![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
164 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
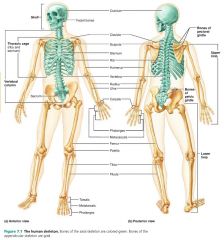
skeletal system |
system consisting of bones, cartilages, joints, and ligaments; roughly 20% of body mass |
|
|
|
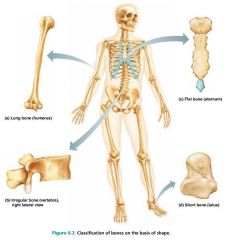
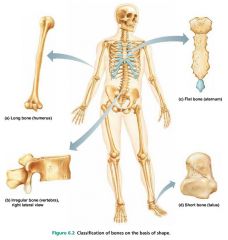
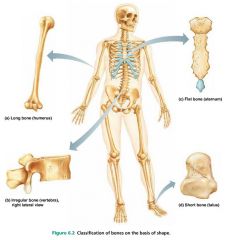
long bones |
bones longer than they are wide; limb bones |
|
|
|
short bones |
cube-shaped bones; wrists and ankles |
|
|
|
sesamoid bones |
special type of short bones, form within tendons; patella (kneecap) |
|
|
|
flat bones |
thin bones; sternum, skull |
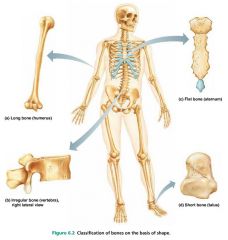
|
|
|
irregular bones |
bones with complicated shapes; vertebrae, hip bones |
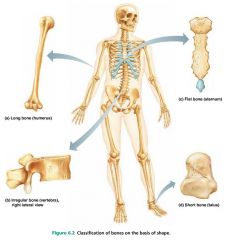
|
|
|
bone markings |
projections, depressions, and openings on bone surfaces that serve as sites of muscle, ligament, and tendon attachment, as joint surfaces, or as conduits for blood vessels and nerves |
|
|
|
1. attachment sites (muscles, ligaments, tendons) 2. joint surfaces 3. passageways (blood vessels, nerves) |
3 functions of bone markings |
|
|
|
1. tuberosity 2. tubercle 3. crest 4. line 5. spine 6. trochanter 7. epicondyle 8. process |
8 attachment sites (bone markings) |
|
|
|
tuberosity |
large rounded projection |
|
|
|
tubercle |
small rounded projection |
|
|
|
crest |
narrow ridge of bone |
|
|
|
line |
narrow ridge of bone; less prominent than a crest |
|
|
|
spine |
sharp pointed process |
|
|
|
trochanter |
large, irregular-shaped projection |
|
|
|
epicondyle |
projection above a condyle |
|
|
|
process |
any bone prominence |
|
|
|
1. head 2. facet 3. condyle 4. ramus 5. fossa |
5 joint surfaces (bone markings) |
|
|
|
head |
bony expansion carried on a narrow neck |
|
|
|
facet |
smooth, nearly flat articular surface |
|
|
|
condyle |
rounded articular projection |
|
|
|
ramus |
armlike bar of bone |
|
|
|
fossa |
shallow depression in a bone |
|
|
|
1. groove (sulcus) 2. fissure 3. foramen 4. notch 5. meatus 6. sinus |
6 passageways (bone markings) |
|
|
|
groove (sulcus) |
furrow |
|
|
|
fissure |
narrow, slitlike opening |
|
|
|
foramen |
round or oval opening through a bone |
|
|
|
notch |
indentation at the edge of a structure |
|
|
|
meatus |
canal-like passageway in a bone |
|
|
|
