![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
45 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
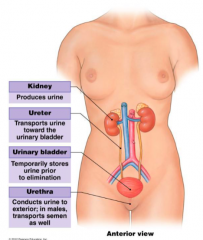
What does the urinary system consist of? (In order) |
2 kidneys 2 ureters 1 urinary bladder 1 uretha |
|
|
|
What are the primary functions of the kidneys? |
1. Excretion |
All involved in making urine. |
|
|
What is excreted via the kidneys? |
1. Urea, uric acid, creatinine, bile pigments 2. Excess water, ions, toxins 3. Drugs like penicillin |
|
|
|
How do the kidneys regulate acid-base / pH balance? |
They excrete hydrogen ions (which increase acidity) and reabsorb bicarbonate ions (which increase alkaline) |
|
|
|
What is osmoregulation? |
The maintenance of water content, blood volume and electrolytes |
|
|
|
What are the secondary functions of the kidneys? |
1. Production of Renin (which helps regulation BP & kidney function) 2. Production of erythropoietin 3. Conversion of Vit D to active Calcitriol (increases calcium levels) 4. Gluconeogenesis (makes glucose from carbs) 5. Detoxification |
|
|
|
What is renin and what does it do? |
An enzyme Regulates BP & kidney function |
|
|
|
What does erythropoietin do? |
Stimulates RBC production/haematopoeisis |
|
|
|
What is calcitriol and how is it made? |
A hormone that increases calcium levels. Vitamin D is converted into calcitriol in the kidneys. |
|
|
|
What is gluconeogenesis? |
New glucose being made from substrates. |
|
|
|
Where are the kidneys located? |
Bean shaped organs. Located in the higher abdominal region, on the post abdominal wall, under the floating ribs. Retroperitoneal. |
|
|
|
Which kidney is slightly lower than the other? Why? |
The right is slightly lower than the left. Because the liver pushes the right kidney down. |
L |
|
|
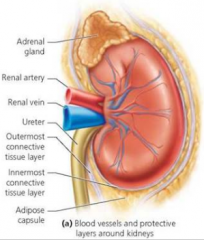
Describe the external anatomy of the kidney. |
3 layers of connective tissue coverings. 1. Renal fascia. Innermost. Collagen fibres. Anchors kidney to supporting structures. 2. Adipose tissue. middle. Cushions kidney. 3. Renal capsule. Collagen fibres. Transparent. Prevents infections. |
|
|
|
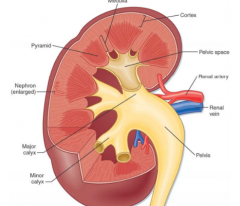
What are the three regions of the kidney internally? |
1. Cortex. Outer zone. 2. Medulla. Inner zone. Pyramids make nodes. 3. Renal pelvis. Funnel-shaped. Minor and major calyx. Continuous with ureter. |
|
|
|
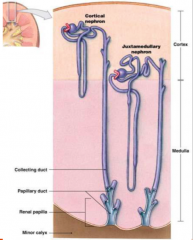
What is the functional unit of the kidney? How many exist in each kidney? |
Nephron. More than 1 million per kidney. |
|
|
|
What are the 2 kinds of nephrons? What % of each? |
Cortical nephrons & juxtamedullary nephrons (cortical are more in the cortex, juxta more in the medulla) |
C & J |
|
|
What are the roles of nephrons?
