![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
125 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
1. skeletal 2. cardiac 3. smooth |
3 types of muscle tissue |
|
|
|
muscle fibers |
elongated skeletal and smooth muscle cells are also known as... |
|
|
|
skeletal muscle tissue |
muscle tissue attached to and covering the bony skeleton, responsible for body motility; 40% of body mass |
|
|
|
- voluntary - striated - multinucleate |
Describe skeletal muscle (movement, appearance, nucleus): |
|
|
|
cardiac muscle tissue |
muscle tissue forming the walls of the heart, help pump blood through the cardiovascular system |
|
|
|
- involuntary - striated - uninucleate or binucleate |
Describe cardiac muscle (movement, appearance, nucleus): |
|
|
|
smooth muscle tissue |
muscle tissue found in the walls of hollow organs, propels substances and maintains blood pressure |
|
|
|
- involuntary - nonstriated, spindle-shaped - uninucleate |
Describe smooth muscle (movement, appearance, nucleus): |
|
|
|
1. excitability 2. contractility 3. extensibility 4. elasticity |
4 special characteristics of muscle tissue |
|
|
|
excitability (responsiveness) |
the ability to receive and respond to a stimulus |
|
|
|
contractility |
the ability to shorten forcibly when stimulated |
|
|
|
extensibility |
the ability to extend or stretch |
|
|
|
elasticity |
the ability of a muscle cell to recoil and resume its resting length after stretching |
|
|
|
1. movement 2. posture 3. joint stability 4. body heat 5. protection |
5 most important functions of muscle |
|
|
|
fascia |
connective tissue that binds separate muscles into functional groups |
|
|
|
1. muscle 2. fascicle 3. muscle fiber 4. myofibril 5. myofilament |
5 levels (of rods) forming a muscle |
|
|
|
1. epimysium 2. perimysium 3. endomysium |
3 connective tissue sheaths surrounding muscle fibers (superficial to deep) |
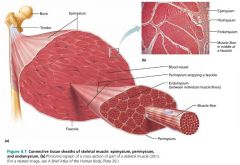
|
|
|
epimysium |
the layer of dense irregular connective tissue surrounding the whole muscle |
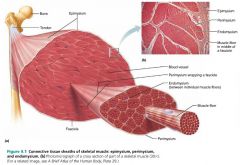
|
|
|
fascicle |
a group of muscle fibers within each skeletal muscle; resembles a bundle of sticks |
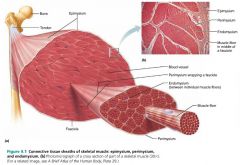
|
|
|
perimysium |
the layer of fibrous connective tissue surrounding each fascicle |
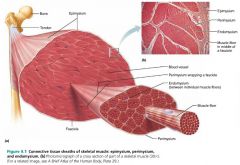
|
|
|
endomysium |
the layer of areolar connective tissue surrounding each muscle fiber |
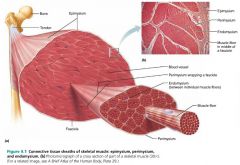
|
|
|
origin |
where muscle is attached to an immovable or less movable bone |
|
|
|
insertion |
where muscle is attached to a movable bone |
|
|
|
direct attachment (fleshy attachment) |
muscle attachment in which the muscle itself is fused to bone or cartilage |
|
|
|
indirect attachment |
common muscle attachment in which muscle connective tissue extends as a tendon or aponeurosis that anchors it to the skeleton |
|
|
|
tendon |
flexible but inelastic tissue attaching a muscle to a bone |
