![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
116 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What makes up the anterior arch of the pelvis
|
the ischium and pubic bone
|
|
|
What makes up the posterior arch of the pelvis
|
the sacrum and pubic bone
|
|
|
What is an anterior arch fracture of the pelvis
|
any fracture of the ischium or pubic bone (think of them together forming one ring and dont be confused because they form a ring themselves)
|
|
|
What percent of pelvic fractures are considered stable
|
66%
|
|
|
What is considered a stable fracture
|
a single break in ring or a peripheral fx
|
|
|
What are unstable fractures
|
fractures of both the anterior and posterior arches (33%)
|
|
|
What are the stable pelvic fractures
(4) |
solitary ischial ramus fracture
unilateral fracture of both rami (superior pubic ramus and ishiopubic ramus) iliac wing fractures isolated sacral fractures |
|
|
What is another name for a iliac wing fracture
|
Duverny fracture
|
|
|
What is a major point of confusion when discussing ramus of the pelvis
|
When they say pubic ramus it is implied to means superior pubic ramus (the of the ring around the obturator foramen)
Even though technically a pubic ramus fracture can be on the bottom of the ring of the obturator (the inferior pubic ramus portion located medially) |
|
|
What is the mc pelvic fracture
|
solitary fracture of the ischial ramus or inferior pubic ramus
(this can happen in both areas and so I think a better name would be a solitary fracture of the ischiopubic ramus) |
|
|
Is a solitary fracture of the ischial ramus stable
|
yes
|
|
|
What population commonly get ischial ramus fractures
|
osteoporotic females (insufficiency fracture)
|
|
|
Another point of confusion: 'a solitary fracture of both rami' really means a fracture of the top of the ring of the obturator foramen and the bottom of the ring of the obturator foramen. What would be a better name
|
a solitary fracture of both the superior pubic ramus and the ischiopubic ramus
OR a solitary fracture of the superior pubic ramus AND the inferior pubic ramus OR the ischial ramus |
|
|
Is a solitary fracture of both rami a stable fracture
|
yes
|
|
|
What is the cause of an iliac wing fracture (duverny) fracture
|
direct lateral compression
|
|
|
What is a potential complication of an iliac wing fracture
|
fracture can perforate bowel
|
|
|
What is the orientation of a isolated sacral fracture
|
transversly oriented
|
|
|
What view is best to detect an isolated fracture of the sacrum
|
lateral which may show angulation of sacrum or coxcy
|
|
|
What is the direction of fractures associated with other sacral fractures
|
vertically
|
|
|
What are the 4 unstable fractures of the pelvis
|
malgaigne (Mal-gain-e)
straddle pelvic dislocation bucket handle fracture |
|
|
What is the mc unstable pelvic fracture
|
malgaigne (mal-gain-e)
|
|
|
What percent of all pelvic fractures are malgaine
|
14%
|
|
|
What is the mechanism by which a malgaigne fracture occurs
|
vertical shearing
|
|
|
What happens to the hip in a malgaigne fracture
|
it is commonly displace upward
|
|
|
Where is the MC fracture line of the pelvis in a malgagne fracture
|
the pubic rami (superior and ishiopubic ramus) and the sacroiliac joint
|
|
|
What makes up the 3 sacral lines seen on AP frontal view of the pelvis
|
the roof the the 1st, 2nd and 3rd sacral foramina
|
|
|
What should always be checked in a AP of the pelvis
|
symmetry and continuity of the sacral lines from one side to the other
|
|
|
Are straddle fractures stable
|
no
|
|
|
What is a straddle fracture
|
a fractue of the superior pubic ramus and the ischiopubic ramus on both sides
|
|
|
What happens to the fracture fragments in a straddle injury
|
the central portion fracture is elevated
|
|
|
