![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
73 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What percent of facial fractures involve the orbit
|
60%
|
|
|
What are 3 indirect signs of a facial fracture
|
soft tissue swelling
periorbital or intracranial air fluid in a paranasal sinus |
|
|
What is the most common facial fracture
|
Nasal fracture is the most common and Zygomaticomaxillary complex (tripod fracture) fracture is the second most common
|
|
|
What is the third most common fracture
|
LeFort (35%)
I 15 % II 10 % III 10 % |
|
|
What is the 4th mc facial fracture
|
zygomatic arch 10%
|
|
|
What is tied for 5th mc facial fracture
|
Alveolar process of maxilla (5%) and Smash fractures (5%)
|
|
|
What is another name of a tripod fracture
|
zygomaticomaxillary complex fracture
|
|
|
What does a tripod fracture involve
|
separation of all three major attachments of the zygoma to the rest of the face. (think of it as removing the zygoma and therefore fractures move along the zygomaticofrontal, zygomaticomaxillary and zygomaticotemporal sutures)
|
|
|
What 3 fractures make up a tripod fracture
Where exactly is the anterior wall of the maxillary sinus fractured in a tripod fracture |
the zygomatic arch (along where the zygomatic bone joins the temporal bone)
floor of the orbit and includes the maxillary sinus (anterior and posterior wall) lateral orbital rim and wall (at the zygomaticofrontal suture) the anterior maxillary wall is usually fractured along the zygomaticomaxillary suture |
|
|
What is the usual cause of a tripod fracture
|
The tripod fracture is usually secondary to a direct blow to the malar eminence (zygoma bone)
|
|
|
What does a fracture of the anterior and posterior maxillary walls look like
|
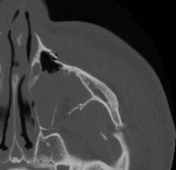
there is a fracture of the anterior and posterior maxilary wall and also the zygomatic process of the temporal bone
|
|
|
What does a fracture of the lateral orbital wall look like on coronal ct
What makes of the zygomatic arch |
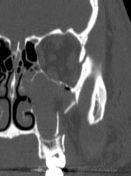
This image shows a fracture in the area of the zygomaticofrontal suture
the zygomatic arch is formed from part of the temporal bone and a small portion of the zygoma |
|
|
What does a fracture of the zygomatic bone look like on axial ct (zygoma makes up the lateral portion of orbit and superior portion of lateral border of maxillary sinus)
What bone makes of the anterior medial and lateral and complete inferior portion of the maxillary sinus What bone makes up the anterior lateral and a small portion of the superior lateral wall of the maxillary sinus |
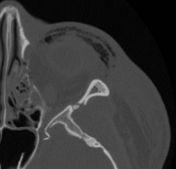
This image shows the lateral orbit fracture which is the zygoma bone
maxilla zygoma |
|
|
What makes of the floor of the orbit
|
the roof of the maxillary sinus
|
|
|
What is the inferior orbital rim
|
the inferior portion of the front of the eye socket (front of roof of maxillary sinus)
|
|
|
What makes of the floor of the orbit
|
the roof of the maxillary sinus
|
|
|
What is the inferior orbital rim
|
the inferior portion of the front of the eye socket (front of roof of maxillary sinus)
|
|
|
What are some complications of a tripod fracture
3 |
impingement of the temporalis muscle, trismus (difficulty with mastication) and may compromise the infraorbital foramen/nerve resulting in hypesthesia within its sensory distribution.
|
|
|
What is the mc facial fracture
|
nasal fx
|
|
|
Where does zygoma usually seperate from the frontal bone in a tripod fracture
|
the separation of the frontal process of the zygoma from the frontal bone usually occurs in the form of a diastasis of the zygomaticofrontal suture (rememeber this the one where all its sutures are being fractured)
|
|
|
Where is the malar eminence
|
malar eminence is the most prominent portion of the zygoma (check bone)
|
|
|
What is a common presentation of a zygomatic arch fracture
|
inability to open their mouth due to impingement of the zygomatic arch fragment upon the coronoid process of the mandible or the temporalis muscle
|
|
|
What is an alveolar process fracture of the maxilla
|
Another focal fracture type is a fracture of the alveolar process of the maxilla, which involves a small piece of the maxilla, associated with several fractured teeth
|
|
|
What is the most common cause of a blowout fracture
|
The usual mechanism is a blow to the eye, with the forces being transmitted by the soft tissues of the orbit downward to the thin floor of the orbit.
|
|
|
Where do bone fragments from a blow out fracture often end up going
|
the maxillary sinus
|
|
|
What % of blow out fractures are associated with occular injury
|
24 % of these fractures are associated with ocular injury as well.
|
|
|
What are 2 common pitfalls for mistaken a nasal fracture
|
Common pitfalls in viewing the nasal bone are the normal sutures lining the nasal bone, as well as the linear channel for the nasociliary nerve, which may all be mistaken for a fracture
|
|
|
What is the pathway of a le fort 1 fracture
|
nasal septum to the lateral pyriform aperature rims, travels horizontally above the teeth apices, crosses below the zygomaticomaxillary junction( and therefore the zygoma is not involve), continues across the inferior lateral wall of the maxillary sinus, and traverses the pterygomaxillary junction to interrupt the pterygoid plates.
