![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
60 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
Label
|
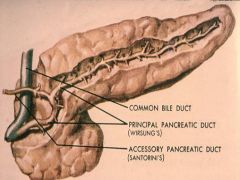
-
|
|
|
What are the 2 potential benign tumors of the Exocrine Pancreas?
|
Serous Cystadenoma
Mucinous Cystadenoma |
|
|
What are the 2 Malignant and Solid tumors of the Exocrine Pancreas?
|
Ductal Adenocarcinoma
Acinar Cell Carcinoma |
|
|
What are the 3 Cystic tumors of the Exocrine Pancreas?
|
Serous Cystadenoma
Mucinous Cystic Neoplasms Intraductal Papillary Mucinous Neoplasms (IPMNS) |
|
|
Rare tumors that most frequently occur in females in the 7th decade of life and are almost always benign
|
Serous Cystadenomas
|
|
|
Describe the microscopic appearance of Serous Cystadenomas
|
Multiple cysts lined by CUBOIDAL cells with CLEAR, GLYCOGEN-rich cytoplasm
|
|
|
What part of the pancreas are Serous Cystadenomas usually localized?
|
Body or Tail
|
|
|
Serous Cystadenoma
|
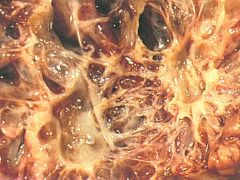
What pancreatic tumor is this?
|
|
|
Serous Cystadenoma
-multiple cysts -Cuboidal cells with glycogen-rich cytoplasm |
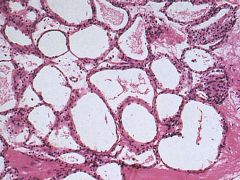
What pancreatic tumor is this?
|
|
|
Serous Cystadenoma
-cuboidal epithelium with clear cytoplasm (glycogen) Benign |
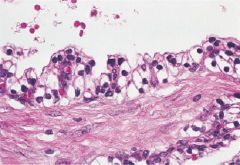
What pancreatic tumor is this?
Benign or Malignant? |
|
|
Rare pancreatic tumor that occurs almost exclusively in WOMEN and differs from Serous Cystadenoma b/c it can be benign, borderline, or malignant
|
Mucinous Cystic Neoplasms
|
|
|
Where do Mucinous Cystic Neoplasms usually localize in the pancreas?
|
Body or Tail
|
|
|
Describe the microscopic appearance of Mucinous Cystic Neoplasms
|
Cysts lined by COLUMNAR MUCINOUS cells with and associated OVARIAN-LIKE STROMA
|
|
|
With which tumor is complete excision critical: Serous or Mucinous Cystic Neoplasms?
Why? |
Mucinous Cystic Neoplasms
They have malignant potential |
|
|
Mucinous Cystic Neoplasm
-lined by columnar mucinous cells |
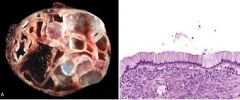
What pancreatic tumor is this?
|
|
|
Mucinous Cystic Neoplasm
-Columnar smoky white cells -Ovarian-like stroma -Goblet-like looking cells |
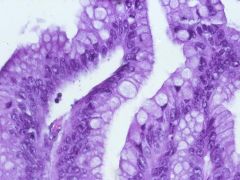
What pancreatic tumor is this?
What features does it have? |
|
|
Pancreatic tumor that occurs more frequently in MEN and usually is located in the HEAD of the pancreas
|
Intraductal Papillary Mucinous Neoplasms
|
|
|
Where do Intraductal Papillary Mucinous Neoplasms arise from?
How are they different from Mucinous Cystic Neoplasms? |
Main Pancreatic Ducts
Lack Ovarian-like stroma |
|
|
Intraductal Papillary Mucinous Neoplasm
Main Pancreatic Ducts |
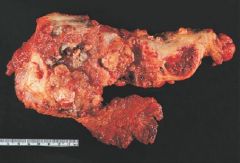
What pancreatic tumor is this?