What are straddle injuries associated with
|
urethral injuries (20%)
|
|
|
What is another name for a pelvic dislocation
|
a sprung pelvis
|
|
|
What 2 unstable fractures are associated with GU injury
|
pelvic dislocation and straddle fracture
|
|
|
What is the normal measurement of the SI joint
|
1-4mm
|
|
|
What is the normal measurement of the symphysis pubis
|
5mm
|
|
|
What happens to the size of the symphysis pubis and SI joints in a sprung pelvis
|
they increase in size
|
|
|
What is a bucket handle fracture
|
fracture of the anterior arch and the contralateral posterior arch
|
|
|
Is a bucket handle fracture common
|
no, it is rare
|
|
|
What is the posterior urethra
|
the membranous or prostatic urethra
|
|
|
Where do GU injuries tend to occur from pelvic fractures
|
the posterior urethra
|
|
|
If someone has a straddle injury or a sprung pelvis what should be done prior to insertion of a foley to prevent further injury
|
a retrograde urethrogram
|
|
|
What is a an open book fracture
|
a straddle injury in the front and Bilateral SI joint disocciation in the posterior arch
|
|
|
Besides posterior urethral injuries what other GU injury may occur with a sprung pelvis or a straddle fracture
|
a ruptured bladder
|
|
|
What is more common an extraperitoneal or intraperitoneal rupture of the pelvis
|
extraperitoneal (80%)
|
|
|
Where does the contrast remain in an extraperitoneal rupture of the bladder
|
adjacent to the bladder
|
|
|
What happens to the contrast in an intraperitoneal rupture
|
the dome is damaged and the contrast flows freely
|
|
|
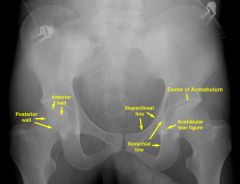
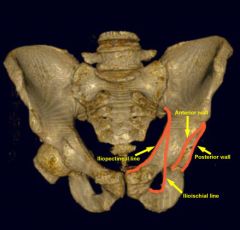
Where is the posterior rim of the acetabulum, roof of the acetabulum, ilioischial line, iliopectineal line, teardrop
|
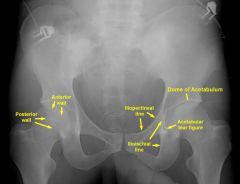
|
|
|
What are the 2 columns of the acetabulum
|
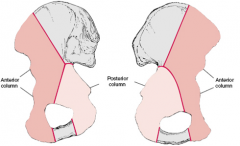
the anterior and posterior column
|
|
|
What makes up the anterior column of the acetabulum
5 |
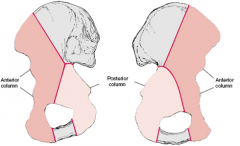
Anterior column includes
1- anterior aspect of the iliac Roof of acetabulum wing 2- pelvic brim 3- superior pubic ramus 4- anterior wall of acetabulum 5- teardrop. |
|
|
t
|
T
|
|
|
What is another name of the iliopectineal line
|
the ileal pubic line
|
|
|
What represents an injury to the anterior column
Is a tear fracture anterior or posterior |
injury to the iliopubic (iliopectineal line)
tear fractures are anterior column fractures anterior acetabular wall |
|
|
What represents the posterior column on a radiograph
What makes up the medial line of the acetabular tear drop |
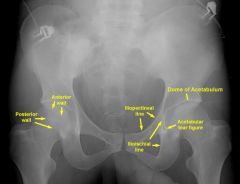
the ilioischial line
Posterior acetabular wall The ilioischial line |
|
|
What is the most common mechanism for a posterior column injury
|
anterior force on femoral head
|
|
|
What is the most common mechanism for a anterior column injury
|
Posterior force on femoral head
|
|
|
What makes up the posterior column
|
posterior ilium, posteriorwall of acetabulum, ischium, medial acetabular wall
|
|
|
Where is the iliopubic (iliopectineal) line of the anterior column
|
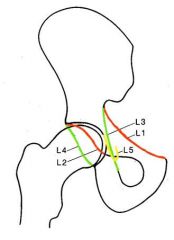
L1
|
|
|
Where is the anterior rim of the acetabulum
|
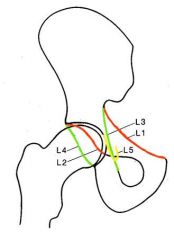
L2
|
|
|
Where is the ilioischial line and what forms this
|
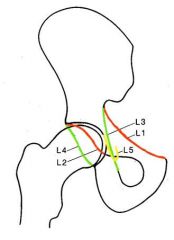
L3 (, formed by the posterior portion of the quadrilateral plate (surface) of the iliac bone)
|
|
|
Where is the posterior rim of the acetabulum
|
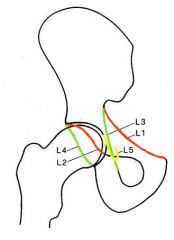
L4
|
|
|
Where is the tear drop and what forms it
|
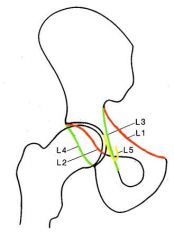
L5 (formed by the medial acetabular wall, the acetabular notch, and the anterior portion of the quadrilateral plate)
|
|
|
What does the iliopectineal line look like on plain film
