![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
140 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
nervous system |
the master controlling and communicating system of the body |
|
|
|
1. sensory input 2. integration 3. motor output |
3 overlapping functions of the nervous system |
|
|
|
sensory input |
the information gathered by the millions of sensory receptors of the nervous system, monitoring changes inside and outside of the body |
|
|
|
integration |
the nervous system processes and interprets sensory input and decides what should be done at each moment |
|
|
|
motor output |
the nervous system activates effector organs (the muscles and glands) to cause a response |
|
|
|
1. central nervous system (CNS) 2. peripheral nervous system (PNS) |
2 principal parts of the nervous system |
|
|
|
central nervous system (CNS) |
the integrating and control center of the nervous system; the brain and spinal cord |
|
|
|
peripheral nervous system (PNS) |
the part of the nervous system outside the CNS; consists mainly of nerves that extend from the brain and spinal cord |
|
|
|
1. sensory division (afferent) 2. motor division (efferent) |
2 functional subdivisions of the PNS |
|
|
|
sensory division (afferent division) |
PNS subdivision consisting of nerve fibers (axons) carrying impulses to the CNS from sensory receptors throughout the body |
|
|
|
somatic sensory fibers |
fibers conveying impulses from the skin, skeletal muscles, and joints to the CNS |
|
|
|
visceral sensory fibers |
fibers transmitting impulses from the visceral organs |
|
|
|
motor division (efferent division) |
PNS subdivision transmitting impulses from the CNS to effector organs (muscles and glands) |
|
|
|
1. somatic nervous system 2. autonomic nervous system (ANS) |
2 main parts of the motor division (efferent division) of the PNS |
|
|
|
somatic nervous system |
the part of the motor division that conducts impulses from the CNS to skeletal muscles; voluntary nervous system |
|
|
|
autonomic nervous system (ANS) |
the part of the motor division that regulates the activities of smooth muscles, cardiac muscles, and glands; involuntary nervous system |
|
|
|
1. sympathetic division 2. parasympathetic division |
2 subdivisions of the autonomic nervous system (involuntary nervous system) |
|
|
|
sympathetic division |
division of the autonomic nervous system that mobilizes body systems during emergencies; fight or flight |
|
|
|
parasympathetic division |
division of the autonomic nervous system that conserves energy; promotes non-emergency functions (resting) |
|
|
|
1. neurons (nerve cells) 2. neuroglia (glial cells) |
2 main cell types of the nervous system |
|
|
|
neuroglia (glial cells) |
supporting cells that surround and wrap the more delicate neurons |
|
|
|
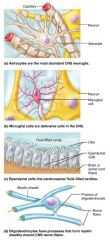
1. astrocytes 2. microglial cells 3. ependymal cells 4. oligodendrocytes |
4 types of neuroglia in the CNS |
|
|
|
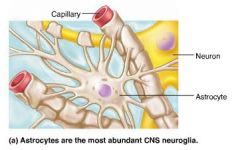
astrocytes |
CNS neuroglia that support and brace neurons and anchor them to nutrient supply lines; most abundant and versatile |
|
|
|
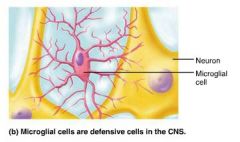
microglial cells |
CNS neuroglia that monitor neuron health and phagocytize debris |
|
|
|
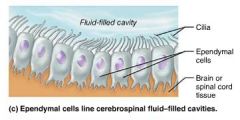
ependymal cells |
CNS neuroglia that line the central cavities of the brain and spinal cord, forming a permeable barrier |
|
|
|
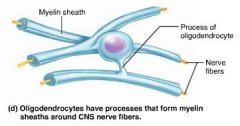
oligodendrocytes |
CNS neuroglia that tightly wrap nerve fibers forming the insulating myelin sheath |
|
|
|
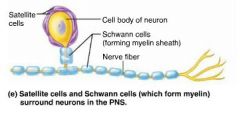
1. satellite cells 2. Schwann cells |
2 types of neuroglia in the PNS |
|
|
|
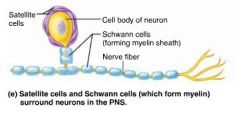
satellite cells |
PNS neuroglia that surround neurons; similar functions to astrocytes of the CNS |
|
|
|
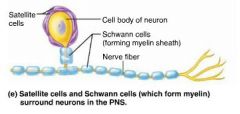
Schwann cells (neurolemmocytes) |
PNS neuroglia that form myelin sheaths around nerve fibers; similar function to oligodendrocytes of the CNS |
|
|
|
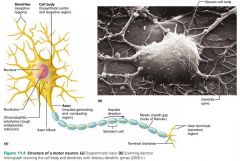
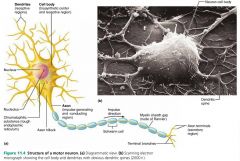
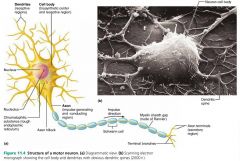
