![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
63 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What are the 3 rules of 3 of cervical spine
What are the major C-spine fractures |
predentate space should be less than 3mm
prevetebral soft tissue at C3 is 3mm anterior wedging of 3mm or more suggest a compression fracture jeffersons (burst of C1) hangmans (pars of C2) extension teardrop (anterior inferior avulsion) burst clay shovelers (spinous process) perched/locked facets and alantoaxial dislocation (ligament injury) |
|
|
What are the 3 parallel lines of the c-spine
|
anterior bodies (anterior long ligament)
posterior bodies (posterior long ligament) Spinolaminar white line |
|
|
What is the spinolaminar white line
|
the junction between the spinous process and the lamina
|
|
|
What is the mechanism of alantoaxial dislocation
|
hyperflexion
|
|
|
What is th relative movement of C1 and C2 in an alantoaxial dislocation
|
C1 forward on C2
|
|
|
Are neurologic injuries common with alantoaxial dislocations
|
yes
|
|
|
What measurement is increased in an alantoaxial dislocation
What is the cause of alanto-axial disassociation |
predentate space
Forward movement of the atlas on the axis is normally restricted by the transverse ligament The transverse ligament is the primary restraint against atlantoaxial, anteroposterior movement. Alanto axial disassoication will occur if this ligament is injured |
|
|
What is the most common fracture of C1
|
neural arch fracture
|
|
|
What is the mechanism of a neural arch fracture
|
hyperextension
|
|
|
What is a common pitfall of a neural arch fracture
|
congenital anomaly
|
|
|
What does the atlas (c-1) and axis (C-2) look like
|
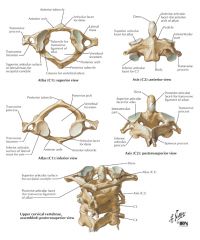
|
|
|
What part of the atlas (C-1) is fractured in a burst fractue
|
anterior and posterior arches of the neural arch
|
|
|
What is the mechanism of a burst fracture
|
compressive force such as diving accident
|
|
|
What is another name for a burst fracture
|
jefferson fracture
|
|
|
What is the best way to evaluate a burst (jefferson) fracture using plain film
|
open mouth view
|
|
|
What does an open mouth view look like
|
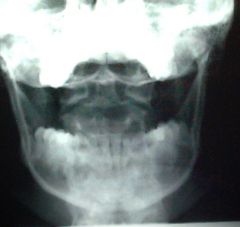
|
|
|
What is the most common fracture of C2
|
hangmans fracture
|
|
|
Describe a hangmans fracture of C2
|
fracture through pedicles or pars of C2 with anterior slip of C2 on C3 (pedicle and pars are used interchangeable when refering to C2. This is bc the exact anatomy is not agreed on)
This results in anterior subluxation of the anterior vetebral body (dens) of C2 Also there is posterior displacement of the posterior element of C2 |
|
|
What is the MC cause of a hangmans fracture
|
hyperextension compression (MVA)
(chin on dashboard) |
|
|
Are hangmans fractures associated with neuroloical defect
|
no if associated with MVA
|
|
|
What fracture is associated with an hangmans fracture
|
a teardrop avulsion fracture of the anterior-inferior aspect of C2
|
|
|
What is the MC cause of a dens fracture
|
hyperextension injuries
|
|
|
What is the movement of C1 and C2 with a dens fracture
|
forward subluxation of C1 on C2
|
|
|
What are the 3 major types of dens fractures
|
tip of dens (5%)
base of dens (65%) sub-dentate (30%) |
|
|
What is the mc type of dens fracture
|
base of dens
|
|
|
What are 3 pitfalls to dens fractures
|
Mach-lines
Non-union ossification centers Non-union of previous fracture |
|
|
What is a mach line
|
Mach bands are an optical phenomenon in which dark
and light lines appear at the borders of structures of different radiodensity on radiographs. I |
|
|
What type of film is a mach line of the base of the dens seen
(plain film) |
coronal and the lateral film should be checked to determine if it is truly a fracture
|
|
|
Where is the mach line seen at the base of the dens
|
where the C1 anterior arch overlaps the bens