|
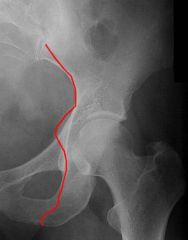
|
|
|
What does the iliopectineal line look like on plain film
|
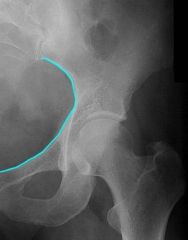
|
|
|
What does the a fracture of the anterior lip and teardrop look line on plain film and what does it indicate
|
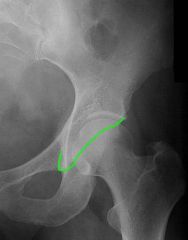
Discontinuity of the anterior lip suggests an anterior wall fracture
|
|
|
What does the posterior lip of the acetabulum look like on plain film
|
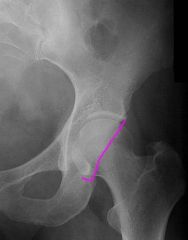
If there is discontinuity there is a fx of the posterior wall of the acetabulum
|
|
|
What does the dome of the acetabulum look like on plain film
|
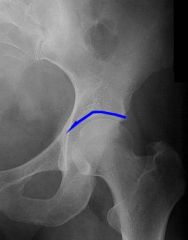
|
|
|
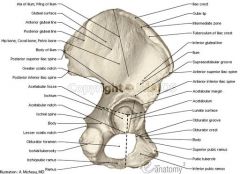
What is the quadrilateral plate of the hip
|
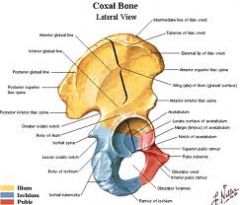
Quadrilateral plate is the junction where 3 parts of innominate bone, the Ilium, the Ischeum and the Pubis meet.
|
|
|
anatomy
|
|
|
|
What is the ilioischial line
|
the posterior aspect of the acetabulum and runs from the ilium to the ischium
|
|
|
What percent of pelvic fractures involve the acetabulum
|
20%
|
|
|
What additional views besides AP are used to look at acetabular fractures
|
judget views (45 degree oblique views)
|
|
|
What view is good for looking at acetabular postererior displacements and symphysis diastasis
|
inlet view (AP view with the x-ray beam angled 20 degrees caudal)
|
|
|
What view is good to look at vertical shifts of bones of the pelivis and the sacrum
|
outlet views (AP pelvis with beam tilted 35 degrees cephalad)
|
|
|
What 4 types of acetabular fxs
|
posterior rim fractures
transverse acetabular fractures anterior column fractures posterior column fractures |
|
|
What percent of acetabular fractures are posterior rim fxs
|
22%
|
|
|
What is a common cause of a posterior rim fx
|
posterior disloacation of the hip (MVA)
|
|
|
What is another name for the hip bone
|
inominate bone
|
|
|
Is the hip bone a group of bones
|
yes
|
|
|
What is the definition of the hip bone (innominate bone)
|
either of the two bones (2 halfs of the pelvis) that form the sides of the pelvis, consisting of three fused components, the ilium, ischium, and pubis
|
|
|
What is an transverse acetabular fracture
|
a transverse fracture through the acetabulum that seperates the hip into 2 halves (4% of acetabular fractures)
|
|
|
What lines will be disrupted in a transverse acetabular fracture
|
the iliopubic and ilioischial lines
|
|
|
What can happen to the femoral head in a severe case of a transverse acetabular fracture
|
central dislocation (femoral head is in the middle of the pelvis)
|
|
|
What percent of acetabular fractures are anterior column fxs
|
4%
|
|
|
What line is disrupted in a anterior acetabular fracture
|
the iliopubic
|
|
|
Can an acetabular fracture lead to central dislocation of the femoral head
|
yes
|
|
|
What is more common; fx of both columns or isolated column fractures
|
fracture of both columns
|
|
|
What does an anterior column fx look like on CT
|
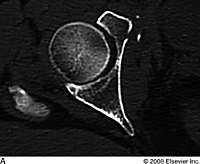
|
|
|
Visualize how the anterior column fracture on the previous slide disrupts the iliopubi (iliopectineal line)
|
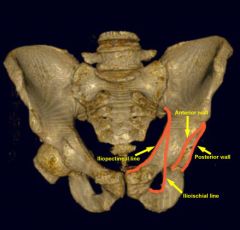
|
|
|
Now look at this lateral and visualize the fracture through the pubic bone
|
|
|
|
What is more common anterior or posterior column fractures
|
anterior column (4%)
posterior column (2%) |
|
|
What are posterior colum fractures associated with
|
posterior dislocation of the femoral head
|
|
|
What are 4 most common avulsion fractures of the pelvis
|
ASIS
AIIS Ischial tuberosity Pubis |
|
|
What are the common demographic of people with avulsion fractures
|
athletic males in puberty
|
|
|
What are apophyses
|
natural protuberance from a bone for the attachment of muscles.