|
|
|
aponeurosis |
a sheet of fibrous tissue that takes the place of a tendon in sheetlike muscles with a wide area of attachment |
|
|
|
sarcolemma |
a muscle fiber's plasma membrane |
|
|
|
sarcoplasm |
a muscle fiber's cytoplasm |
|
|
|
1. glycosomes 2. myofibril |
2 special inclusions in muscle fiber sarcoplasm |
|
|
|
glycosomes |
granules of stored glycogen that provide glucose during muscle cell activity |
|
|
|
myoglobin |
a red pigment that stores oxygen in the sarcoplasm |
|
|
|
myofibrils |
hundreds to thousands of parallel-running rods that make up a single muscle fiber; 80% of cell volume |
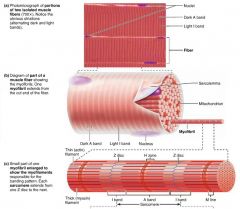
|
|
|
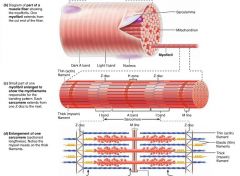
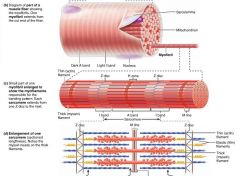
A band |
the dark area of a myofibril |
|
|
|
H zone |
the light area in the middle of an A band on a myofibril |
|
|
|
M line |
the dark line running through each H zone on a myofibril, holds thick filaments together |
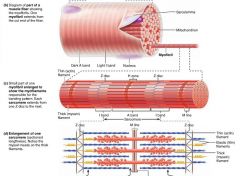
|
|
|
I band |
the light area of a myofibril |
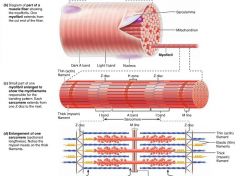
|
|
|
Z disc |
the dark, "zig-zag" line intersecting each I band on a myofibril |
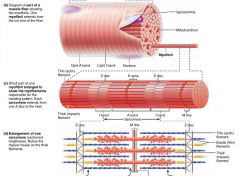
|
|
|
sarcomere |
the region of a myofibril between two Z discs; the functional unit of skeletal muscle |
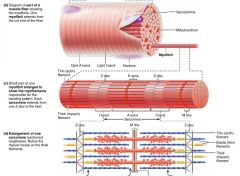
|
|
|
myofilaments |
filaments that create the banding pattern of myofibrils |
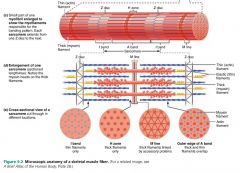
|
|
|
thick filaments |
myosin-containing filaments (red) that extend the entire length of the A band, connect at the M line |
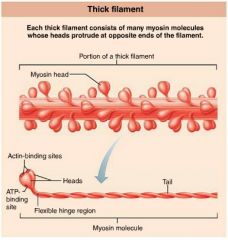
|
|
|
thin filaments |
actin-containing filaments (blue) that extend across the I band and part of the A band |
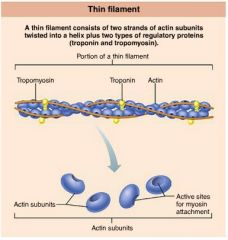
|
|
|
myosin |
protein with two globular heads that form cross bridges during muscle contraction |
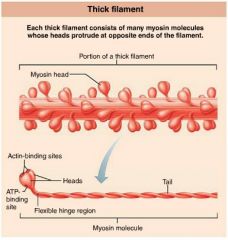
|
|
|
cross bridges |
the point where thick and thin filaments link together during muscle contraction |
|
|
|
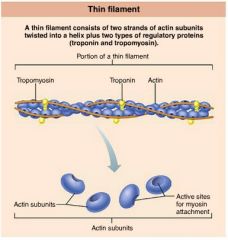
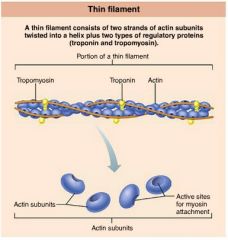
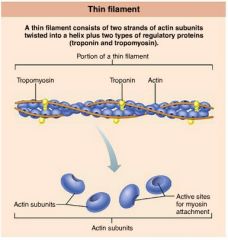
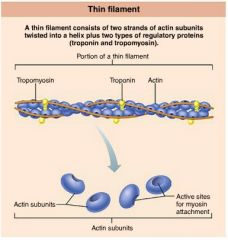
actin |
protein forming intertwined strands that serve as an attachment site for myosin's globular heads |
|
|
|
1. tropomyosin 2. troponin |
2 regulatory proteins found on thin filaments |
|
|
|
tropomyosin |
polypeptide strands spiraling around actin filaments to help stiffen and stabilize them |
|
|
|
troponin |
globular complex located on thin filaments that binds to actin, tropomyosin, and calcium ions |
|
|
|
elastic filament |
filament holding the thick filaments in place, prevents excessive stretching; composed of the protein titin |
|
|
|
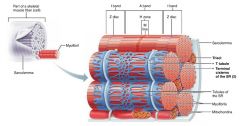
1. sarcoplasmic reticulum 2. T tubules |
2 types of intracellular tubules that help regulate muscle contraction |
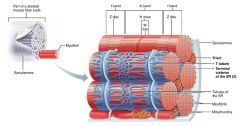