sinus |
cavity within a bone; filled with air and lined with mucous membrane |
|
|
|
1. axial skeleton 2. appendicular skeleton |
2 divisions of the skeletal system |
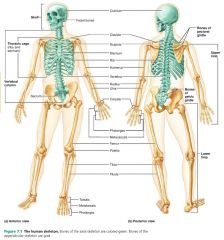
|
|
|
axial skeleton |
group of 80 bones forming the long axis of the body; protect, support, or carry other body parts |
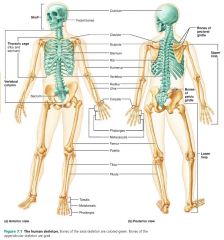
|
|
|
1. skull 2. vertebral column 3. thoracic cage |
3 major regions of the axial skeleton |
|
|
|
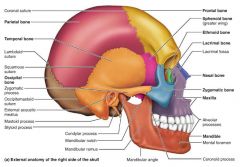
skull |
the body's most complex bony structure; 22 cranial and facial bones |
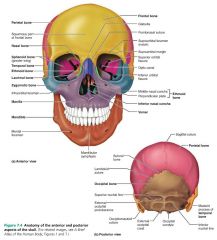
|
|
|
1. cranium (8 cranial bones) 2. face (14 facial bones) |
2 parts of the skull and their # of bones |
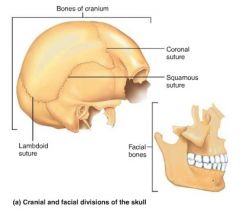
|
|
|
cranium (cranial bones) |
encloses and protects the brain, and furnishes attachment sites for head and neck muscles; 8 bones |
|
|
|
1. frontal 2-3. parietal (x2) 4. occipital 5-6. temporal (x2) 7. sphenoid 8. ethmoid |
8 bones of the cranium |
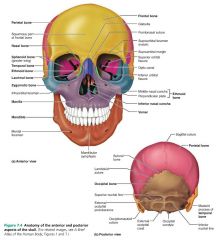
|
|
|
frontal bone [1] |
anterior bone of the cranium |
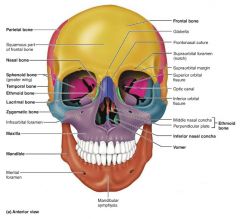
|
|
|
parietal bones [2-3] |
superiolateral bones of the cranium |
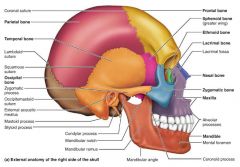
|
|
|
occipital bone [4] |
cranial bone forming the posterior aspect and most of the base of the skull |
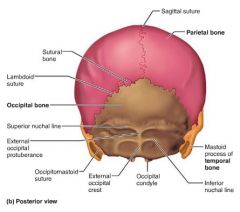
|
|
|
foramen magnum |
passageway where the spinal cord meets the brain stem |
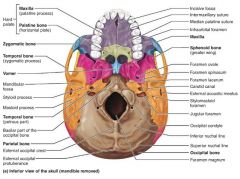
|
|
|
occipital condyle |
where the skull articulates with the atlas vertebra (C1) |
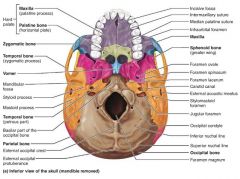
|
|
|
temporal bones [5-6] |
inferiolateral bones of the cranium; contribute to the middle cranial fossa |
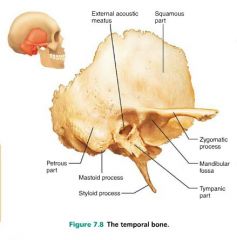
|
|
|
zygomatic arch |
connection place of temporal and zygomatic bone; cheek bone |
|
|
|
external auditory (acoustic) meatus |
external ear canal, where sound enters |
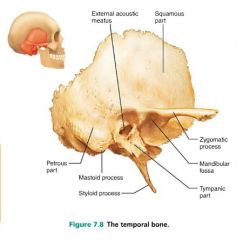
|
|
|
sphenoid bone [7] |
butterfly-shaped keystone of the cranium; articulates with all the other bones |
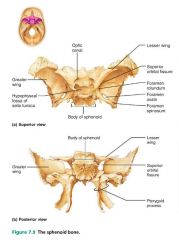
|
|
|
sella turcica |
where the pituitary gland sits in the sphenoid bone |
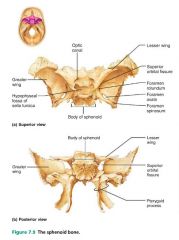
|
|
|
ethmoid bone [8] |
