![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
12 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What is "canned speech" and when it can be used? |
The speech signals recorded and saved as they are. Playback with as they are, segment boundaries can be manipulated a little. Used when vocabulary small. |
|
|
What are the classes of speech output systems? Describe them. What do they convert to speech? What steps do they include? |
1. Announcement machine: phonetics to speech |
|
|
What steps does symbolic processing have? |
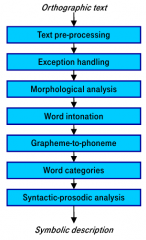
1. Preprocessing: write out abbreviation, distinguish main clauses and subordinate clauses
|
|
|
What are the two approaches for speech prosody generation?
|
1. Based on rules
- Fujisaki: Word and phrase components superimposed on a declination line, processed by a 2nd-order system - Adriaens: Copy contours - Mersdorf: LPC parametrization 2. Based on data - Neural networks - Classification trees |
|
|
Explain how formant synthesis works. What are the control parameters? |
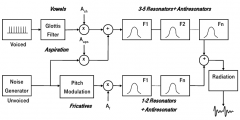
Idealized excitation signals: voiced impulse comb and unvoiced noise. Two formant filter lines: longer (3-5 filters/resonators) for vowels, shorter (1-2 filters/resonators) for fricatives. Aspirated sounds use both. Control parameters: fundamental frequency, frequencies and bandwidth of formant filters, amplitudes of excitation signals. |
|
|
How does LPC synthesizer work? What are its control parameters?
|
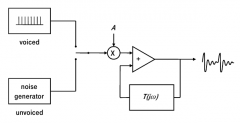
|
|
|
What is articulatory synthesis? |
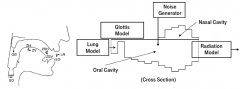
Parametric synthesis, modelling the exact movement of articulators in vocal tract. Computationally heavy. Source-filter model picture (diameters of different parts in vocal tract). |
|
|
What are advantages and disadvantages of parametric syntesis? Name another type of syntesis. |
1. Formant synthesis: Difficult determination of parameter values Another type: Concatenative Synthesis - concatenation of individual elements (phones, diphones, demisyllables, syllables, etc.)
|
|
|
What is concatenation synthesis? How does it work? |
Lots of pre-recorded material, choosing short pieces and concatenating so that the transition are smooth. |
|
|
How does PSOLA work? What are the benefits of PSOLA in speech synthesis? |
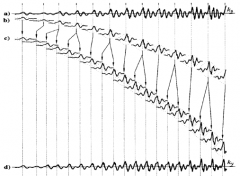
Recorded signal cut into elementary components (at fundamental period markers), which are overlaid and added to make a new signal with different fundamental frequency. Fundamental frequency and thus prosody can be adjusted by elementary component distances. Smooth changes of f0 makes the speech more natural. However, manipulation causes artefacts. |
|
|
What is unit-selection synthesis? How long are the units? How does it decide what units to select? What kind of labelling is needed? When does it work correctly and when not? |
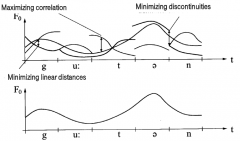
Choose as long speech units as possible without manipulating. Requires lots of recordings (high effort). Units that 1) match the text to be synthesized 2) can be used together with minimal discontinuities in signal are chosen, based on a cost function. The costs are called 1) cost of units 2) concatenation costs. Units need to be labelled both phonemically and prosodically. Text to be synthesized needs to have labels too, in real-time. Unit-selection achieves quite natural speech if the text is found in the inventory. |
|
|
How can HMM be used for speech synthesis?
|
1. Best-fitting connection of elements/units
->Representation as an HMM -> Elements = States of the HMM, each linked to a parametric signal representation (e.g. LPC) 2. Synthesis = Finding the optimum path through all states (elements) |

