![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
81 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What are the small bones located at the head of the 1st metatarsal
|
sesmoids
|
|
|
What is the Chopart (showpart) joint
|
the junction between the hindfoot and midfoot. (talus and navicular on lateral view)
|
|
|
What is the hindfoot
|
the talus and calcaneous
|
|
|
What is the junction between the midfoot and metatarsals
|
the lisfanc joints
|
|
|
What is the midfoot
|
Navicular (behind the cuneiforms), cuneiforms (big toe), and cuboid (little toe)
|
|
|
What is the forefoot
|
Metatarsals and phalanges
|
|
|
What is the most common fx of the 5th metatarsal
|
avulsion fx
|
|
|
What is the cause and exact location of an avulsion fx of the 5th metatarsal
|
inversion and avulstion of the 5th metatarsal tuberosity
|
|
|
What is the cause of an avulsion fx of the 5th metatarsal tuberosity
What is considered adduction of the toes? |
pull of the peroneus brevis tendon
There is an imaginary line on the 2nd toe and if a toe is moving towards that line it is considered adduction. Note for the fingers it is the middle finger. |
|
|
Where does the peroneus brevis insert
|
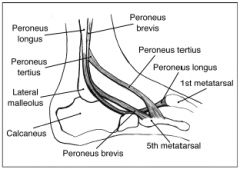
|
|
|
Where is an avulstion fx of the 5th metatarsal (i think tuberosity and styloid are used interchangeable)
|
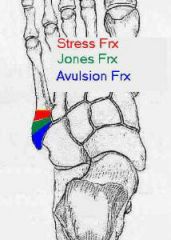
|
|
|
What is a pitfall of diagnosing a 5th metatarsal avulsion fx
|
normal apophysis of child (it is oriented longitudinaly)
|
|
|
Where is the location of a true jones fx
|
transverse fx of the base that occurs3/4 to 1' from the base of the 5th metatarsal
|
|
|
What heals more slowly jones fx or avulsion fx
|
jones fx (has increased risk of delayed or fibrous union)
|
|
|
What is the cause of stress fx of the metatarsal
|
repetitive microfx
|
|
|
What demographic do stress fx of the metatarsals occur in
|
dancers or soldiers
|
|
|
What happens when the stress fx occur to the metatarsals
|
microcallus formation which leads to reinforcement (endosteal thickening)
|
|
|
In the metatarsal stress fx where does this mc occur
|
2nd and 3rd MT
|
|
|
What is the gold standard for detecting stress fx
|
bone scan (100% sensitive after 72h)
|
|
|
What is visible on a plain film in a stress fx
|
the periosteal thickening
|
|
|
What is the MC fx of the navicular
|
avulsion fx of the dorsal aspect
|
|
|
What is associated with a doral avulsion fx of the navicular
|
avulsion of the dorsum of the calcaneous
|
|
|
What is the cause of avulsion fx of the navicular
|
twisting of the midfoot
|
|
|
What is the best projection and tx for a navicular avulsion
|
requires lateral projection and is treated conservatively
|
|
|
Where is the dorsum of the navicular
|
the top
|
|
|
What is the MC fx tarsal bone
|
calcaneous
|
|
|
What is the MC mechanism for calcaneal injury
|
falls or jumps from heigh
|
|
|
What is more common intra-articular or extra-articular
|
intra-articular (75%)
|
|
|
What is important to evaluate in a calcaneal fx
|
the subtalar joint
amount of depression of the posterior facet |
|
|
What is the subtalar joint
|
the articulation of the calcaneous with the talus
|
|
|
What are the superior articular surface facets
|
posterior
middle and anterior facets |
|
|
What are the location of the articular facets of the talus and calcaneous
|
posterior facet is the largest and is the major weight bearing surface
middle facet is anteromedial on sustentaculum tali anterior facet is often confluent with middle facet |
|
|