|
|
|
sarcoplasmic reticulum |
interconnecting tubules surrounding each myofibril; regulate intracellular calcium levels |
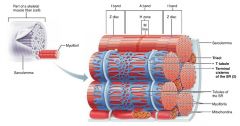
|
|
|
terminal cisternae |
large, perpendicular cross channels of sarcoplasmic reticulum at each A band-I band junction |
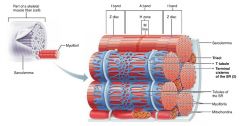
|
|
|
T tubules |
tubules from the sarcolemma that protrude deep in to the muscle fiber, increasing surface area; relay nerve impulses to all cells |
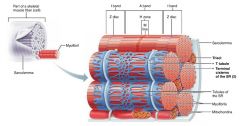
|
|
|
triad |
each terminal cistern-T tubule-terminal cistern pairing |
|
|
|
contraction |
the activation of myosin's cross bridges; muscle "shortening" |
|
|
|
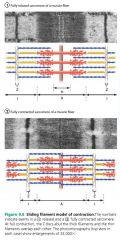
sliding filament model |
states that during contraction the thin filaments slide past the thick ones so that their myosin and actin overlap to a greater degree |
|
|
|
action potential |
an electrical current generated by the sarcolemma |
|
|
|
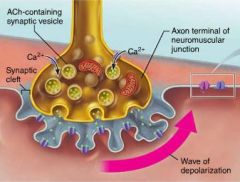
neuromuscular junction (end plate) |
junction between a single muscle fiber and an axon's branches, connecting the brain and muscle |
|
|
|
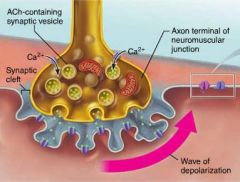
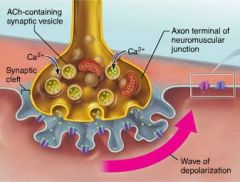
synaptic cleft |
space separating an axon terminal and a muscle fiber; filled with glycoproteins and collagen fibers |
|
|
|
synaptic vesicles |
small membranous sacs in the axon terminal that deliver ACh (acetylcholine) to the synaptic cleft |
|
|
|
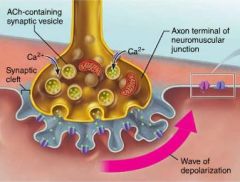
acetylcholine (ACh) |
neurotransmitter delivered by axons to muscle fibers; opens Na+ channels on the sarcolemma |
|
|
|
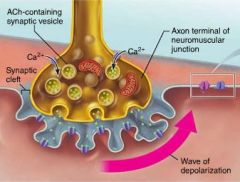
junctional folds (motor end plate) |
trough-like folds full of ACh receptors, increase surface area on the sarcolemma |
|
|
|
acetylcholinesterase |
the enzyme that breaks down ACh to its building blocks after it binds to ACh receptors; ends muscle contraction |
|
|
|
myasthenia gravis |
disease involving a shortage of ACh receptors, resulting in muscle weakness (such as droopy eyelids, difficulty swallowing) |
|
|
|
excitation-contraction coupling |
the sequence of events leading to muscle contraction, starting with the propagation of an action potential along the sarcolemma until the myofilaments slide |
|
|
|
rigor mortis |
muscle stiffening after death, due to lack of ATP (that ordinarily end contractions) |
|
|
|
muscle tension |
the force exerted by a contracting muscle on an object |
|
|
|
load |
the opposing force exerted on the muscle by the weight of an object |
|
|
|
motor unit |
one motor neuron and all the muscle fibers it innervates |
|
|
|
myogram |
a recording of contractile activity |
|
|
|
muscle twitch |
a motor unit's response to a single action potential of its motor neuron |

|
|
|
1. latent period 2. contraction 3. relaxation |
3 distinct phases of a twitch myogram |
|
|
|
graded muscle responses |