|
|
|
What is the most common apiphyse to be avulsed
|
the ischial tuberosity
|
|
|
What muscle causes an avulsion fracture of the ischial tuberosity
|
the hamstrings
|
|
|
What do avulsed ischial tuberosity fractures look like upon healing
|
lots of callous formation leading to marked enlargement of the ischial tuberiosity
|
|
|
Where is the ischial tuberosity on AP plain film
|
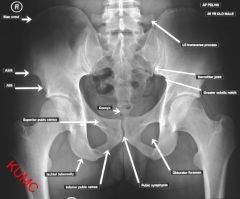
|
|
|
Where is the ASIS on plain film
|
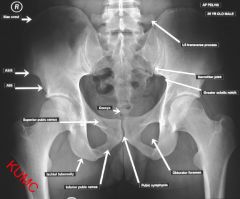
|
|
|
Where is the AIIS on plain film
|
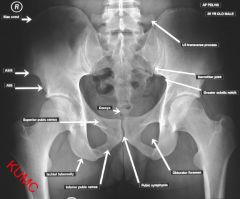
|
|
|
What muscle inserts into the AIIS
|
rectus femoris
|
|
|
What is the second most common avulsion fracture of the pelvis
|
AIIS and ASIS are tied
|
|
|
What muscle inserts to the ASIS
|
sartorius
|
|
|
Where is the lesser and greater trochanters of the femur
|
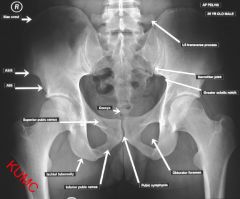
|
|
|
What muscle inserts into the lesser trochanter
|
iliopsoas
|
|
|
What muscle inserts into the greater trochanter
|
gluteal muscles
|
|
|
What muscles insert into the iliac creast
|
abdominal muscles
|
|
|
What muscles attach to symphysis
|
the abductor group of muscles
|
|
|
What is the most common artery to be lacerated from pelvic trauma
|
the hypogastric artery
|
|
|
What is a clue that there may be a pelvic hematoma
|
displacement of the bladder
|
|
|
What is the Dennis Classification of sacral fractures
|
a system to determine likely hood of neuroligic injury based on the location of a vertical fracture in relation to the neural formain
|
|
|
What are the 3 zones of Dennis classification of fracture
|
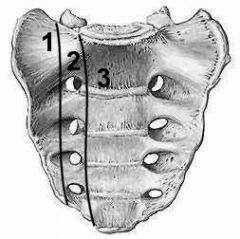
|
|
|
What is a zone 1 dennis classification fracture of the sacrum
|
I- injuries are entirely lateral to the neuroforamina: 6% neurological problem
|
|
|
What is a zone 2 dennis classification fracture of the sacrum
|
II- injuries involve the neuroforamina but not the spinal canal; 28% of neurological problem
|
|
|
What is a zone 3 dennis classification fracture of the sacrum
|
III- injuries extend into the spinal canal with primary or associated fracture lines: 57% neurological problems
|
|
|
What are the most common dennis classification of vertical sacral fractures
|
I>II>III
|

