) of the diameter of the area surrounding the Antimicrobial impregnated disk without bacteria.
|
zone of inhibition
|
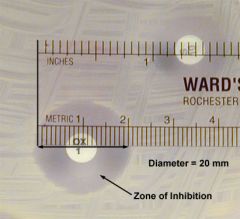
|
|
|
the three terms referring to the diameter of the zone of inhibition are:
|
intermediate susceptible |
|
|
|
Is the disk diffusion technique measuring bacteriostatic or bactericidal activity? Explain. |
bacteriostatic, until a subculture is inoculated to measure bactericidal action. |
|
|
|
In which growth phase is an organism most sensitive to an antimicrobial agent?
|
Log phase |
|
|
|
Bacitracin Cycloserine Ethambutol Isoniazid Vancomycin Beta-lactams Monobactams |
Inhibit cell wall synthesis |
Spectrum of action: narrow Gram + bacteria Va=MRSA Cyloserine=TB ethambutol=TB Isoniazid=TB |
|
|
Aminoglycosides: -Neomycin -Streptomycin -Tobramycin Chloramphenicol Lincosamides -Clindamycin Macrolides -Azithromycin -Erythromycin Tetracyclines Linezolid |
Inhibit protein synthesis |
Gram + Gram - some fungi some protozoa Chloramphenicol= Typhoid FV |
|
|
Polymyxin pyrazinamed (TB) |
alter cytoplasmic membranes |
mostly gram+ |
|
|
Dapsone Sulfonamides Trimethoprim |
Antimetabolites |
Gram + Gram - |
|
|
-Ciprofloxacin Metronidazole Rifampin |
Inhibit nucleic acid synthesis |
spectrum of action: broad Gram- |
|
|
What effect would the presence of tetracycline in the body have on penicillin therapy?
|
tetracycline decreases effects of penicillin by pharmacodynamics antagonism. possible serious or life threatening reaction. |
|
|
|
|
|
|