cranial bone forming much of the medial orbit and nasal cavities; helps form the anterior cranial fossa |
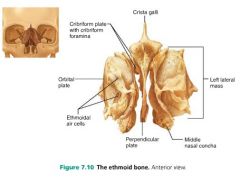
|
|
|
sutures |
interlocking joints uniting the skull bones |
|
|
|
1. coronal 2. sagittal 3. squamous 4. lambdoid |
4 major sutures of the skull |
|
|
|
coronal suture |
parietal-frontal suture |
|
|
|
sagittal suture |
parietal-parietal suture |
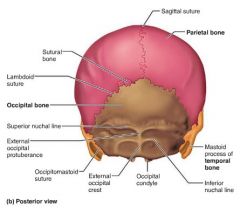
|
|
|
lambdoid suture |
parietal-occipital suture |
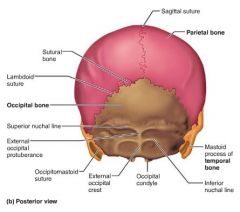
|
|
|
squamous suture |
parietal-temporal suture |
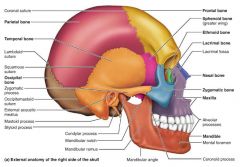
|
|
|
cranial fossae |
bony ridges dividing the skull base (anterior, middle, and posterior) |
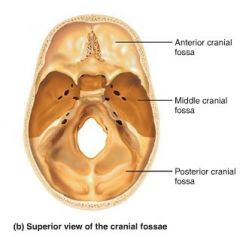
|
|
|
1. facial framework 2. facial muscles 3. air/food 4. teeth 5. sensory cavities
|
5 purposes of the facial bones |
|
|
|
1. mandible 2-3. maxilla (x2) 4-5. zygomatic (x2) 6-7. lacrimal (x2) 8-9. palatine (x2) 10-11. nasal (x2) 12. vomer 14. inferior nasal conchae (x2) |
14 facial bones |
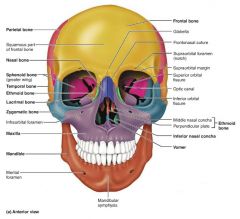
|
|
|
mandible [1] |
lower jaw bone, largest and strongest bone of the face |
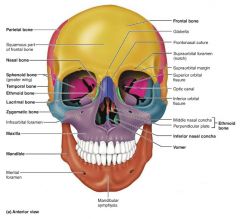
|
|
|
mandibular condyle |
part of the mandible that articulates with the temporal bones, forming the temporomandibular joint (TMJ) |
|
|
|
maxilla [2-3] |
upper jaw bones; articulate with most other facial bones |
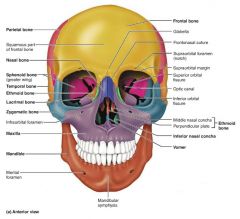
|
|
|
zygomatic [4-5] |
facial bones that form the cheeks and part of the orbits |
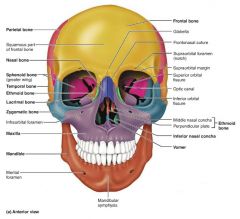
|
|
|
lacrimal [6-7] |
facial bones that form the medial orbit walls |
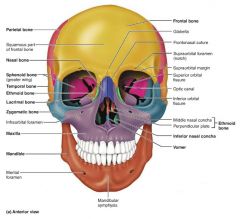
|
|
|
palatine [8-9] |
facial bones that form the posterior portion of the hard palate |
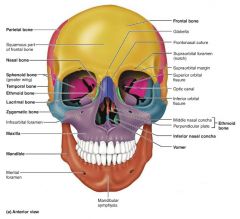
|
|
|
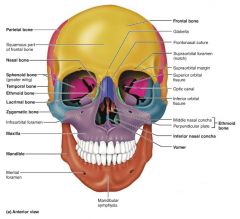
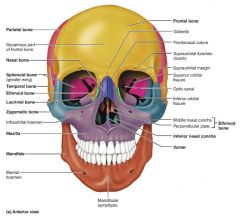
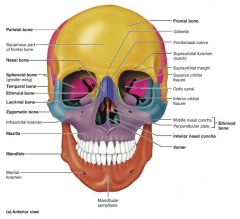
nasal [10-11] |
facial bones that form the bridge of the nose |
|
|
|
vomer [12] |
facial bone forming the inferior part of the nasal septum |
|
|
|
inferior nasal conchae [13-14] |
facial bones that project from the lateral walls of the nasal cavity |
|
|
|
1. orbits (7) 2. nasal cavity (9) |
2 restricted regions of the skull and the # of bones forming them |
|
|
|
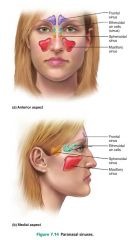