the varying degrees of muscle contractions, depend on the demands placed on the muscle |

|
|
|
TREPPE |
the staircase effect of muscle warm-up; increased calcium and heat makes enzymes more effective |
|
|
|
temporal (wave) summation |
successive twitches get stronger, and appear to ride on the shoulders of the previous twitch |

|
|
|
incomplete (unfused) tetanus |
a sustained but quivering muscle contraction |

|
|
|
complete (fused) tetanus |
a smooth, sustained muscle contraction; appears as a plateau on a myogram |

|
|
|
subthreshold stimuli |
stimuli that produce no observable contractions |
|
|
|
threshold stimulus |
the stimulus at which the first observable contraction occurs |
|
|
|
maximal stimulus |
the strongest stimulus that increases contractile force |
|
|
|
1. isotonic 2. isometric |
2 main categories of contractions |
|
|
|
isotonic contractions |
muscle length changes and moves a load, and tension remains relatively constant |
|
|
|
1. concentric 2. eccentric |
2 types of isotonic contractions |
|
|
|
concentric contractions |
contractions in which the muscle shortens and does work; ex. picking up a book, kicking a ball |
|
|
|
eccentric contractions |
contractions in which the muscle generates force as it lengthens; ex. walking up a steep hill |
|
|
|
isometric contractions |
contractions that occur when a muscle attempts to move a load that is greater than the force the muscle can develop; muscle neither shortens nor lengthens |
|
|
|
muscle tone |
the slightly contracted state of a relaxed muscle; helps with joint stability and posture |
|
|
|
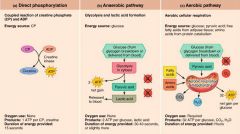
1. direct phosphorylation 2. anaerobic pathway 3. aerobic pathway |
3 pathways of regenerating ATP during muscle activity |
|
|
|
direct phosphorylation |
regenerates ATP using creatine phosphate and ADP; creatine phosphate + ADP ---> creatine + ATP; 15 seconds worth |
|
|
|
creatine phosphate |
a unique high-energy molecule stored in muscle that helps regenerate ATP (by direct phosphorylation) |
|
|
|
anaerobic pathway |
relies on glycolysis to create ATP; 30-40 seconds |
|
|
|
glycolysis |
the breakdown of glucose by enzymes, releasing ATP and pyruvic acid |
|
|
|
lactic acid |
accumulates under anaerobic conditions; comes from pyruvic acid |
|
|
|
aerobic pathway |
relies on cellular respiration to create ATP; glucose + oxygen ---> carbon dioxide + water + ATP; hours |
|
|
|
aerobic endurance |
the length of time a muscle can continue to contract using aerobic pathways |
|
|
|
anaerobic threshold |
the point at which muscle metabolism converts to anaerobic glycolysis |
|
|
|
muscle fatigue |
the inability of a muscle to contract, even though it's still receiving stimuli |
|
|
|
excess postexercise oxygen consumption (EPOC) |
the extra amount of oxygen that the body must take in to restore its reserves after exercise |
|
|
|
1. number of muscle fibers 2. size of muscle fibers 3. frequency of stimulation 4. degree of muscle stretch |
