![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
97 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Can plain film be normal even when there is extensinve soft tissue injury to the knee
|
yes
|
|
|
What is the imaging modaility of choice for occult bone injuries and soft tissue injuries of the knee
|
MRI
|
|
|
What are 3 clues on MR that there is pathology involving a ligament
|
non-visualization, disruption, increased signal.
|
|
|
What are 6 possible views of the knee
|
AP
Lat Inter and external oblique tunnel (AKA knotch) Axial ( AKA; skyline, tangential, sunrise, merchant view) |
|
|
AP anatomy of the knee
|
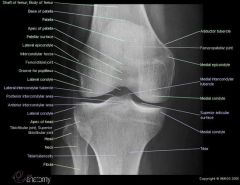
|
|
|
Lateral anatomy of the knee
|
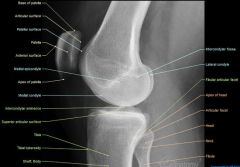
|
|
|
What is are two important landmarks that lay underneath the quadraceps femoris tendon
|
suprapatellar fat body
suprapatellar bursa (underneath the fat pad) |
|
|
What does the quadriceps femoris tendon attach to
|
the patella
|
|
|
What is the ligment that inferiorly attaches to the patella
|
the patellar ligament
|
|
|
What fat pad is underneath the patellar ligament
|
the infrapatellar fat pad.
|
|
|
What is another name for the infrapatellar fat pad
|
hoffas fat pad
|
|
|
What does the patellar ligament insert on
|
the tibial tuberosity
|
|
|
What does the ACL arise from
|
lateral femoral condyle (top)
|
|
|
What does the ACL insert into
|
anterior to the medial tibial spine
|
|
|
Where does the PCL arise from
|
the medial femoral condyle (top)
|
|
|
Where does the PCL insert
|
posterior to the lateral tibial spine
|
|
|
Where does anterior an posterior part of the the name of ACL and PCL come from
|
there location on the tibia
|
|
|
What is another name for the medial collateral ligament
|
tibial collateral ligament
|
|
|
Where does the MCL arise from and insert
|
the medial femoral condyle and inserts into the medial condyle of the tibia
|
|
|
Are the deep fibers of the MCL bound to the articular capsule of the knee
|
yes, (this is my MCL injuries are almost always associated with medial meniscus injuries)
|
|
|
What is another name for the LCL
|
the fibular collateral ligament
Note the the Lateral collateral ligament is part of the lateral capsular complex which is the LCL, iliotibial band and bicep femoris |
|
|
Where does the lateral collateral ligament insert and attach
|
attach: lateral femoral condyle
insert: head of the fibula |
|
|
What are 2 ST clues to injury of the knee
|
joint effusions
lipohemarthrosis |
|
|
Where do joint effusions of the knee occur
|
above the patellar and posterior to the quadricepts tendon
|
|
|
What happens when the suprapatellar effusion becomes large enough
|
they will tilt the superior portion of the patella forward.
|
|
|
What happens to the clear space above the patellar when there is a joint effusion
|
the clear space (fat) becomes obliterated and is replaced with a soft tissue density area that fills it and bulges the adjacent ST outward
|
|
|
What else besides an effusion will cause the patella to tilt forward
|
rupture of the quadriceps femoris tendon
|
|
|
What is the difference in appearance of a ruptured quadriceps tendon and effusion
|
the fat pad will not be obliterated in a rupture of the tendon
|
|
|
What is the cause of a lipohemarthrosis
|
fat exiting the marrow cavity 2/2 a fx
|
|
|
What is the most common cause of a lipohemarthrosis of the knee
|
a tibial plateau fx
|
|
|
Does fat float on the blood
|
yes
|
|
|
What is a important technical aspect of X-ray postioning to see a lipohemarthrosis
|
requires a horizontal beam
|
|
|
What does a fat fluid level look like
|
there is soft tissue density with the more lucent fat density on top
|
|
|
Can there be a triple level lipohemarthrosis
|
yes from cells layering out
|
|
|
What are the 3 categories of distal femur fx
|
supracondylar, condylar, intercondylar
|
|
|
What is the MCC of a distal femoral fx
|
axial loads (MVA, falls)
|
|
|
What are common associated injuries of distal femur fx
|
ligament injuries, vascular, tibial plateau fx
|
|
|
What is the MC ligament injured from a distal femur fx
|
ACL
|
|
|
Are dislocations of the knee common
|
no
|
|
|
How are tibiofemoral dislocations of the knee described
|
by the resting place of the tibia
|
|
|
What are two dislocations of the knee
|
tibiofemoral/patellar femoral
|
|
|
Which way is the patellar usually dislocated
|
laterally
|
|
|
Why is the patellar more commonly displaced lateral
|
the lateral femoral condyle is more shallow
|
|
|
What is more common a subluxation of the the knee or dislocaiton
|
subluxation
|
|
|
What is more common an anterior or posterior dislocation of the tibia
|
anterior
|
|
|
What are two diseases of the patella
|
osgood schlatter and sinding-larsen-johannson disease
|
|
|