paranasal sinuses |
mucosa-lined, air-filled cavities found in the skull bones |
|
|
|
1. frontal 2. ethmoid 3. sphenoid 4. maxilla |
4 locations of paranasal sinuses |
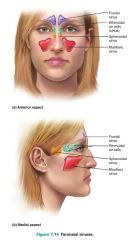
|
|
|
1. warm air 2. lighten the skull 3. resonate the voice |
3 functions of the paranasal sinuses |
|
|
|
fontanelles |
"soft spots" where bones grow and fit together; compressed during childbirth |
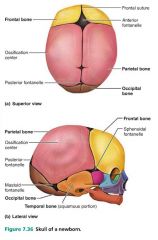
|
|
|
1. anterior 2. posterior 3. sphenoidal 4. mastoid |
4 main fontanelles |
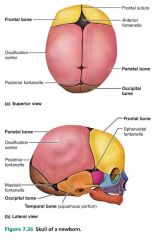
|
|
|
hyoid bone |
bone that has attachment points for neck muscles (swallowing and speech); does not articulate with any other bone |
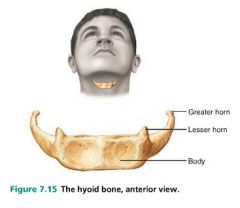
|
|
|
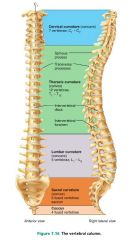
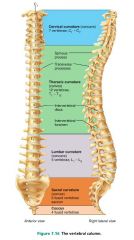
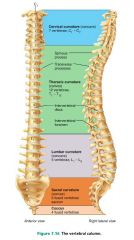
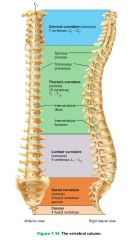
vertebral column (spine) |
the axial support of the trunk, from the skull to the pelvis; transmits weight to lower limbs |
|
|
|
vertebrae (26) |
bones of the vertebral column |
|
|
|
1. cervical (7) 2. thoracic (12) 3. lumbar (5) 4. sacrum (5 fused) 5. coccyx (4 fused) |
5 divisions of the vertebral column and their # of vertebrae |
|
|
|
1. cervical (concave) 2. thoracic (convex) 3. lumbar (concave) 4. sacral (convex) |
4 curvatures of the vertebral column giving it its S shape (support, stability, springiness) |
|
|
|
1. scoliosis 2. kyphosis 3. lordosis |
3 abnormalities of the vertebral column |
|
|
|
scoliosis |
abnormal lateral curvature of the vertebral column, most often in the thoracic region; common in childhood, particularly in girls |
|
|
|
kyphosis (hunchback) |
exaggerated thoracic curvature; common in elderly people (because of osteoporosis) |
|
|
|
lordosis (swayback) |
exaggerated lumbar curvature; common in pregnant woman |
|
|
|
longitudinal ligaments |
major supporting ligaments of the vertebral column |
|
|
|
anterior longitudinal ligaments |
vertebral ligaments attached to both the vertebrae and the discs; resists hyperextension (bending too far backward) |
|
|
|
posterior longitudinal ligaments |
vertebral ligaments attached only to the discs; resists hyperflexion (bending too far forward) |
|
|
|
ligamentum flavum |
vertebral ligament connecting adjacent vertebrae |
|
|
|
intervertebral discs |