|
|
|
What does a bilat pterygoid fracture look like
|
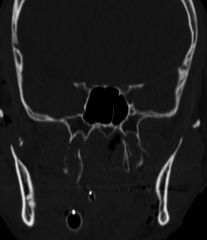
|
|
|
What portion of the temporal bone forms a joint with the zygomatic bone
What is medial wall of the maxillary sinus |
the zygomatic process of the temporal bone
lateral wall of the nasal cavity |
|
|
What bone is the pterygoid part of
|
sphenoid
|
|
|
Where is the pterygoid plates
|
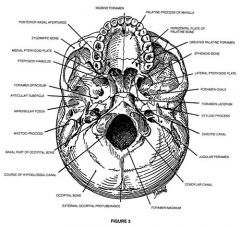
|
|
|
Where are the pterygoids plates on the sphenoid
What does the ptyergoid plates have sutures with |
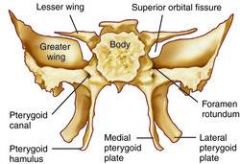
the palantine (centrally) and the maxilla laterally
|
|
|
Where is the zygomaticmaxillary junction that le fort 1 goes below
|
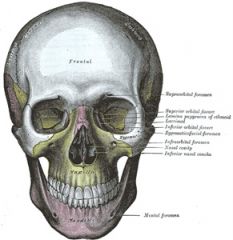
|
|
|
Are le fort fractures bilateral
|
yes
|
|
|
How many lefort fractures are there
|
three
|
|
|
Describe a le fort II fracture
|
Le Fort II fracture crosses the nasal bones on the ascending process of the maxilla to the medial orbital rib and then the medial orbital wall (lacrimal bone) to the medial orbital floor and crosses the inferior orbital rim. It then goes towards the maxilla just above the teeth and moves along the inferior lateral maxillary sinus like a le fort 1 fracture
|
|
|
When is the only le fort fracture to break the medial and inferior orbital rib
|
2
|
|
|
What is a pt complication of a le fort 2 fracture
Does a le fort 1 or 2 involve the zygoma |
Because of this proximity to the infraorbital foramen, type II fractures are associated with the highest incidence of infraorbital nerve hypesthesias
no |
|
|
What is a common mechanism of a le fort 2 fracture
|
A common mechanism is a downward blow to the nasal area.
|
|
|
What is the most severe le fort fracture
|
The most severe of the classic LeFort fracture complexes is the LeFort III
|
|
|
Are pure le fort injuries common
|
no
|
|
|
What are some variants of le fort fractures
|
Lefort I/ lefot II
Lefort II/ tripod a mixed LeFort II/LeFort III complex LeFort III/LeFort II/tripod complex. |
|
|
What do all three lefort fractures look like from the front
|
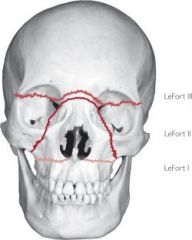
|
|
|
What does a le fort 3 look like
|
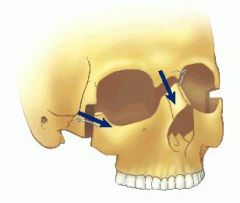
|
|
|
If the orbital rim is involved; what type of lefort fracture is it
|
2
|
|
|
What is fractured in a le fort 1 fracture
|
nasal septum to the lateral pyriform aperature rims, travels horizontally above the teeth apices, crosses below the zygomaticomaxillary junction( and therefore the zygoma is not involve), continues across the inferior lateral wall of the maxillary sinus, and traverses the pterygomaxillary junction to interrupt the pterygoid plates.
|
|
|
What is fractured in a le fort 2 fracture
|
Le Fort II fracture crosses the nasal bones on the ascending process of the maxilla to the medial orbital rib and then the medial orbital wall (lacrimal bone) to the medial orbital floor and crosses the inferior orbital rim. It then goes towards the maxilla just above the teeth and moves along the inferior lateral maxillary sinus like a le fort 1 fracture
|
|
|
What is fractured in a le fort 3 fracture
|
craniofacial disjunction
fracture line passes through nasofrontal suture, maxillo-frontal suture , orbital wall and zygomatic arch. |
|
|
What does a fracture throught the anterior maxillary sinus look like
|
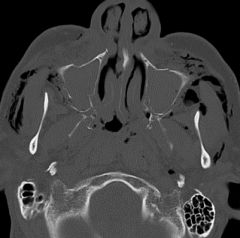
|
|
|
What does a fracture through the nasofrontal suture area look like (lefort 2)
|
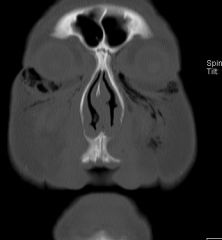
|
|
|
If the pterygoid plate is not broken can it still be a le fort fracture
|
no
|
|
|
What does a lefort 1 fracture to the lateral nose look like on coronal CT
|
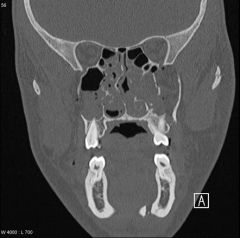
|
|
|
What part of the maxilla does a le fort 1 involve
|
Fracture line: Piriform aperture, inferior lateral maxillary wall, pterygoid process of the sphenoid bone
|
|
|
What is the path of le fort 2 fracture
|
Le Fort II fracture crosses the nasal bones on the ascending process of the maxilla to the medial orbital rib and then the medial orbital wall (lacrimal bone) to the medial orbital floor and crosses the inferior orbital rim. It then goes towards the maxilla just above the teeth and moves along the inferior lateral maxillary sinus like a le fort 1 fracture
|
|
|
What does the word antral refer to
|
maxillary
|
|
|
What is the piriform appeture
|
the anterior end of the bony nasal opening, connecting the external nose with the skull.