What are some similarities between these diseases
|
adolescents
repetitive trauma |
|
|
Where does Sinding-Larsen-Johansson disease occur
|
proximal end of patellar tendon
|
|
|
Where does OS disease occur
|
the distal end of the patella tendodn ( tibial tuberosity)
|
|
|
Are OS and SLJ diseases clinical diagnoses
|
yes (local pain and tenderness)
|
|
|
Is imaging needed to diagnose OS and SLJ diseases
|
no
|
|
|
What is the cause fo SLJ disease
|
traction stress on the proximal end of the patellar ligament (inferior pole of the patella)
|
|
|
What are the imaging findings of SLJ disease
|
fragmentation, osteophytes and STS on inferior pole of the patellla
heterotopic calcification of the patella tendon |
|
|
What is Osgood-schlatter disease
|
a traction apophysitis (osteochondritis) 2/2 repetitive stress injury at the site of the tibial tuberosity
|
|
|
What percent of OS is bilateral
|
25-50 %
|
|
|
What are the imaging findings of OS disease
|
fragmentation, STS
|
|
|
If there are radiographic findings consistent with either SLJ and OS disease is it diagnostic
|
no, if the pt doesnt have the symptoms
|
|
|
What is the unhappy triad of athletes
|
ACL
MCL Medial meniscus |
|
|
Where is the seperate ossification center of a bipartite patella located
|
superolateral pole
|
|
|
What % of bipartite patellas are bilateral
|
50%
|
|
|
Describe the margins of a bipartite patella
|
smooth and corticated
|
|
|
What does a patella fx that occurs as a result of a direct blow generally look like
|
comminuted with articular cartilage damage
|
|
|
What does a patellar fx as a result of an indirect fx look like
|
articular cartilage is spared and these are avulsion injuries
|
|
|
What is the main cause of an indirect patellar fx
|
avusion 2/2 jumping
|
|
|
Are most patellar fx transverse or vertical
|
transverse
|
|
|
What additional finding do you expect to see in a pt with a patella fx
|
an effusion
|
|
|
What happens to the fragments of the patella following a complete transverse fx
|
they become distracted
|
|
|
What is the most common fx of the proximal tibia
|
tibial plateau fxs
|
|
|
What is more common the lateral or medial plateau
|
lateral
|
|
|
What is the MC mechanism of a tibial plateau fx
|
a compressive force of the femoral condyles (fall from height) or can be from a car bumper
|
|
|
What is the general rule of thumb with fractures of the tibial plateau and ligaments
|
there is commonly injury to the opposite ligament
|
|
|
What causes a depressed fx of the tibial plataue
|
depressed fx are caused by downward force by the condyle of the femur
|
|
|
What are 3 types of osteochondral injuries
|
osteochondral fractures
osteochondral dissecans spontaneous osteonecrosis |
|
|
Are osteochondral injuries usually acute and sports related
|
yes
|
|
|
What osteochondral areas are most often involved in osteochondral injuries
|
the femoral condyles, tibial plateaus, patella
|
|
|
What often occurs following an osteochondral fx
|
a loose body fragment
|
|
|
What is an osteochondral fx often confused with
|
osteochondritis dissecans
|
|
|
What is the clinical SS of an osteochondral fx
|
sudden onset of severe pain
|
|
|
What is the demographic of a pt with osteochondritis dissecans
|
adolescent and young adult males
|
|
|
Is osteochondritis dissecans a chronic condition
|
yes
|
|
|
Does osteochondritis dissecans always affect bone and cartilage
|
no, it can be both or just cartilage
|
|
|
Where is the classic location for osteochondritis dissecans
|
lateral aspect of the medial condyle
|
|
|
What is the MC cause of a loose body
|
osteochondritis dissecans
|
|
|
If there is an unstable fragment does it almost always require surgery
|
yes
|
|
|
Where is the lateral aspect of the medial femoral condyle
|
centrally located
|
|
|
What is SONK stand for
|
spontaneous osteonecrosis
|
|
|
What is the typical onset for SONK
|
older adult with acute onset of pain
|
|
|
Does osteochondritis dissecans occur on the weight bearing surface of the medial condyle
|
no
|
|
|
Does SONK occur on the weight bearing surface of the medial femoral condyle
|
yes
|
|
|
What type of fracture is SONK
|
insufficiency fx (makes sense it happens in older people)
|
|
|
Is SONK acute in onset
|
yes
|
|
|
What are bony clues to a ST injury of the knee
|
avulsion of intercondylar eminence, segond fx, avulsion of the proximal posterior tibia
|
|
|
What is avulsion of the intercondylar eminence associated with
|
tear of the ACL
|
|
|
What is a clue that there is a MCL ligament tear
|
widening of the medial portion of the knee joint space
|
|
|
What is a segund fx
|
an avulsion fx of the lateral boder of the proximal tibia
|
|
|
What are segond fx associated with
|
ACL tears (100%)
medial mensiscus (75%) |
|
|
What is an avulsion fx of the posterior portion of the proximal tibia
|
PCL tear
|