|
|
|
What is the mechanism of a C3-C7 burst fractures
|
axial loading from MVA
|
|
|
Do burst fractures commonly result in comminuted vertical fractures through the vetebral body
|
yes
|
|
|
What should be carefully looked for in a pt with a burst fracture
|
fragments that are retropulsed into the spinal canal
|
|
|
Do burst fractures sometimes result in a flexion tear drop fracture
|
yes
|
|
|
Describe a flexion tear-drop fracture
|
avulsed anterior/inferior triangular shaped fragment which is displaced anteriorly
|
|
|
Besides a vertically comminuted fracture of the vetebral body and sometimes a flexion tear drop fracture what else occurs to burst fractues of C3-C7
|
facet joints and interspionous distance widened
|
|
|
What percent of pt with burst fractures of C3-C7 have neurologic deficits
|
70%
|
|
|
What is the interspinous distance
|
the distance between the posterior spinous process on lateral films
|
|
|
Do burst fractures result in disc space narrowing
|
yes
|
|
|
What is the mechanism of a simple compression fracture of the C-spine
|
flexion type injury
|
|
|
Does anterior wedging of 3mm or more suggest a compression fracture
|
yes
|
|
|
Which endplate is usually invoved in a compression fracture
|
superior endplate
|
|
|
What is a clay-shovelers fracture
|
avulsion fracture of spinous process of C6 or C7
|
|
|
Which cervical level is more common for a clay-shovlers fracture
|
C7
|
|
|
What is the mechanism of a clay-shovelers fracture
|
rotation of trunk relative to the neck
|
|
|
Which direction to the inferior facets of the cervical vertebrae face
|
they face posteriorly while the superior facets face anteriorly
|
|
|
What is the mechanism by which a ligamentous injury to the spinal cord occurs
|
flexion/distraction
|
|
|
How does a distraction injury occur
|
if your head gets stuck and body is being pulled away
|
|
|
What is the opposite of a distraction injury
|
compression/axial loading
|
|
|
What are the findings on lateral plain film in a pt with a ligamentous injury of the C-spine
|
disk space is narrower anteriorly
|
|
|
Is there widening of the interspinous distance on lateral film in a ligamentous injury
|
yes sometimes
|
|
|
Can a ligamentous injury result in widening of a facet joint
|
yes, typically this occur more posteriory (on lateral film)
|
|
|
What are 2 potential complications of ligamentous injuries
|
subluxation of the vetebral body or perched/locked facets
|
|
|
What is more posteriorly located; superior or inferior facet
|
inferior is more posterior
|
|
|
What is the mechanism of a unilateral locked facet
|
flexion/distraction/rotation
|
|
|
What percent of unilateral locked facets result in a neurologic deficit
|
30%
|
|
|
What is seen on the lateral view in a pt with unilateral locked facets
|
some vetebral bodies appear true lateral and other appear oblique
|
|
|
What is the bowtie sign
|
this is when some bodies appear lateral and some appear appear oblique in unilateral locked facets
|
|
|
What will be seen on frontal film in a pt with unilateral locked facets
|
the posterior spinous process will not line up
|
|
|
On the lateral view what does the vetebrae with the unilateral locked facet look like
|
t
|
|
|
What is damaged in ligamentous injury of the cervical spine
|
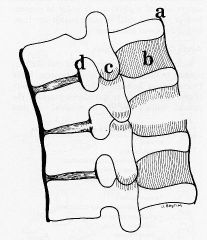
Posterior ligamentous structures involved in flexion injury are
(a) supraspinous ligament (b) interspinous ligament (c) facet joint capsule (d) posterior longitudinal ligament |
|
|
What percent of the vetbral body will be subluxed in bilateral locked facets
|
at least 50%
|
|
|
What is both bilateral and unilateral locked facets associated with
|
a ligamentous injury
|
|
|
What are the majore fractures of the cervical spine
|
jeffersons
hangmans extension teardrop flexion teardrop burst clay shovelers compression perched/locked facets |