|
- Filter blood to form urine - Adjust levels of wastes and nutrients in blood and help maintain homeostasis by selective reabsorption & active secretion |
|
|
|
List the path of blood supply to the kidneys. |
Abdominal aorta > renal artery > artery branches > afferent arteriole > nephron > efferent arteriole > peritubular capillaries > venules > small veins > renal veins > inferior vena cava |
A R A A N E P V S R I All real Aces are nasty, especially proud, very stubborn, rarely interesting. |
|
|
What are the kidneys controlled by? What system regulates? |
Autonomic control by the renal plexus (in the kidneys). The Sympathetic NS. |
NO parasympathetic influence at all. |
|
|
How does the sympathetic NS innervate the kidneys? |
Sympathetic fibres regulate blood flow in response to body's requirements. Stimulates: Constricts. No stimulate: relax. |
Stimulation vs no stimulation |
|
|
What are ureters? Where are they located? What is their role? |
-Muscular tubes -Retroperitoneal and attached to the abdominal wall - Transport urine from renal pelvis to urinary bladder by peristalsis |
|
|
|
What are the three layers of the ureters? |
• Inner mucosa– Transitional epithelium– Surrounds lamina propria • Muscularis– Middle muscular layer– Longitudinal and circular smooth muscle • Adventitia– Outer connective tissue |
|
|
|
What is the shape of the urinary bladder? What does it do? Where is it located? What muscular feature does it inc? |
• Hollow, muscular organ • Stores urine before voiding • Located in the pelvic cavity posterior to thepubic symphysis, anterior to the vagina + rectum • Internal urethral sphincter (smooth muscle) |
|
|
|
Describe the female Urethra. |
- 4cm long - merely a passage for urine - Voluntary sphincter |
|
|
|
Describe the male Urethra. |
- 20cm long - Three parts: prostatic urethra, membranous urethra & penile urethra – Passage of semen and urine - Voluntary sphincter |
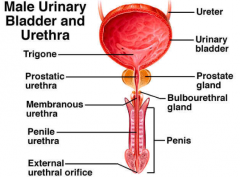
|
|
|
Describe the path of urine flow. |
Urine drains out of kidney pyraminds > minor calyces > major calyces > pelvis > ureter > bladder > urethra > exit |
P M M P U B U E Personally my mum prepares unbelievably beautiful Ugandan eggs |
|
|
How does the renal system work with the musculoskeletal system? (4) |
- a sphincter controls urination by closing the urethral opening - muscles of trunk protect renal organs - floating ribs protect kidneys - pelvis protects bladder |
|
|
|
How does the renal system work with the integumentary system? |
- sweat glands eliminate water & salts - keritinised epidermis prevents fluid loss - epidermis produces Vit D for renal production of calcitriol |
|
|
|
Which other body systems does the renal system work with? |
- Musculoskeletal - Integumentary system - Digestive system - Respiratory system - Cardiovascular - Exocrine + Endocrine |
M I D R C |
|
|
How does the renal system work with the digestive system? |
- DS absorbs water needed to excrete wastes in the kidney - Absorbs ions needed to maintain normal body concentrations - Kidneys excrete toxins & excess fluid absorbed by the DS |
|
|
|
How does the renal system work with the respiratory system? |
-RS assists kidneys in pH balance. Hypervent to eliminate c02. Kidneys = eliminate hydrogen ions & reabsorb bicarbonate ions to bind with H (& increase ph) |
|
|
|
How does the renal system work with the cardiovascular system? |
- CVS delivers blood to the nephrons for filtration - accepts fluids and solutes reabsorbed during urine production |
|
|
|
How does the renal system work with the exocrine system? |
- produces renin, and enzyme which increases BP |
|
|
|
What is Renin? When is it released? What does it convert? What does it do? |
- an enzyme produced by the kidney - in response to decreased renal blood flow - converts angiotensinogen to angiotensin I - increase blood pressure |
|
|
|
How does the renal system work with the endocrine system? |
- produces erythropoietin - influenced by aldosterone - influenced by ADH |
|
|
|
What does erythropoietin do? Where is it produced? When is it secreted? |
- promotes RBC production in the bone marrow - the kidneys - in response to decreased renal o2 levels |
|
|
|
Where is aldosterone produced? What does it do? |
- The adrenal gland - Adjusts rates of electrolyte (Na+ & K+) & fluid reabsorption by kidneys |
|
|
|
Where is ADH synthesised? Where is it secreted? What does it do? |
The Hypothalamus. The posterior pituitary. Makes kidneys retain water & decrease urination for elevation of BV & BP |
|
|
|
What is the name of the big muscle in the bladder AKA the one that contracts when voiding? |
The Detrousal muscle |
|
|
|
What is the pathway of urine from kidney to the outside of the body? |
Collecting duct > minor calyx > major calyx > renal pelvis > ureter > bladder > urethra |
|
|
|
How are two ways kidney function is tested? |
GFR is tested via a creatinine excretion measure Blood-urea nitrate test (sees if urea is actually exiting or not) |
|
|
|
What is the GFR? What does it measure? |
Glomerular filtration rate. The amount of filtrate the kidneys produce in a minute into to Bowman's capsule. 90-120ml p/m. |
|
|
|
What does renin do to angiotensinogen? |
Renin turns angiotensinogen (made in liver) into angiotensin 1. (this takes place in the lungs.) |
|
|
|
What turns angiotensin into angiotensin II? |
ACE aka Angiotensin-converting enzyme |
|
|
|
What does Angiotensin II accomplish? |
Vasoconstriction & Encourages the release of Aldosterone (which causes water to be reabsorbed along with sodium) AKA it increases S.V & therefore BP |
|