What does it arise from? |
|
|
Intraductal Papillary Mucinous Neoplasm
**can be benign, borderline, or malignant |
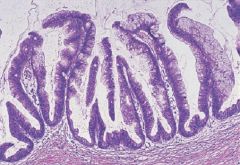
What pancreatic tumor is this?
|
|
|
what is the most common tumor of the Pancreas?
|
Ductal Adenocarcinoma
|
|
|
This is the 4th most common cause of cancer related death
|
Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma
|
|
|
Describe the age and gender statistics of Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma
|
Tumor of elderly individuals = 60-80 year olds
Male predominance in younger age groups, equal distribution in old age |
|
|
What is the most common cause of Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma?
|
Smoking
|
|
|
What are 6 risks associated with Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma?
|
1. Smoking
2. Chemical carcinogens 3. Dietary factors 4. Diabetes Mellitus 5. Chronic Pancreatitis 6. Molecular genetics **not associated with Alcohol |
|
|
What 4 genes are associated with Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma?
|
1. K-ras
2. p16 3. SMAD4 4. p53 |
|
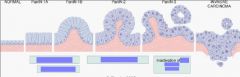
Fill in
|
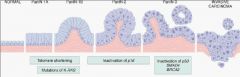
-
|
|
|
Ductal Adenocarcinoma
|
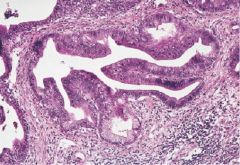
What pancreatic tumor is this?
|
|
|
What are 4 clinical presentations of Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma?
|
1. gradually increasing upper abdominal pain radiating to the back
2. weight loss, anorexia 3. painless obstructive jaundice = blockage of CBD 4. Migratory thrombophlebitis = Trousseau syndrome -redness and tenderness on palpation of his extremities |
|
|
What are 2 tumor markers for Ductal Adenocarcinoma?
|
CEA & CA19-9
|
|
|
List the 3 most common locations of Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma
|
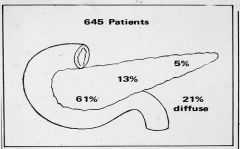
1. Head = 60%
2. Body = 15% 3. Tail = 5% |
|
|
Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma
CBD obstruction causing Jaundice |
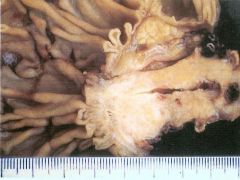
What is seen here?
What can this cause? |
|
|
Describe the microscopic pathology of Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma
|
-Malignant glands lined by anaplastic Cuboidal-to-Columnar epithelial cells and secrete mucin
-highly INVASIVE -Elicit a DESMOPLASTIC STROMAL rxn -Perineural invasion is common |
|
|
Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma
-tumor is present in the pancreatic duct |
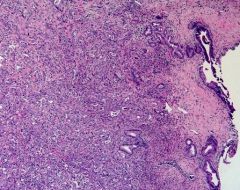
What pancreatic tumor is this?
|
|
|
Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma
-arise from duct epithelium -stromal fibrosis |
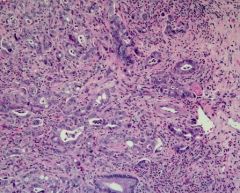
What pancreatic tumor is this?
|
|
|
Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma with PERINEURAL invasion
-causes pain |
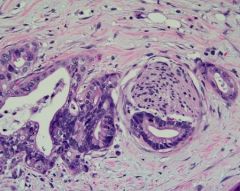
Describe what you see here
|
|
|
Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma that is present in the Lymph Node
-blue circles are nodes of Lymphocytes |
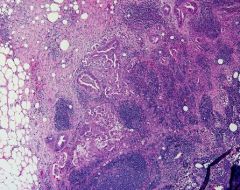
Describe what this is
|
|
|
Where do Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinomas most commonly metastasize to?
|
Regional Lymph nodes and the LIVER
|
|
|
What is the prognosis of Ductal Adenocarcinoma?
