![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
10 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What are 3 techniques for speech signal analyse? |
1. Spectral analysis |
|
|
What is the basic principle of Tunable bandpass and Search-tone method methods? |
The idea behind Tunable bandpass and Search-tone method methods is to use a filter (band pass, low pass) to get the parts of the spectrum you are currently interested and to suppress the rest of the spectrum. |
|
|
Explain the flow of Tunable bandpass method. |
For spectral analysis you can use a tunable bandpass which lets pass only frequencies of a small range (ΔΩ) close to the center frequency Ωm. |
|
|
What is different in Search-tone method compare to Tunable bandpass method. |
Search-tone method (windowing in the temporal domain) |
|
|
What is the main problem of Tunable bandpass and Search-tone method methods and what's the solution? |
For calculating the entire spectrum at all frequencies we need to store the signal and calculate the spectrum sequentiall. |
|
|
What is bandpass filter bank method about? |
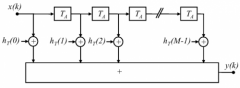
Analysis all of the frequencies at the same time (with parallel filters) with absolute or relative ∆Ω |
|
|
What is the difference between different window functions? |
When selecting the shape of the window you need to consider the following criteria: |
|
|
What Radix-2/Decimation-in-Time algorithm is about? |
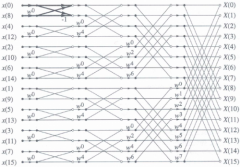
Reduces the number of FFT needed to be counted |
|
|
What is cepstrum and what is used for? |
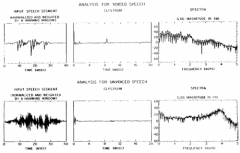
A cepstrum is the result of taking the Inverse Fourier transform (IFT) of the logarithm of the estimated spectrum of a signal. |
|
|
What is idea of linear prediction? |
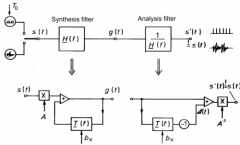
Makes inverse filtering |