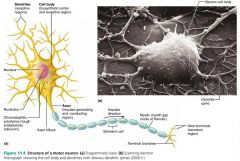
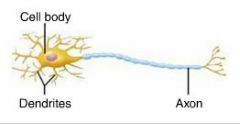
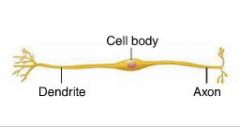
neuron |
the structural unit of the nervous system; conducts electrical signals |
|
|
|
1. longevity (100+ years) 2. amitotic 3. high metabolic rate |
3 special characteristics of neurons |
|
|
|
neuron cell body (perikaryon, soma) |
the major biosynthetic center of a neuron; synthesizes proteins |
|
|
|
Nissl bodies (chromatophilic substance) |
the protein- and membrane-making rough ER of a neuron |
|
|
|
neurofibrils |
bundles of intermediate filaments that, along with microtubules, help maintain nerve cell shape and integrity |
|
|
|
nuclei |
clusters of neuron cell bodies in the CNS |
|
|
|
ganglia |
clusters of neuron cell bodies that lie along the nerves of the PNS |
|
|
|
processes |
extensions from the neuron cell body |
|
|
|
tracts |
bundles of neuron processes in the CNS |
|
|
|
nerves |
bundles of neuron processes in the PNS |
|
|
|
1. dendrites 2. axons |
2 types of neuron processes |
|
|
|
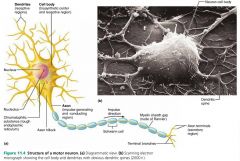
dendrites |
short, branching extensions of neuron cell bodies that receive signals from other neurons and relay the signal to the cell body |
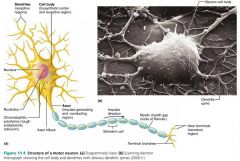
|
|
|
axons |
long extensions of neuron cell bodies; generate and transmit nerve impulses |
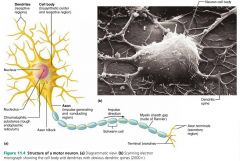
|
|
|
nerve fiber |
a long axon |
|
|
|
axon hillock |
cone-shaped area of the cell body where an axon arises |
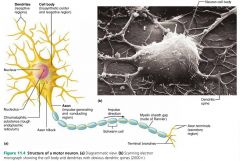
|
|
|
axon collaterals |
branching axons |
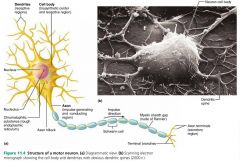
|
|
|
terminal branches |
the end branches of an axon; 10,000 or more per neuron |
|
|
|
axon terminals (terminal boutons) |
the knoblike endings of axon branches |
|
|
|
axolemma |
the plasma membrane of neuron cell bodies |
|
|
|
neurotransmitters |
signaling chemicals usually stored in vesicles; excite or inhibit neurons |
|
|
|
anterograde movement |
movement away from the cell body |
|
|
|
retrograde movement |
movement toward the cell body |
|
|
|
myelin sheath |
a white, fatty layer covering nerve fibers; protects and electrically insulates |
|
|
|
myelinated fibers |
axons bearing a myelin sheath; conducts nerve impulses rapidly |
|
|
|
nonmyelinated fibers |
axons without a myelin sheath; conduct nerve impulses more slowly |
|
|
|
myelin sheath gaps (nodes of Ranvier) |
gaps between myelin sheaths, occur at regular intervals |
|
|
|
white matter |
regions of the brain and spinal cord with dense collections of myelinated fibers |
|
|
|
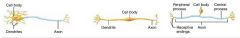
1. multipolar 2. bipolar 3. unipolar |
3 structural classes of neurons |
|
|
|
multipolar neurons |
neurons with three or more processes; one axon and the rest dendrites; ex. brain and motor neurons |
|
|
|
bipolar neurons |
neurons with two processes; one axon and one dendrite; ex. some sensory neurons |
|
|
|
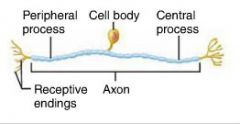
(pseudo)unipolar neurons |
neurons with a single short process that divides in to proximal and distal branches; ex. sensory neurons |
|
|
|
1. sensory neurons (afferent) 2. motor neurons (efferent) 3. interneurons |
3 functional classes of neurons |
|
|
|
sensory neurons (afferent neurons) |
class of neurons that transmit impulses from sensory receptors in the skin or organs toward the CNS; unipolar |
|
|
|
motor neurons (efferent neurons) |
class of neurons that carry impulses away from the CNS to the effector organs (muscles and glands); multipolar |
|
|
|
interneurons (association neurons) |
class of neurons that shuttle signals through CNS pathways, where integration occurs; 99% of all neurons; multipolar |
|
|
|
voltage |
the measure of potential energy generated by separated charge |
|
|
|
current |
the flow of electrical charge from one point to another |
|
|
|
resistance |
the hindrance to charge flow provided by substances through which a current must pass |
|
|
|
leakage channels (nongated) |
plasma membrane channels that are always open |
|
|
|
1. chemically gated (ligand-gated) 2. voltage-gated 3. mechanically gated |