fibrocartilage pads forming cushions between the body of each vertebra; 25% of the height of the vertebral column |
|
|
|
nucleus pulposus |
inner gelatinous "rubber ball" that gives the vertebrae their elasticity and compressibility |
|
|
|
anulus fibrosus |
strong collar surrounding the nucleus pulposus, limiting its expansion |
|
|
|
1. collagen fibers (outside) 2. fibrocartilage (inside) |
2 constituents of the anulus fibrosus |
|
|
|
herniated disc (slipped disc) |
rupture of the anulus fibrosus allowing the nucleus pulposus to protrude; can press on the spinal cord or nerves |
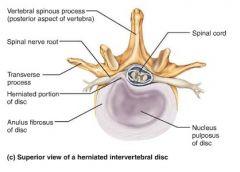
|
|
|
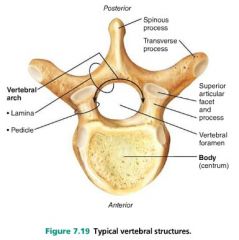
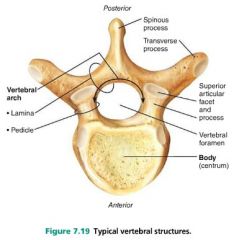
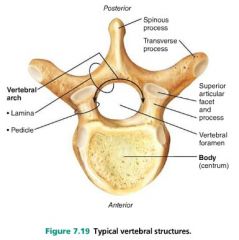
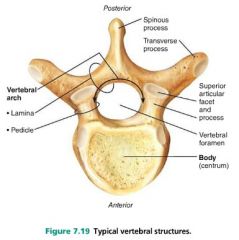
1. body (centrum) 2. arch |
2 main parts of a vertebra |
|
|
|
spinous process |
posterior projection of a vertebra |
|
|
|
vertebral foramen |
opening through each vertebra |
|
|
|
vertebral canal |
long canal through which the spinal cord passes, created by successive vertebral foramina |
|
|
|
1. flexion and extension 2. lateral flexion 3. rotation |
3 movements that can occur between vertebrae |
|
|
|
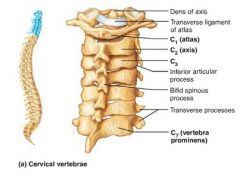
cervical vertebrae |
smallest, lightest vertebrae; triangular, large foramen |
|
|
|
atlas (C1) |
vertebra that carries the skull ("yes" movement), articulates with the occipital condyles, no body or spinous process |
|
|
|
axis (C2) |
vertebra that allows the atlas to pivot ("no" movement) due to the knoblike dens |
|
|
|
dens (odontoid process) |
knoblike projection of the axis vertebra; "missing body" of the atlas |
|
|
|
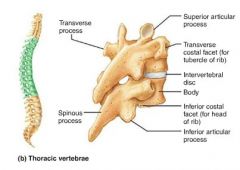
thoracic vertebrae |
vertebrae that articulate with the ribs; increase in size from first to last; "giraffe" |
|
|
|
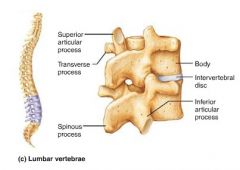
lumbar vertebrae |
massive, kidney-shaped vertebrae; weight-bearing; "moose" |
|
|
|
sacrum |
triangular bone forming the posterior wall of the pelvis; five fused vertebrae |
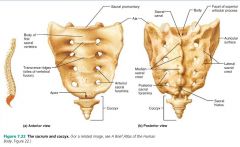
|
|
|
coccyx |
small triangular tailbone; four fused vertebrae |
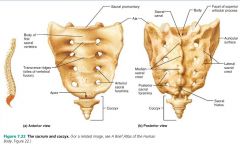
|
|
|
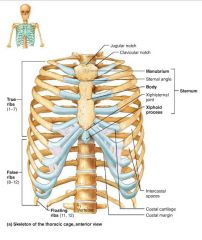
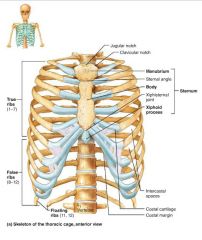
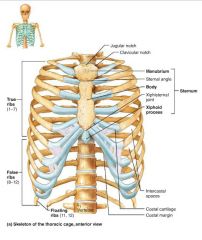