What is the treatment? |
Poor: 1 year survival = 10%
Surgical Excision = Whipple procedure **Early detection is critical |
|
|
An uncommon pancreatic tumor that is more frequent in MALES than females, age 50-80 years. Grossly well-circumscribed nobular mass with SOFT consistency
|
Acinar Cell Carcinoma
**Ductal Adenocarcinoma is hard |
|
|
Acinar Cell Carcinoma
-uniform tumor cells with rich GRANULAR cytoplasm |
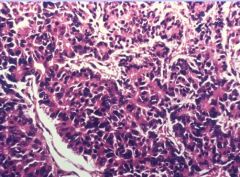
What pancreatic tumor?
|
|
|
Acinar Cell Carcinoma
-granulocytes containing enzymes |
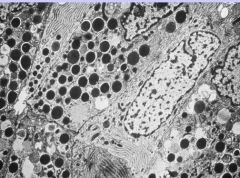
What pancreatic tumor is this? How do you know?
|
|
|
Pancreatic tumor associated with a syndrome characterized by Polyarthralgia-polyarthritis and disseminated fat necrosis (mainly subcutaneous) that is most likely due to unregulated release of pancreatic enzymes
|
Acinar Cell Carcinoma
|
|
|
Beta cell tumors = 1
Pancreatic Gastrinomas = 2 Alpha cell tumors = 3 Delta cell tumors = 4 D1 tumors = 5 |
1. Insulinomas
2. Zollinger-Ellison syndrome 3. Glucagonomas 4. Somatostatinomas 5. VIPomas |
|
|
Most common of the Islet Cell tumors (75%)
|
Insulinomas
|
|
|
Where do most Insulinomas occur in the Pancreas?
|
Body or Tail
|
|
|
Are most Insulinomas benign or malignant?
|
Benign
|
|
|
What are the 3 unequivocal criteria for Insulinomas to be considered malignant?
|
1. metastases to regional lymph nodes or distant organs
2. Vascular invasion 3. Gross invasion of adjacent organs |
|
|
What is the triad called in Insulinomas and what does it consist of?
|
Whipple's Triad
1. Hypoglycemia (<50 mg/dl) 2. Symptoms of Hypoglycemia: confusion, lethargy, sweating, tachycardia, tremor 3. Symptoms relieved by glucose intake **too much insulin causes Glucose to be stored |
|
|
Second most common Islet cell tumor
|
Pancreatic Gastrinoma = Zollinger-Ellison Syndrome
|
|
|
Describe Pancreatic Gastrinoma (Zollinger-Ellison Syndrome)
|
G cells in the Pancreas (not normal in Islets) that secrete Gastrin
-cause Parietal cells in the stomach to release HCl -intractable Stomach hypersecretion -Severe, multiple Peptic Ulcers (unusual sites) -high levels of Gastrin in the blood |
|
|
Describe the age and gender predominances of Zollinger-Ellison Syndrome
|
Most common between ages 30 and 50
MALE predominance |
|
|
Are the majority of Pancreatic Gastrinomas benign or malignant?
|
MALIGNANT
|
|
|
Describe Multiple Endocrine Neoplasia Syndrome Type 1 (MEN type 1)
|
3 P's:
Adenomas in the Pituitary, Parathyroid, and endocrine Pancreas **infrequent familial disorder |
|
|
What is MEN type 1 frequently associated with?
|
Zollinger-Ellison Syndrome
|
|
|
How would you decipher between exogenous Insulin and Insulin overproduced by an Insulinoma?
|
C-peptide marker is present in Insulinomas but absent in exogenous Insulin (removed during the purification of commercial insulin preps)
|
|
|
Islet cell tumor that may cause Mild Diabetes and Hyperglycemia
|
Glucagonoma
*Glucagon causes an increase in Blood glucose |
|
|
What characteristic lesion is associated with Glucagonoma?
|
Necrotizing Migratory Erythema
*Anemia may also occur **Hyperglycemia may occur as well |
|
|
Describe the symptoms of VIPoma
|
WDHA syndrome:
1. Water Diarrhea 2. Hypokalemia 3. Achlorohydria |
|
|
Insulinoma
|
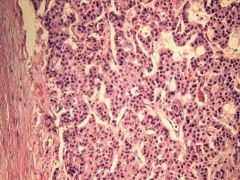
What pancreatic tumor is this?
|