The facets of the ankle, subtalar, and talocalcaneonavicular joints. A, Diagram of the talus from above to show the three-surfaced trochlea that fits into the mortise formed by the lower ends of the tibia and fibula. B, Diagram of the calcaneus from above to show the posterior facet (P) for the subtalar joint, separated by the canalis and sinus tarsi from the middle (M) and anterior (A) facets of the talocalcaneonavicular joint. The socket of this latter joint is completed by the spring ligament and the concavity of the navicular. C, Diagram of the talus from below to show its corresponding facets for the subtalar and calcaneonavicular joints. Cf. fig. 12-36. A broad arrow in A emphasizes that the head of the talus is directed anteromedially
|
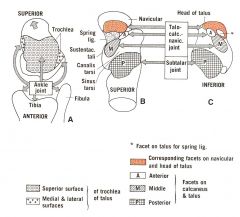
The facets of the ankle, subtalar, and talocalcaneonavicular joints. A, Diagram of the talus from above to show the three-surfaced trochlea that fits into the mortise formed by the lower ends of the tibia and fibula. B, Diagram of the calcaneus from above to show the posterior facet (P) for the subtalar joint, separated by the canalis and sinus tarsi from the middle (M) and anterior (A) facets of the talocalcaneonavicular joint. The socket of this latter joint is completed by the spring ligament and the concavity of the navicular. C, Diagram of the talus from below to show its corresponding facets for the subtalar and calcaneonavicular joints. Cf. fig. 12-36. A broad arrow in A emphasizes that the head of the talus is directed anteromedially
|
|
|
What are the 3 landmarks that are used in boehlers angle
|
anterior superior spine (calcaneus)
Posterior facet of the subtalar joint posterior tuberosity |
|
|
boehlers angle
|
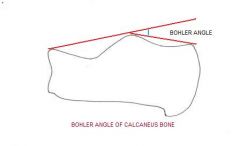
|
|
|
What is a normal boehlers angle
|
20-40%
|
|
|
Are stress fx of the calcaneous common
|
no
|
|
|
What demographic gets calcaneal fxs
|
runners
|
|
|
What portion of the calcaneous typicaly gets stress fx
|
posterior/dorsal aspect
|
|
|
What are the plain film findings
|
2-4 wks normal
then sclerotic band will form |
|
|
What 2 studies will be more sensitive for detecting stress fx in general
|
bone scan and MRI
|
|
|
What should the lateral border of the first metatarsal line up with
|
the lateral boder of the first (medial) cuneiform
|
|
|
anatomy of foot
|
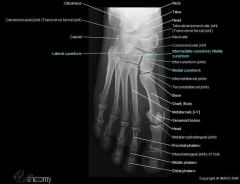
|
|
|
What is the normal anatomic relation of the 2nd metatarsal
|
the medial border of the 2nd metatarsal should align with the medial border of the 2nd cuneifom
|
|
|
What is the normal anatomic relation of the 3rd metatarsal and cuneiform
|
the medial and lateral border of the 3rd metatarsal should align with the medial and lateral borders of the 3rd (lateral) cuneiform.
|
|
|
What is the normal anatomic relationship of the 4th toe
|
the medial border of the 4th metarsal should align with the medial border of the cuboid
|
|
|
What is the normal anatomic alignment of the lateral margin of the 5th metatarsal
|
the 5th metatarsal styloid should project lateral to the cuboid by less than 3mm (OBLIQUE VIEW)
|
|
|
What is the most common dislocation of the foot
|
lisfranc
|
|
|
how often are lisfranc fx missed
|
20%
|
|
|
What are the bones in which a lisfanc dislocation occurs
|
the tarsal and metatarsal bones
|
|
|
What is the MOI
|
severe plantar flexion of the foot
|
|
|
What activities commonly result in lisfranc fx/dislocaiton
|
sports, MVC, falls
|
|
|
What disease will predispose a pt to a lisfranc fx/dislocation
|
diabetes
|
|
|
What does the lisfranc ligament connect
|
the base of the 2nd metatarsal diagnol with the the medial aspect of the first cuneiform
|
|
|
What happens if there is a lisfranc dislocation and the lisfranc ligament stays intact
|
there will be a fx of the lateral aspect of the 1st cuneiform or the base of the 2nd metatarsal.
