![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
31 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
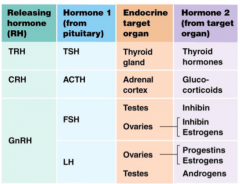
What are the major hormones of the reproductive system? (Male or female) |
- Testosterone (androgen) - Oestrogen - LH (pitu) - FSH (pitu) - GnRH (hypoth) - Progesterone |
|
|
|
1. When is there an increase production of testosterone? 2. What are its (5) roles? |
1. Puberty 2. i) sperm production ii) libido iii) stimulate bone + muscle growth iv) male secondary characteristics e.g. facial hair v) maintain accessory glands. |
|
|
|
1. When is there an increase production of oestrogen? 2. What are its 5 roles? |
1. Puberty. 2. i) stimulate muscle and bone growth. ii) secondary characteristics (boobs) iii) maintaining accessory organs iv) libido v) endometrial growth and secretion |
|
|
|
Describe the chain of hormone events that produces testosterone + oestrogen (as well as inhibit) |
1. Hypothalamus releases GnRH 2. Anterior pituitary releases LH & FSH. Reaches testes & ovaries. 3. FSH = makes testes secrete inhibin. make ovaries secrete inhibin or oestrogen. LH = makes testes secrete androgens. makes ovaries secrete progesterone or estrogen. |
|
|
|
What hormones are essential for spermatogenesis? Where are they released from? |
LH & FSH released from the anterior pituitary. |
|
|
|
What hormones influence nurse cells? What does it do? |
FSH Stimulates production of inhibin Helps nurse cells support and regulate |
|
|
|
What hormones influence interstitial cells? What does it do? |
LH Produce testosterone |
|
|
|
What are the (2) ways negative feedback helps regulate hormonal control n men? |
1. Inhibin produced by FSH in testes will act on the hypothalamus to reduce GnRH secretion. 2. Testosterone reaches outside of the testes, brain will recognise high levels and reduce LH output |
|
|
|
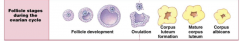
What is happening to the follicle in the ovary in days 0-13 of the cycle? What happens on day 14? |
Primordial follicles are maturing into primary, secondary, tertiary: AKA development. 14: Ovulation. Egg released to uterine tube with some cells. Most follicle tissue left behind. |
|
|
|
What happens to the cells left behind when the egg leaves during ovulation? Inc. function here. What happens to this structure if you don't fall pregnant? |
These develop into the corpus luteum, which has a hormone-releasing function. Regresses and dies, turns into corpus albicans |
|
|
|
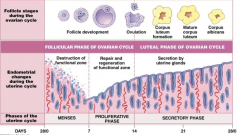
What happens during days 0-7 of the cycle in the uterus. |
Mensies/the destruction of the functional. Cells dying. Passing out of body. |
|
|
|
What happens days 7-14 of the cycle, in the uterus? |
Proliferation stage. Repair of endometrium. |
|
|
|
What happens during days 14-28 of the cycle, in the uterus? |
Secretory phase. Glands secreting nutrients, mucous etc hoping to be pregnant |
|
|
|
What happens when the corpus luteum dies? |
The hormone it produces |
|
|
|
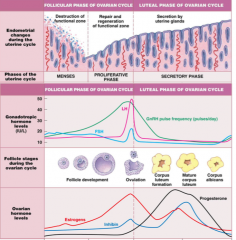
1. What happens in the first pre-ovulation / follicular phase? (Name days) (5 things) |
days 1-5 1. endo from last cycle shed 2. GnRH released from hypoth 3. FSH released from ant. pit 4. follicle in ovary contains egg 5. FSH stimulates follicle |
|
|
|
What happens in the second pre-ovulatory/follicular phase? (name days) (7 things) |
days 6-13 1. About 20 follicles start to grow 2. Follicles secrete inhibin + progesterone 3. One becomes dominant, rest regress 4. Rising estrogen & inhibin reduces FSH & LH (negative feedback) (makes only 1 follicle leave) 5. Rising estrogen stimulates endometrium (begins proliferation again) 7. LH levels surge |
|
|
|
what happens when LH surges? |
Ovulation. Day 14. |
|
|
|
What happens during the post-ovulation/luteal phase (5)? What days are this? |
15-28 1. Corpus luteum forms from remenants of follicle 2. Progesterone being produced from CL 3. Endo keeps developing. 4. @ 12 days (if no pregnancy), CL dies. 5. Therefore: progesterone stops being made, lining no longer supported, lining shed - back to the start! |
|
|
|
What are the two zones of the endometrium? Describe them. |
1. Functional zone. Regularily grows and is shed. 2. Basilar zone. Permanent. Attaches endo to myo. |
|
|
|
1. What is degenerated during menses? 2. How is this achieved? 3. What is safe? |
1. The functional zone. 2. Artery constriction to zone because of lower progesterone. 3. The basilar zone. |
|
|
|
1. What is the dominant hormone during the proliferation phase? 2. What produces it? 3. What does it achieve (3)? |
1. Oestrogen. 2. Follicles. 3. Glycogen to endo, more vascularisation and growth |
|
|
|
1. What is the most important hormone during the secretory phase? Where is it made? 2. What happens now? 3. What dies during this phase? |
1. Progesterone from corpus lutem. 2. Increased vascularisation, secretions increase, glands enlarge. |
|
|
|
What happens if there IS fertilisation and implantation during the secretory phase? What initiates this? |
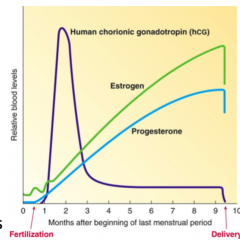
The corpus luteum DOESN'T die! Lining is NOT shed. 1. The implanted egg sends out hCG. Human chorionic gonadotropin. |
|
|
|
1. What is hCG? 2. What does it act on to do? |
1. Human chorionic gonadotropin. 2. Acts on corpus luteum to stay alive and keep producing progesterone. |
|
|
|
When does the CL finally die off? (If fertilization + implantation has happened)
What product decreases at this point as well? |
When the placenta has matured enough to be its own source of progesterone and estrogen.
Human chorionic gonadotropin. |
|
|
|
What does progesterone from the placenta do? (2) |
1. Maintains endometrium. 2. Suppresses uterine contractions. |
|
|
|
What does oestrogen do throughout pregnancy? (2) |
Mamary gland development
Myometrium preparation (increased sensitivity) |
|
|
|
1. What causes menopause? 2. What is a hormonal result? 3. What are 3 results in oestrogen loss? |
1. Follicular shortage. 45-50. 2. Oestrogen production drops, no ovulation. 3. osteoporosis, neural effects (depression, hot flash), increased CVD risk |
|
|
|
What causes the surge of LH at day 14? |
The oestrogen levels being produced by the stimulated/growing follicles It is a feedback mechanism of sorts |
|
|
|
What is the name of the hormone that the early fertilised + implanted embryo releases and sends as a message to the ovary? |
HcG Human chorionic gonadotropin |
|
|
|
What is the role of HCG in the body? |
It encourages the corpus leteum to stay alive and continue producing progesterone |
|