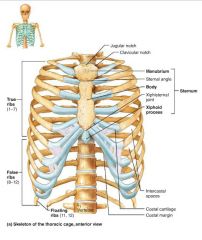
thoracic cage (bony thorax) |
forms a protective cage around the vital organs of the thoracic cavity, supports limbs, site of muscle attachment |
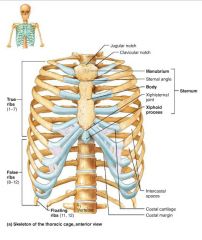
|
|
|
1. sternum 2. ribs |
2 parts of the thoracic cage |
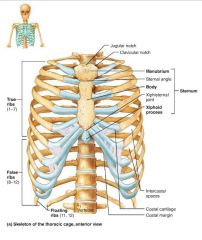
|
|
|
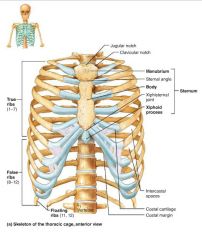
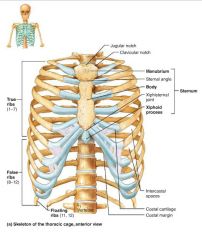
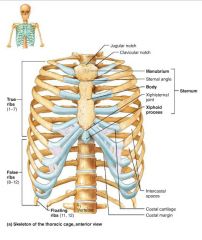
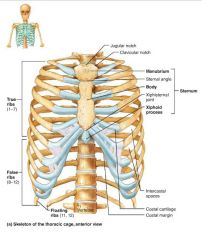
sternum (breastbone) |
flat bone lying on the anterior midline of the thorax |
|
|
|
1. manubrium 2. body 3. xiphoid process |
3 fused bones of the sternum |
|
|
|
manubrium |
part of the sternum that articulates with the clavicles and costal cartilages 1-2 |
|
|
|
body |
part of the sternum that articulates with the costal cartilages 2-7 |
|
|
|
xiphoid process |
small part of the sternum that serves as an attachment point for abdominal muscles |
|
|
|
ribs |
twelve pairs of thoracic cage bones that articulate with the vertebrae |
|
|
|
true ribs |
superior ribs that attach directly to the sternum via costal cartilages (1-7) |
|
|
|
costal cartilages |
bars of hyaline cartilage attaching the ribs to the sternum |
|
|
|
intercostal spaces |
spaces between the ribs occupied by muscles |
|
|
|
false ribs |
inferior ribs that attach indirectly to the sternum or not at all (8-12) |
|
|
|
floating ribs |
ribs with no anterior attachments (11-12) |
|
|
|
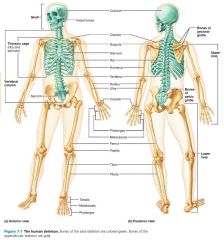
appendicular skeleton |
bones of the limbs and their girdles; movement and manipulation |
|
|
|
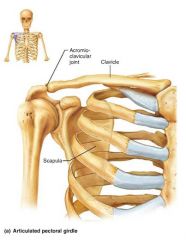
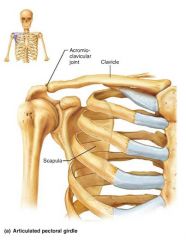
pectoral girdles |
attach the upper limbs to the body trunk |
|
|
|
1. clavicle 2. scapula |
2 bones of the pectoral girdle |
|
|
|
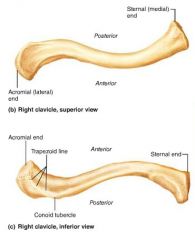
clavicles (collarbones) |
slender, S-shaped bones that extend horizontally across the superior thorax; anchor muscles and act as braces |
|
|
|
scapulae (shoulder blades) |
triangular, flat bones on the dorsal surface of the rib cage; forms the shoulder joint |
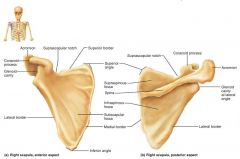
|
|
|
glenoid cavity |
shoulder blade cavity that articulates with the humerus, forming the shoulder joint |
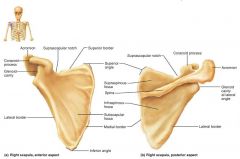
|
|
|
1. arm 2. forearm 3. hand |
3 parts of the upper limb |
