![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
48 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Define Lymphoblastic Lymphoma
|
Neoplasm of precursor T cells
|
|
|
Neoplasm of precursor T cells that affects Adolescent Males and presents with an Anterior Mediastinal mass
|
Lymphoblastic Lymphoma
|
|
|
How does Lymphoblastic Lymphoma present usually?
|
Anterior Mediastinal Mass in Adolescent Males
- can present with pulmonary symptoms related to the mass -compress the trachea and major bronchi and lead to airway obstruction |
|
|
Mimics B cell ALL morphologically
|
Lymphoblastic Lymphoma
|
|
|
Define Burkitt Lymphoma
|
highly aggressive neoplasm of MATURE B cells
|
|
|
Describe the pathogenesis of Burkitt Lymphoma
|
1. Viral infection (HIV or EBV)
2. C-myc proto-oncogene overexpression 3. t(8;14) translocation |
|
|
Describe the pathology of Burkitt Lymphoma
|
1. Diffuse infiltrate of Intermediate size Lymphocytes = effaces the lymph node architecture
2. High mitotis activity 3. Tumor cell apoptosis 4. Starry sky pattern |
|
|
Describe the Endemic type of Burkitt Lymphoma
|
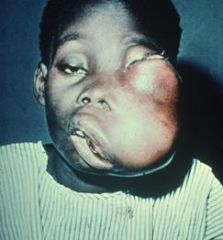
1. Africa or New Guinea
2. Children are affected 3. Mandible involvement 4. associated with EBV |
|
|
Describe the Sporadic type of Burkitt Lymphoma
|
1. USA
2. Children or young adults 3. Abdominal mass 4. associated with HIV |
|
|
Neoplasm of CD4+ cells that is endemic to Japan and Caribbean
|
Adult T cell Leukemia/Lymphoma
|
|
|
What does the pathogenesis of Adult T cell Leukemia/Lymphoma involve?
|
HTLV-1 infection
|
|
|
List the clinical symptoms of Adult T cell Leukemia/Lymphoma (3)
|
1. Skin lesions
2. HYPERCALCEMIA 3. Enlargement of the Spleen, Lymph Nodes, and Liver |
|
|
Adult T cell Leukemia/Lymphoma
|
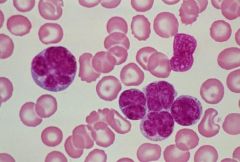
Hyperlobated "4-leaf clover" lymphocytes in the peripheral blood
|
|
|
What is the prognosis of Adult T cell Leukemia/Lymphoma?
|
median survival < 1 year
|
|
|
Define Mycosis Fungoides/Sezary Syndrome
|
Skin neoplasm of CD4+ T cells
|
|
|
Skin neoplasm of CD4+ T cells that produces skin plaques, then nodules, then tumors
|
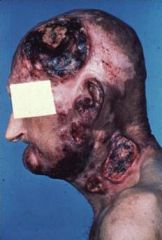
Mycosis Fungoides
|
|
|
Skin neoplasm of CD4+ T cells that presents with Diffuse Erythroderma (redness)
|
Sezary Syndrome
|
|
|
What is the prognosis of Mycosis Fungoides / Sezary Syndrome?
|
median survival > 5 years
|
|
|
What is the treatment for Mycosis Fungoides / Sezary Syndrome?
|
Chemotherapy
Light Therapy = kills lymphocytes --> palliates disease |
|
|
Describe the histology of Mycosis Fungoides / Sezary Syndrome
|
Epidermotropic lymphocytes
- Pautrier microabscesses of the skin - Cerebriform nucleus (nuclear membrane folding) of lymphocytes |
|
|
List the 3 general features of Hodgkin Disease
|
1. B cell neoplasm
2. Neoplastic cell is Reed-Sternberg Cell 3. CONTIGUOUS spread = goes from one node to adjacent lymph node |
|
|
Describe Nodular Sclerosis Hodgkins Disease (5)
|
1. Most common HD = 70%
2. affects YOUNG FEMALES 3. Anterior Mediastinal mass 4. Lymphoid nodules surrounded by fibrotic bands 5. Lacunar Cells (RS variant) |
|
|
Describe Mixed Cellularity HD
|
1. affects Males
2. comprises 25% of HD's 3. Diffuse Polymorphous infiltrate = lymphocytes, eosinophils, plasma cells, histiocytes |
|
|
Describe Lymphocyte Predominant HD
|
1. Least common = 5%
2. Males most affected 3. Nodules of small mature Lymphocytes = Popcorn cells (RS variant) 4. associated with "good prognosis" |
|
|
List the clinical features of Hodgkin Disease
|
1. Localized lymphadenopathy (especially Axillary & Cervical)
2. B symptoms -fever, night sweats, weight loss 3. Pruritis 4. Alcohol induced lymph node pain |
|
|
Describe Stage I HD
|
Single Lymph Node group
|
|
|
Describe Stage II HD
|
2 or more lymph node groups on the same side of the Diaphragm
|
|
|
Describe Stage III HD
|
Lymph Node regions on both sides of Diaphragm
|
|
|
Describe Stage IV HD
|
Disseminated disease
|
|
|
Describe the treatment for the Stages of HD
|
Stage 1 & 2 can have Radiation alone
Stage 3 & 4 need radiation and Chemo combo |
|
|
What is the survival rate for Stage I and II HD?
