![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
41 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
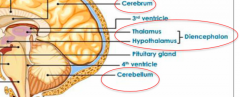
What is in the diencephalon? |
Hypothalamus & thalamus |
|
|
|
What is the spinal cord comprised of? |
Medulla Oblongata Pons Midbrain |
|
|
|
1. What is the cerebrum comprised of? 2. What is it separated by? 3. What is it connected by? 4. List the lobes |
|
|
|
|
Where is the grey matter? Where is the white matter? |
Grey matter on the outside White matter on the inside |
|
|
|
1. Where is the frontal lobe located? 2. What is it associated with? |
1. The very front of the brain 2. Personality & cognition & intellect AND voluntary muscle contraction - PRIMARY MOTOR CORTEX |
|
|
|
Where is the Broca's area? What is it responsible for? |
In the frontal lobe. Generation and articulation of speech. |
|
|
|
Where is the primary somatosensory cortex? |
The parietal lobe. |
|
|
|
What is the parietal lobe associated with? |
Taste, temp. Conscious perception of touch, pressure, pain, vibration. |
|
|
|
Where is the temporal lobe? What is its role? |
Temple, below frontal lobe - Auditory cortex, olfactory cortex. Hippocampus is here (memory). |
|
|
|
Where is the Wernicke's area? What is it associated with? |
In the temporal lobe. Helping us to understand and spoken language. |
|
|
|
What is the role of the occipital lobe? |
Visual association area/visual cortex |
|
|
|
What are the 4 lobes of the brain? |
Occipital Frontal Temporal Parietal |
|
|
|
Where is the pineal gland in relation to the pituitary? What does it secrete? |
Further toward the posterior of the brain Melatonin for day/night recognition and sleep/wake |
|
|
|
How many cranial nerves are there? What do they connect do what? How many sensory? How many motor? How many both? |
12 pairs Brain to PNS 3 sensory (only) 5 motor, 4 both |
|
|
|
What is so special about the Vagus nerve (X)? What is its role? |
- only nerve that continues down beyond the head and spine into the chest and abdomen - acts as an interface with the autonomic NS & the heart and digestive tract |
|
|
|
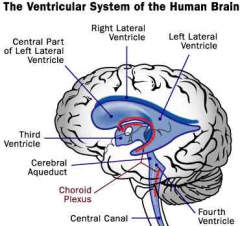
Where is the choroid plexus? What is its roles (2)? |
-Found in the lateral ventricles of the brain -Generates CSF (cerebral spinal fluid) - is a barrier b/w blood & CSF |
|
|
|
What is the shape and length of the spinal cord? What does the length span to and from? |
45cm cylindrical Medulla to L2 |
|
|
|
What are the divisions of the spinal cord? |
Cervical Thoracic Lumbar Sacral Coccyx |
|
|
|
What does the cervical portion of the spinal cord link/operate? |
The upper limbs |
|
|
|
What does the Lumbar portion of the spinal cord work with/operate? |
The lower limbs. |
|
|
|
What is the role of the spinal cord? (2) |
1. Transmit info to and from the peripherals / up and down the CNS too 2. Reflexive actions to protect the body |
|
|
|
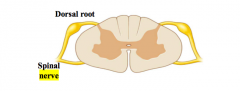
Where are the spinal nerves located? How many pairs are there? What type of fibres do they carry? |
Either side of the spine. 31 pairs. Both sensory & motor fibres. |
|
|
|
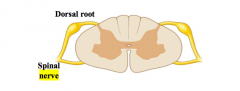
What combines to form the spinal nerve? |
The ventral root and the dorsal root |
|
|
|
Where is the diencephalon located? |
Posterior part of the forebrain, b/w the hemispheres & above the midbrain & pons |
|
|
|
What is the thalamus involved in? |
Arousal, wakefulness & alertness - Relays sensory and motor signals to the cerebral cortex |
|
|
|
1. What does CSF stand for?
2. Where is it made? 3. Where does it circulate? 4. What are its main roles? |
1. Cerebrospinal Fluid 2. Choroid plexus 3. Within and around the brain & spinal cord through ventricles 4. Cushions delicate cerebral structures (1), (2) transports nutrients, chemical messages & waste (neuronal waste) |
|
|
|
1. Where is the cerebellum? 2. What is it's nickname? |
1. On top of the pons, behind the brain stem 2. "The Little Brain" |
|
|
|
What does the cerebellum control/get involved in? (3) |
1. Posture (receives msgs from balance organs) 2. Proprioception (awareness of body in space) 3. Motor coordination & motor memory |
|
|
|
Where is the brain stem? |
Centre of the brain at the base, connecting through to the neck |
|
|
|
What does the brain stem comprise? |
Pons, Medulla, Midbrain |
|
|
|
What is the midbrain the reflex centre for? |
Head and eye movements |
|
|
|
What does the medulla control? |
Vital autonomic functions like heart rate, RR, BP, vomiting and coughing |
|
|
|
What does the Pons connect? |
The medulla to the cerebellum. Modifies respiration rates. |
|
|
|
What special centres live in the Pons? |
Pneumotaxic centre Apneustic centre |
|
|
|
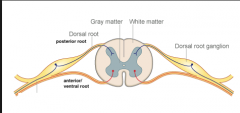
What does SPAM stand for in the cross section of the spinal cord? |
Axons of SENSORY neurons = posterior/dorsal root Axons of MOTOR neurons = anterior/ventral root (If you were drawing it, anterior is closer to the bottom of the page) |
|
|
|
What is the dorsal root ganglia? |
cell bodies of sensory neurons headed into the spinal cord |
|
|
|
List the layers of the skull/meninges working from bone inward. |
Epidural Dura Mater Subdural Arachnoid Subarachnoid Pia Mater |
|
|
|
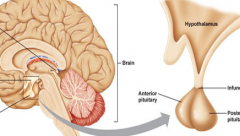
What system is the pituitary gland involved in? What is its main concern? |
Endocrine Controls growth, development & the function of other endocrine glands |
|
|
|
What protects the CNS? (4) |
- Cranial bones + vertebrae - Meninges - CSF - Blood brain barrier |
|
|
|
How does the BBB protect the CNS? |
Blood Brain Barrier: capillaries that are semi-permiable AKA let in glucose/energy/nutrients, but not much else |
|
|
|
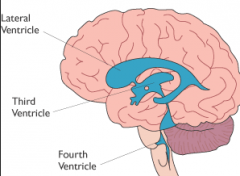
- How many chambers are there in the brain? - what are they called? - which one extends down into the spinal cord? - what are there names & composition? |
- 4 - ventricles - the 4th - 2 x lateral, then the 3rd and 4th |
|