|
|
|
arm |
the proximal portion of the upper limb |
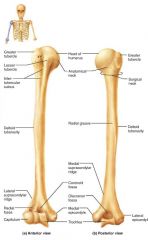
|
|
|
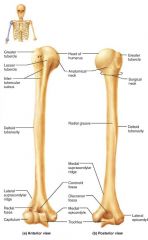
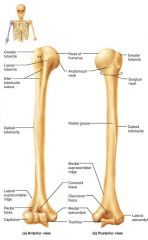
humerus |
the sole bone of the arm, semi-spherical head |
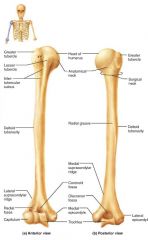
|
|
|
1. glenoid cavity (shoulder) 2. olecranon process (elbow) |
2 places the humerus articulates |
|
|
|
trochlea |
hourglass-shaped distal end of the humerus; articulates with the ulna |
|
|
|
olecranon fossa |
distal part of the humerus that receives the olecranon of the forearm |
|
|
|
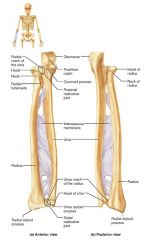
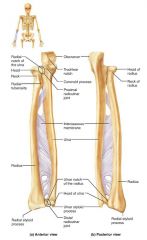
forearm |
the middle portion of the upper limb |
|
|
|
1. radius 2. ulna |
2 bones of the forearm |
|
|
|
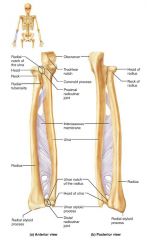
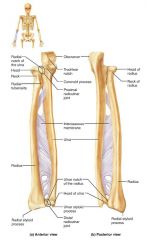
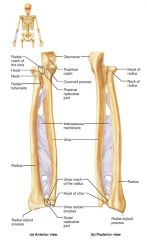
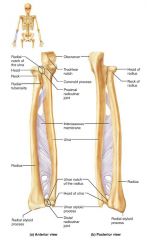
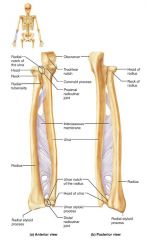
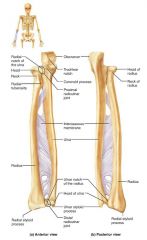
ulna |
medial, longer bone of the forearm; strong articulation with the elbow joint |
|
|
|
olecranon (elbow) |
forms part of a hinge that allows the forearm to bend and straighten |
|
|
|
trochlear notch |
concavity of the ulna where the trochlea fits, allowing the forearm to bend and straighten |
|
|
|
ulnar styloid process |
distal bump of the ulna; ligament runs from here to the wrist |
|
|
|
radius |
the lateral, shorter bone of the forearm; strong articulation with the wrist/hand |
|
|
|
radial styloid process |
distal bump of the radius; anchoring site for ligaments that run to the wrist |
|
|
|
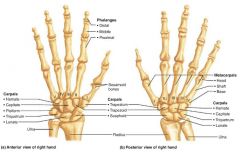
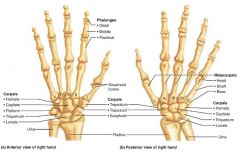
hand |
the distal portion of the upper limb |
|
|
|
1. carpus (8) 2. metacarpus (5) 3. phalanges (14) |
3 parts of the hand and their # of bones |
|
|
|
carpus |
the wrist; 8 small bones |
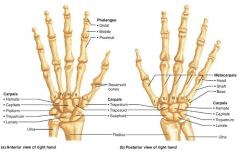
|
|
|
metacarpus |
the palm; 5 bones labeled 1-5 (lateral to medial) |
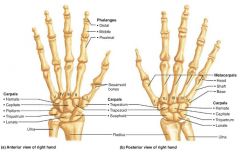
|
|
|
phalanges |
the fingers; 14 bones |
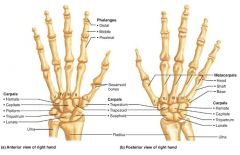
|
|
|
pelvic girdle |
attaches the lower limbs to the axial skeleton |
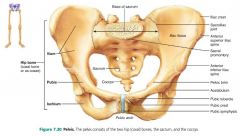
|
|
|
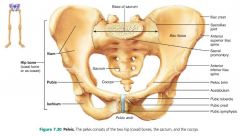
1. sacrum 2. os coxae (hip bones) |
2 parts of the pelvic girdle |