4 factors affecting the force of muscle contraction (the number of cross bridges that attach) |
|
|
|
internal tension |
the force generated by cross bridges |
|
|
|
external tension |
the force transferred from cross bridges to the load |
|
|
|
1. muscle fiber type 2. load 3. recruitment |
3 factors affecting the velocity and duration of muscle contraction |
|
|
|
1. slow 2. fast |
2 types of muscle fibers (based on speed) |
|
|
|
1. oxidative 2. glycolytic |
2 types of muscle fibers (based on method of forming ATP) |
|
|
|
oxidative fibers |
muscle fibers that rely mostly on oxygen-using aerobic pathways for ATP |
|
|
|
glycolytic fibers |
muscle fibers that rely mostly on glycolysis for ATP |
|
|
|
1. slow oxidative 2. fast oxidative 3. fast glyolytic |
3 classes of muscle fibers |
|
|
|
endurance exercise |
exercises such as swimming, jogging, or biking; stamina, no hypertrophy, aerobic |
|
|
|
resistance exercise |
exercises such as weightlifting that pit muscles against high-resistance forces; strength, leads to hypertrophy, anaerobic |
|
|
|
cross training |
use of both aerobic and anaerobic exercises |
|
|
|
disuse atrophy |
degeneration and loss of muscle mass due to inactivity |
|
|
|
1. longitudinal layer 2. circular layer |
2 layers of smooth muscle |
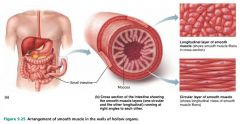
|
|
|
peristalsis |
the propulsive action of smooth muscle, created by alternating contraction and relaxation of its layers |
|
|
|
variscosities |
bulbous nerve fiber ends that release neurotransmitter in to smooth muscle cells |
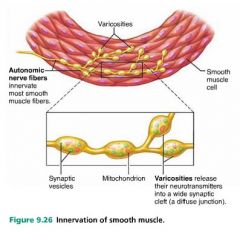
|
|
|
diffuse junctions |
the junctions between smooth muscle cells and variscosities |
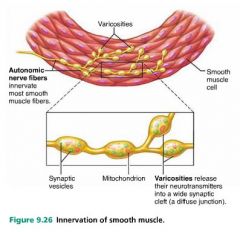
|
|
|
caveolae |
pouchlike infoldings of the smooth muscle sarcolemma that intake extracellular fluid with high Ca2+ concentration; replace T tubules |
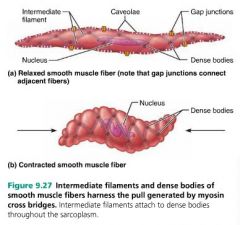
|
|
|
dense bodies |
act as anchoring points for thin filaments in smooth muscle; replace Z discs |
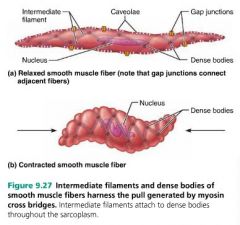
|
|
|
calmodulin |
the calcium-binding protein in smooth muscle; replaces troponin |
|
|
|
1. slow contraction 2. contraction in unison 3. anaerobic glycolysis 4. regulation 5. stretch 6. hyperplasia |
6 special characteristics of smooth muscle |
|
|
|
1. neural stimulation 2. hormones 3. local chemicals |
3 regulators of smooth muscle contraction |
|
|
|
1. unitary 2. multi unit |
2 main types of smooth muscle |
|
|
|
unitary smooth muscle (visceral muscle) |
type of smooth muscle forming the walls of all hollow organs except the heart |
|
|
|
multi unit smooth muscle |
type of smooth muscle in large airways and arteries, arrector pili, and internal eye |
|
|
|
myoblasts |
embryonic mesoderm cells from which all three types of muscle tissue derive |
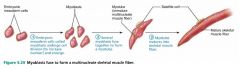
|
|
|
muscular dystrophy |
a group of inherited muscle-destroying diseases that generally appear during childhood |
|