|
90% 5 year survival
|
|
|
What is the survival rate for Stage IV HD?
|
60-70% 5 year survival
|
|
|
What are the complications of HD?
|
Secondary Malignancy
1. Carcinoma = lung, breast, stomach 2. Hematologic = AML, MDS 3. Sarcoma, Melanoma **due to radiation and chemotherapy |
|
|
Burkitt Lymphoma
-Starry-sky appearance -large cells with clear cytoplasm = macrophages engulfing apoptotic cells |
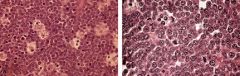
What disease?
|
|
|
Mycosis Fungoides/Sezary Syndrome
Pautrier Microabscess |
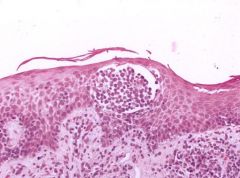
What disease?
What is this called? |
|
|
Reed-Sternberg Cell = owl-eye binucleated cell
Hodgkin Disease |
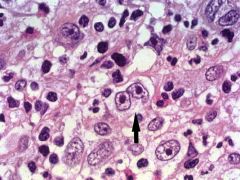
What is the arrow pointing at?
What disease? |
|
|
What is the survival rate for Stage I and II HD?
|
90% 5 year survival
|
|
|
What is the survival rate for Stage IV HD?
|
60-70% 5 year survival
|
|
|
What are the complications of HD?
|
Secondary Malignancy
1. Carcinoma = lung, breast, stomach 2. Hematologic = AML, MDS 3. Sarcoma, Melanoma **due to radiation and chemotherapy |
|
|
-Nodular Sclerosis HD
-Lymphoid nodules surrounded by fibrotic bands -Females |
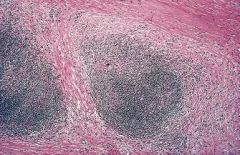
What specific disease?
How do you know? What gender? |
|
|
Reed-Sternberg cell
Hodgkin Disease |
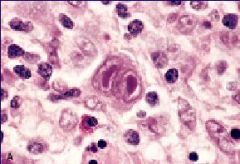
What is this showing?
What disease? |
|
|
Lacunar cells
Nodular Sclerosis |
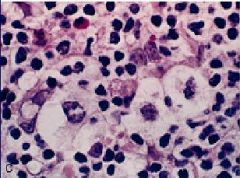
What are these cells called?
What disease? |
|
|
Popcorn Cell = large mononuclear cells with high irregularly folding nucleus
Lymphocyte predominance HD |
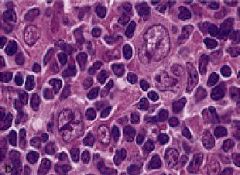
What are these cells called?
What disease? |
|
|
Mycosis Fungoides / Sezary Syndrome
-Cerebriform nucleus = nuclear membrane folding **The cells with the nuclear cleft are malignant CD4 T helper cells, or Sezary cells. They stain positive for PAS (not demonstrated in this slide) and have PAS positive chunks of material located around the nucleus ("ring around the collar" analogous to ringed sideroblasts in sideroblastic anemias"). |
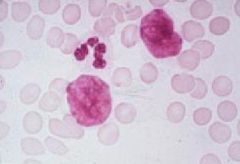
What disease are these cells found in?
|
|
|
B. Hodgkin Disease
|

-
|
|
|
D. Spleen
**Hairy Cell Leukemia results in massive Splenomegaly Mandible = Endemic Burkitts Skin = ATLL or Mycosis Fungoides/Sezary Syndrome Stomach = MALToma or Burkitt |

-
|
|
|
A 22-year-old man presents with a painless lump in his neck. Upon further questioning he has had a low-grade fever, drenching night sweats, 14 lb. weight loss over the past 6 wks, and his skin is itchy. He also states that after a night of drinking he has pain in the lump in his neck
|
Hodgkin Lymphoma
-PAINLESS LYMPHADENOPATHY -Pruritis -Splenomegaly -Low grade fever, night sweats, weight loss |
|
|
T cell cancer associated with Hypercalcemia
|
Adult T cell Leukemia/Lymphoma
|