|
|
|
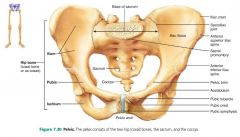
1. ilium 2. pubis 3. ischium |
3 parts of the hip bone (coxal bone) |
|
|
|
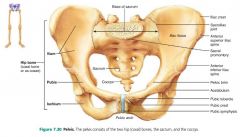
ilium |
large flaring bone that forms the superior part of the coxal bone |
|
|
|
greater sciatic notch |
posterior indentation where the sciatic nerve enters the thigh |
|
|
|
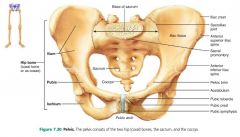
pubis |
the anterior, inferior part of the coxal bone |
|
|
|
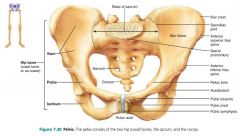
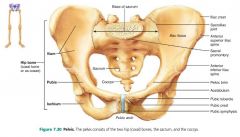
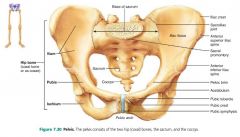
pubic symphysis |
where the two pubic bones join; separated by a fibrocartilage disc |
|
|
|
ischium |
posterior, inferior part of the coxal bone |
|
|
|
acetabulum |
pelvic socket that receives the head of the femur; the hip joint |
|
|
|
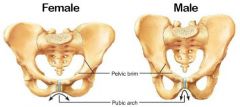
1. pubic arch (wider angle in females) 2. pelvic brim (wider, oval in females) |
2 differences between the pelvis of males and females |
|
|
|
1. thigh 2. leg 3. foot |
3 segments of each lower limb |
|
|
|
femur (thigh) |
the largest, strongest bone of the body |
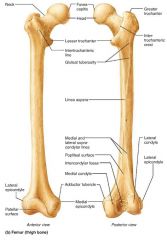
|
|
|
patella (knee cap) |
triangular sesamoid bone that protects knee |
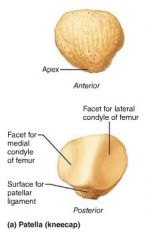
|
|
|
1. tibia 2. fibula |
2 parallel bones of the leg |
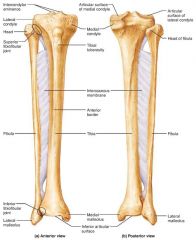
|
|
|
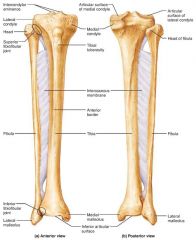
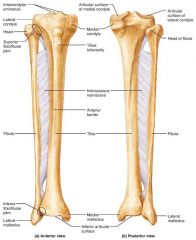
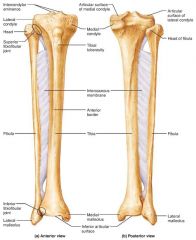
tibia |
medial, weight-bearing bone of the leg |
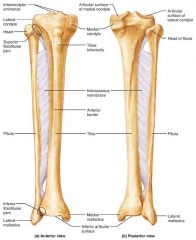
|
|
|
medial malleolus |
medial bulge of the ankle (tibia) |
|
|
|
fibula |
sticklike, lateral bone of the leg; does not bear weight |
|
|
|
lateral malleolus |
lateral bulge of the ankle (fibula) |
|
|
|
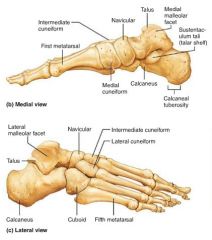
1. tarsus (7) 2. metatarsus (5) 3. phalanges (14) |
3 parts of the foot and their # of bones |
|
|
|
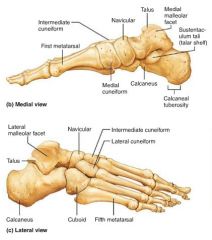
tarsus |
the ankle; 7 smaller bones |
|
|
|
1. talus (ankle) 2. calcaneus (heel bone) |
2 large tarsals that carry most of the body's weight |
|
|
|
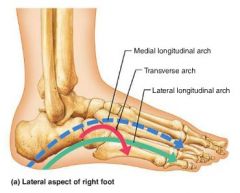
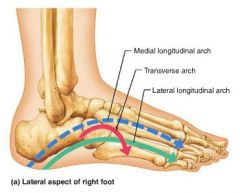
arches |
allow the foot to hold up weight |
|
|
|
1. medial longitudinal 2. transverse 3. lateral longitudinal |
3 arches of the foot |
|