3 main types of gated plasma membrane channels |
|
|
|
chemically gated channels (ligand-gated channels) |
channels that open when the appropriate chemical binds (neurotransmitters) |
|
|
|
voltage-gated channels |
channels that open and close in response to change in the membrane potential |
|
|
|
mechanically gated channels |
channels that open in response to physical deformation of the receptor |
|
|
|
electrochemical gradient |
electrical and concentration gradients combined |
|
|
|
resting membrane potential |
the potential difference in a resting neuron; polarized (approx. -70mV) |
|
|
|
depolarization |
decrease in membrane potential; the inside of the membrane becomes less negative |
|
|
|
hyperpolarization |
increase in membrane potential; the inside of the membrane becomes more negative |
|
|
|
graded potentials |
short-lived, localized changes in membrane potential; used by dendrites, axons, and muscles |
|
|
|
action potential |
a brief reversal of membrane potential; used by nerve axons and muscles |
|
|
|
nerve impulse |
an action potential in a neuron; typically generated only in axons |
|
|
|
resting state (stage 1 of 4) |
Generation of an Action Potential: All gated Na+ and K+ channels are closed. |
|
|
|
depolarization (stage 2 of 4) |
Generation of an Action Potential: Na+ channels open. |
|
|
|
repolarization (stage 3 of 4) |
Generation of an Action Potential: Na+ channels inactivate, and K+ channels open. |
|
|
|
hyperpolarization (stage 4 of 4) |
Generation of an Action Potential: Some K+ channels remain open, and Na+ channels reset. |
|
|
|
sodium-potassium pump |
redistributes ions and restores the membrane potential to its resting state |
|
|
|
threshold |
the critical level that must be reached for depolarization to become self-generating |
|
|
|
all-or-none phenomenon |
an AP either happens completely or not at all |
|
|
|
absolute refractory period |
the period when a neuron cannot respond to another stimulus; from the time Na+ channels open until they begin returning to resting state |
|
|
|
relative refractory period |
the period when a neuron can only generate an AP if the stimulus is great enough; from the time Na+ channels return to their resting state until after hyperpolarization |
|
|
|
saltatory conduction |
an electrical signal jumping from gap to gap along an axon |
|
|
|
multiple sclerosis |
autoimmune disease destruction of myelin sheaths, delaying impulse conduction; characterized by visual disturbances, muscle problems, speech disturbances, etc. |
|
|
|
group A fibers |
nerve fibers with the largest diameter and thick myelin sheaths; ex. somatic sensory and motor fibers |
|
|
|
group B fibers |
nerve fibers with intermediate diameter and lightly myelinated |
|
|
|
group C fibers |
nerve fibers with the smallest diameter and nonmyelinated; slow impulse conduction |
|
|
|
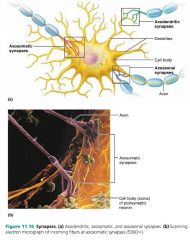
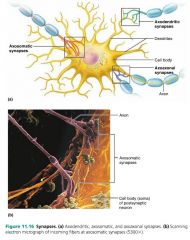
synapse |
a junction that mediates information transfer from one neuron to the next (or to an effector cell) |
|
|
|
axodendritic synapses |
synapses between axon endings of one neuron and the dendrites of other neurons |
|
|
|
axosomatic synapses |
synapses between axon endings of one neuron and cell bodies (soma) of other neurons |
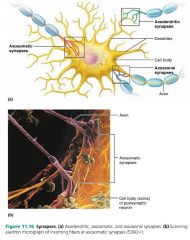
|
|
|
axoaxonic synapses |
synapses between two axons |
|
|
|
presynaptic neuron |
the neuron conducting impulses toward a synapse |
|
|
|
postsynaptic neuron |
the neuron conducting impulses away from the synapse |
|
|
|
1. electrical synapses 2. chemical synapses |
2 varieties of synapses |
|
|
|
electrical synapses |
less common variety of synapses; consist of gap junctions that let ions flow between neurons |
|
|
|
chemical synapses |
variety of synapses that allow the release and reception of neurotransmitters |
|
|
|
synaptic vesicles |
tiny, membrane-bound sacs of the axon terminal that contain thousands of neurotransmitter molecules |
|
|
|
Stage 1 of 6 |
Chemical Synapses: AP arrives at axon terminal. |
|
|
|
Stage 2 of 6 |
Chemical Synapses: Voltage-gated Ca2+ channels open and Ca2+ enters the axon terminal. |
|
|
|
Stage 3 of 6 |
