![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
29 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
1. prime mover (agonist) 2. antagonist 3. synergist 4. fixator |
4 functional groups of skeletal muscle |
|
|
|
agonist (prime mover) |
muscle that produces a specific movement |
|
|
|
antagonist |
muscle that opposes, or reverses, a particular movement |
|
|
|
synergist |
muscle that helps prime movers by adding a little extra force to a movement or by reducing undesirable movements |
|
|
|
fixator |
synergist muscle that immobilizes a bone or a muscle's origin so that the prime mover has a stable base on which to act |
|
|
|
flexion |
a muscle that crosses on the anterior side of a joint produces... |
|
|
|
extension |
a muscle that crosses on the posterior side of a joint produces... |
|
|
|
abduction |
a muscle that crosses on the lateral side of a joint produces... |
|
|
|
adduction |
a muscle that crosses on the medial side of a joint produces... |
|
|
|
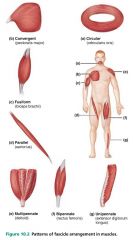
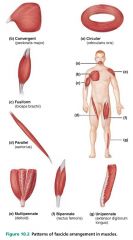
1. circular 2. convergent 3. parallel 4. pennate |
4 main fascicle arrangements |
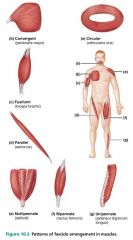
|
|
|
circular |
fascicular pattern when the fascicles are arranged in concentric rings; ex. orbicularis |
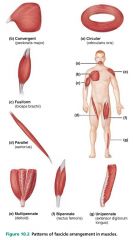
|
|
|
convergent |
fascicular pattern in which the muscle has a broad origin and its fascicles converge toward a single tendon or insertion; ex. pectoralis major |
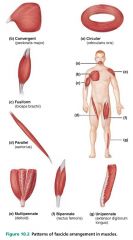
|
|
|
parallel |
fascicular pattern in which the fascicles run along the long axis of the muscle; ex. sartorius (thigh) |
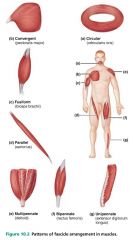
|
|
|
fusiform |
fascicular pattern characterized by a spindle-shaped muscle with an expanded belly; similar to a parallel pattern; ex. biceps brachii |
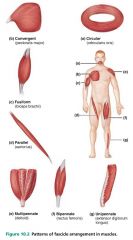
|
|
|
pennate |
fascicular pattern with short fascicles that attach obliquely to a central tendon that runs the length of the muscle; like a feather |
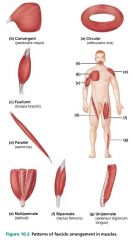
|
|
|
1. unipennate 2. bipennate 3. multipennate |
3 types of pennate muscles |
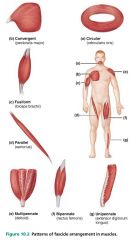
|
|
|
unipennate |
type of pennate muscle in which the fascicles insert into only one side of the tendon; ex. extensor digitorum longus (of the leg) |
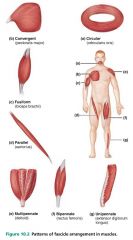
|
|
|
bipennate |
type of pennate muscle in which the fascicles insert into the tendon from opposite sides; ex. rectus femoris (of the thigh) |
|
|
|
multipennate |
type of pennate muscle with multiple "feathers"; ex. deltoid muscle (of the shoulder) |
|
|
|
lever |
a rigid bar that moves on a fixed point (fulcrum) when a force is applied to it |
|
|
|
fulcrum |
a fixed point on which a level moves |
|
|
|
effort |
applied force used to move a load |
|
|
|
load |
the resistance moved by an effort (applied force) |
|
|
|
mechanical advantage |
when a load is close to the fulcrum and the effort applied is far from the fulcrum; power lever |
|
|
|
mechanical disadvantage |
when the load is far from the fulcrum and the effort is applied close to the fulcrum; speed lever |
|
|
|
1. first-class 2. second-class 3. third-class |
3 classes of levers |
|
|
|
first-class lever |
the effort is applied at one end of the lever and the load is at the other, with the fulcrum somewhere in between; power or speed; ex. seesaw |
|
|
|
second-class lever |
the effort is applied at one end of the lever and the fulcrum is located at the other end, with the load somewhere in between; power; ex. wheelbarrow |
|
|
|
third-class lever |
the effort is applied between the load and the fulcrum; speed; ex. tweezers |
|

