![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
9 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Name parts of a sign? (Semiotic approach to speech) |
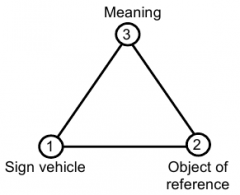
1. Carrier |
|
|
What is phoneme? |
Smallest distinctive unit of a language, does not carry meaning in itself, e.g. /b/ in bit and /p/ in pit. |
|
|
What is morpheme? |
Smallest unit carrying meaning in a language |
|
|
Explain the difference between Information and Meaning. |
• Information: conventionalized or institutionalized code; code means the same for all of us |
|
|
What are different shapes of the language? |
At first, language may be differentiated as • language as a system (French: langue) • language put to practice in form of speech acts (French: parole) Apart from this: • spoken language (or speech): field covered here by speech signal processing • written language (or language): field covered here by natural language processing |
|
|
Name 3 relation between linguistic units
|
The relationships between the elements of a language may also be specified on different levels:• Syntax: relationship between the signs themselves (e.g., rules on how to build the plural, or how to combine a sentence from words)• Semantics: relationship between the signs and the item that signified, the study of the meaning of linguistic signs• Pragmatics: relationship between the sign and its “user”; representation of the “world knowledge” underlying an utterance.
|
|
|
What is prosody? Name three aspects of prosody. |
Prosody indicates the sound shape of spoken language. • Quantity: the time structure of speech, e.g. duration of speech sounds, pauses, etc. • Intensity or Accent: accent and emphasis on word, sentence and utterance level. • Intonation: melodic aspect of speech, which carries information as phrase boundaries, sentence type (illocutionary act, e.g. question, statement, command, …), and focus – thus, which carries information of what is intended to be important for the listener or not explicitly important (or new). Further, the intonation encompasses information on attitudes and emotions of the speaker. |
|
|
Why do we use speech in human-machine communication? |
- The most important medium of human communication - Intuitive and natural - Does not require special knowledge or learning efforts - Applicable in Hands-Busy-Eyes-Busy situations - Especially eligible for the visually handicapped or users who are not sufficiently mobile - Employable independent from location (i.e. per telephone) |
|
|
Which modules are part of Shannon and Weaver’s communication model? |
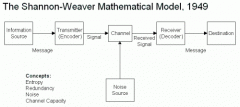
|