|
|
|
What are the 2 types of lisfranc fx/dislocations
|
homolateral and divergent
|
|
|
Where is the lisfranc ligament
|
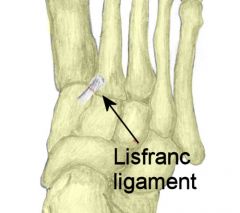
|
|
|
What is a homolateral lisfranc fx/dislocation
|
all MT are dislocated to the same side (usually 2-5th MT dislocated laterally)
|
|
|
What is more common the homolateral or divergent
|
homolateral
|
|
|
What is a divergent type lisfranc dislocation
|
medial displacement of the 1st metatarsal and lateral displacement of 2nd through 5th MT
|
|
|
What is the divergent type of lisfranc associated with
|
frx of the 1st cuneiform
|
|
|
Is it possible for the divergent type to only involve medial displacement of the 1st metatarsal
|
yes
|
|
|
What is a more sever fx a divergent or homolateral lisfranc
|
divergent
|
|
|
What fxs and other dislocations are associated with a lisfranc dislocation
|
base of the 2nd metatarsal
cuboid fracture of shaft of metatarsal dislocation of 1st adn 2nd cuneiforms and cuneonavicular joints fx of the navicular |
|
|
Is there a relationship between lisfranc and charcot arthropathy
|
yes, lisfranc are uncommon in the general population but among diabetics it is more common.
|
|
|
What is a more sever fx a divergent or homolateral lisfranc
|
divergent
|
|
|
What % of pt with charcot arthropathy may have a lisfranc dislocation
|
45%
|
|
|
What fxs and other dislocations are associated with a lisfranc dislocation
|
base of the 2nd metatarsal
cuboid fracture of shaft of metatarsal dislocation of 1st adn 2nd cuneiforms and cuneonavicular joints fx of the navicular |
|
|
What is another clue that a lisfranc dislocation may be present besides the metatarsals lining up with there respective tarsal bones
|
if there is a gap of greater than 5 mm between the bases of the 1st and 2nd metatarsal or 1st and 2nd cuneiform
|
|
|
Is there a relationship between lisfranc and charcot arthropathy
|
yes, lisfranc are uncommon in the general population but among diabetics it is more common.
|
|
|
What % of pt with charcot arthropathy may have a lisfranc dislocation
|
45%
|
|
|
What is another clue that a lisfranc dislocation may be present besides the metatarsals lining up with there respective tarsal bones
|
if there is a gap of greater than 5 mm between the bases of the 1st and 2nd metatarsal or 1st and 2nd cuneiform
|
|
|
What is the MOI for a chopart fx/dislocation
|
falls from heights, MVC, sports related (basketbal)
|
|
|
Where do chopart fx occur
|
the junction of the hind foot and midfoot
|
|
|
What is the joint of the hindfoot and midfoot
|
tarsal --- navicular
calcan---cuboid hindfoot is talus and calcaneous midfoot is navicular and cunieform and other tarsal bones |
|
|
What are the imaging finds of a chopart fx
|
medial and dorsal displacement of distal fragments although lateral displacement can occur
|
|
|
Does the talus continue to articulate with the tibia
|
yes
|
|
|
What are associated fx of the a chopart fx
|
calcaneous
cuboid navicular |
|
|
What does a chopart dislocation look like
|
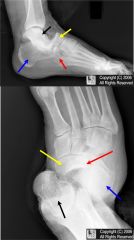
|
|
|
What happens to the navicular compared to the talus in a chopart dislocation
|
it dislocates superiorly (dorsal) compared to the talus (on lat view)
|
|
|
On the frontal view (superior view) what how is the navicular and talus dislocated
|
there is lateral displacement of the entire foot compared to the talus.
|