Chemical Synapses: Ca2+ entry causes synaptic vesicles to release neurotransmitter. |
|
|
|
Stage 4 of 6 |
Chemical Synapses: Neurotransmitter diffuses across the synaptic cleft and binds to specific receptors on the postsynaptic membrane. |
|
|
|
Stage 5 of 6 |
Chemical Synapses: Binding of neurotransmitters opens ion channels, resulting in graded potentials. |
|
|
|
Stage 6 of 6 |
Chemical Synapses: Neurotransmitter effects are terminated by reuptake, degradation, or diffusion. |
|
|
|
excitatory postsynaptic potentials (EPSPs) |
graded potentials that help trigger an AP distally at the axon hillock; both Na+ and K+ channels open, causing depolarization |
|
|
|
inhibitory postsynaptic potentials (IPSPs) |
graded potentials that reduce a postsynaptic neuron's ability to generate an AP; K+ and Cl- channels open, causing hyperpolarization |
|
|
|
temporal summation |
occurs when one or more presynaptic neurons transmit impulses in rapid-fire order and bursts of neurotransmitter are released in quick succession |
|
|
|
spatial summation |
occurs when many presynaptic neurons stimulate the postsynaptic neuron at the same time |
|
|
|
synaptic potentiation |
repeated or continuous use of a synapse enhances its effects; caused by high Ca2+ concentrations |
|
|
|
presynaptic inhibition |
occurs when the release of excitatory neurotransmitter by one neuron is inhibited by the activity of another neuron |
|
|
|
1. acetylcholine (ACh) 2. biogenic amines 3. amino acids 4. peptides 5. purines 6. gases and lipids |
6 classes of neurotransmitters |
|
|
|
acetylcholine |
neurotransmitter used at neuromuscular junctions, and in CNS and autonomic nervous systems |
|
|
|
1. epinephrine 2. norepinephrine |
2 neurotransmitters used in the autonomic nervous system; brain arousal |
|
|
|
serotonin |
neurotransmitter used to stabilize mood |
|
|
|
dopamine |
reward/pleasure neurotransmitter |
|
|
|
endorphins |
natural painkiller neurotransmitters |
|
|
|
neuromodulator |
a chemical messenger released by a neuron that affects the strength of synaptic transmission; doesn't directly cause EPSPs or IPSPs |
|
|
|
1. channel-linked 2. G protein-linked |
2 main classes of neurotransmitter receptors |
|
|
|
channel-linked receptors |
ligand-gated ion channels that mediate direct neurotransmitter action |
|
|
|
G protein-linked receptors |
neurotransmitter receptors that rely on second messengers; slower, but longer lasting effects |
|
|
|
neuronal pools |
functional groups of neurons that integrate incoming information and then forward it to other destinations |
|
|
|
discharge zone |
area of the neuronal pool that receives the bulk of the synaptic contacts; more likely to fire |
|
|
|
facilitated zone |
area of the neuronal pool farther from the center; less likely to fire |
|
|
|
circuits |
the patterns of synaptic connections in neuronal pools |
|
|
|
1. diverging circuit 2. converging circuit 3. reverberating circuit 4. parallel after-discharge circuit |
4 types of circuits in neuronal pools |
|
|
|
diverging circuit |
circuit with one input, many outputs |
|
|
|
converging circuit |
circuit with many inputs, and one output |
|
|
|
reverberating circuit |
circuit in which the signal travels through a chain of neurons, each feeding back to previous neurons; ex. breathing, short term memory |
|
|
|
parallel after-discharge circuit |
circuit in which the signal stimulates neurons arranged in parallel arrays that eventually converge on a single output cell; ex. precise mental functions |
|
|
|
serial processing |
processing in which the input travels along one pathway to a specific destination |
|
|
|
reflexes |
rapid, automatic responses to stimuli, in which a particular stimulus always causes the same response |
|
|
|
reflex arcs |
the neural pathways among which reflexes occur |
|
|
|
parallel processing |
processing in which the input travels along several different pathways to be integrated in different CNS regions; higher brain functions |
|
|
|
neuroblasts |
potential neurons that usually form in the second month of development |
|
|
|
growth cone |
the growing tip of an axon on a neuroblast |
|