|
|
|
Where is the piriform aperature
|
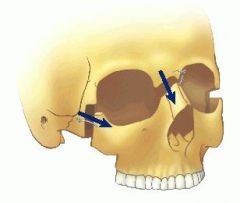
|
|
|
Where is the Zygomaticofacial canal Zygomaticomaxillary suture, and Frontozygomatic suture
|
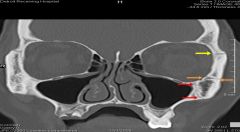
Yellow arrow: Frontozygomatic suture
Orange arrows: Zygomaticofacial canal Red arrows: Zygomaticomaxillary suture |
|
|
What is this image pointing to
|
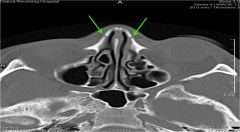
the ethmoidal grooves for the external nasal branches of the anterior ethmoidal nerves.
Comment: These grooves can be mistaken for fractures. They lie anterior to and are distinct from the nasomaxillary sutures. The nasomaxillary sutures are often fused and not visible on CT scans as in these images. |
|
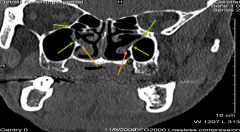
What is the orange arrow pointing to
|
In the coronal image to the left from the posterior nasal cavities, the orange arrows point to the point posterior ends of the inferior nasal conchae
|
|
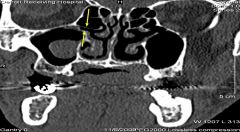
What do the yellow arrows point to
|
In the coronal image to the right from the anterior nasal cavities, the gap between the yellow arrows is the right hiatus semilunaris.
|
|
|
there is a bony gap in the medial wall of each maxillary sinus/lateral wall of each nasal cavity between the green arrows. What is the name of this bony gap?
|
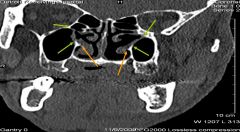
maxillary hiatus (seen posteriorly)
|
|
|
What does the maxillary hiatus look like more anteriorly
|
|
|
|
What are the fractures of a tripod fracture
|
separation of all three major attachments of the zygoma to the rest of the face. (think of it as removing the zygoma and therefore fractures move along the zygomaticofrontal, zygomaticomaxillary and zygomaticotemporal sutures)
|
|
|
What is the shape of the zygoma
|
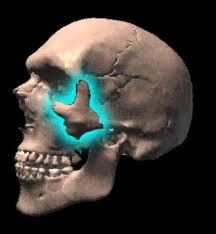
note that this forms 3 sutures
zygomaticomaxillary zygomaticofrontal zygomaticotemporal |
|
|
What bone makes up the nasal septum
|
vomer inferiorly
perpendicular plate superior |
|
|
What is the fracture line of a le fort 3
|
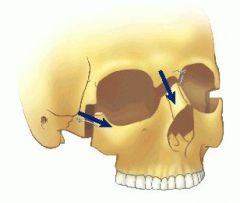
the fracture line passes to the fronto-nasal and fronto-maxillary suture (medial to the frontonasal suture) then to the lacrimal bone (the medial orbital wall) the orbital floor up to the inferior orbital fissure. From there, it extends caudally through the pterygopalatine fossa to the base of the pterygoid processes as well as from the anterior end of the inferior orbital fissure along the lateral orbital wall to the frontozygomatic fissure. The fracture of the midface is completed by the fracture of the zygomatic arch and the cranial bony part of the nasal septum.
|
|
|
What are the 7 fractures of the ramus
|
body, angle, condyle, symphsis, ramus, alveolar, coronoid process
|
|
|
What is the mc fracture of the mandible
|
body (30-40%)
|
|
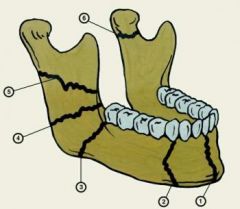
name these fractures
|
1- symphsis
2- body 3-angle 4-ramus 5-ramus 6-condylar 7-coronoid process (not shown but opposite the condyle) |
|
|
What percent of pts have multiple mandibular fracture
|
80% of the time (prezetel bone)
|
|
|
Where do double fractures typically occur
|
When double fractures occur, they are usually on contralateral sides of the symphysis.
|

