![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
26 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What are the three factors determing GFR?
|
Renal blood flow, (2 factors: effective circulating volume, and cardiac output)
Resistance to flow (i.e. vascular tone across afferent and efferent arterioles) Permeability of glomerular basement membrane. |
|
|
What endogenous substances enhance the GFR through affecting the vascular tone? (one for efferent arteriole, one for afferent)
|
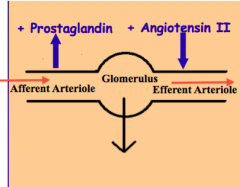
Prostaglandins cause vasodilation, preferentially dilating the afferent arterioles.
Angiotensin causes vasoconstriction, preferentially constricting the efferent arterioles. Both these actions increase GFR. (Also affected by Norepinephrine , ANP, and dopamine) |
|
|
What four factors do you need to know to calculate a patient's creatinine clearance?
|

Age,
Mass (don't do any adjustments to estimate lean body mass), Serum creatinine, Gender. |
|
|
Calculate the creatinine clearance for these two patients with a serum creatinine of 100 umol/L:
40 y.o. 80 kg male, and 60 y.o. 50 kg female. |

Use Cockcrof-Gault:
CrCl = (140-age)(mass)/sCr (*1.2 for males) For the male: CrCl = (140-40)(80)(1.2)/100 = 96 ml/min For the female: CrCl = (140-60)(50)/100 = 40 ml/min |
|
|
What are the three general ways that drugs can damage the kidney?
(hint, same as the general causes of any kidney damage) |
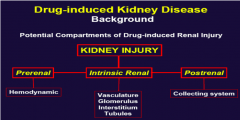
Pre-renal
renal, and Post renal |
|
|
What are the two most common etiologies of intrinsic renal damage caused by drugs?
|
Acute tubular necrosis (ATN),
Allergic interstitial nephritis (AIN). |
|
What five types of drugs are most implicated in causing Acute Tubular Necrosis (ATN).
|
Antibiotics (particularly aminoglycosides [gentamicin])
Immunosuppressants (cyclosporine, tacrolimus) Radiocontrast dyes Statins (inducing rhabdomyolysis) Chemotherapy agents (Cisplatin, and other platinum-based agents) |
|
|
What three types of patients are more at risk for kidney injury from radiocontrast dyes?
|
Patients with:
1) Diabetes Mellitus, 2) Chronic Renal Insufficiency (CRI), 3) Previous Acute Kidney Injury (AKI). |
|
|
What three things can you do to minimize the risk from the test for patients with increased risk for kindey injury?
|
use nonionic form
use the minimum amount find an alternate test |
|
|
What should you do with their medications?
|
HOLD
NSAID and ACEi or ARB |
|
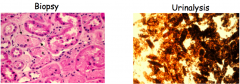
What four measures should you take in treating a patient with nephrotoxic Acute Tubular Necrosis (ATN)?
|
Stop causative nephrotoxic agent(s).
Avoid further kidney insults, Monitor levels and renal function: adjust drug dosages based on renal function. Apply appropriate supportive measures (i.e. dialysis if necessary) |
|
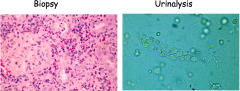
Name four classes of drugs that can cause allergic interstitial nephritis (AIN).
|
Beta-lactams (cephalosporins & penicillins)
Sulfonamides, Quinolones (ciprofloxacin, levofloxacin), NSAIDS (ibuprofen), Diuretics, Proton Pump Inhibitors (omeprazole) Anticonvulsants (phenytoin, carbamazepine) Allopurinol |
|
|
How would you treat someone having a bout of AIN?
|
supportive treatment
stop offending drug avoid others within its class |
|
|
NSAIDs have multiple harmful effects on kidneys (both prerenal and renal).
What are the three sites at which that they directly damage renal function? |
Glomerulus: can cause a) Minimal Change Disease, b) Membranous glomerulopathy, and c) Analgesic nephropathy.
Interstitium: causes Allergic Interstitial Nephritis. Tubules: causes hyperkalemia (by decreasing renin production and GFR) |
|
|
What electrolyte imbalance can result from ACEi and ARB usage? Which drug has the greater effect?
|
They can both cause hyperkalemia, due to decreased effect of aldosterone.
ACEi seem to have the greater effect. |
|
|
What renal insult can be caused by long-term use of pain medications?
|
Analgesic Nephropathy.
|
|
|
What drugs are specifically implicated in analgesic nephropathy?
|
antipyretics (NSAID, phenacetin, acetaminophen)
codeine daily use over years |
|
|
What are four nephrotoxic effects of chronic lithium usage?
|
Glomerular damage (Minimal change disease (MCD) and focal segmental glomerulosclerosis(FSGS))
Nephrogenic Diabetes Insipidus (DI) (from Li accumulation in the collecting tubules) Tubular damage (renal tubular acidosis) Interstitial damage (chronic interstitial nephritis) |
|
|
What are the two indications for diuretic therapy?
|
Hypertension
Edema / volume overload (from CHF, cirrhosis, nephrotic syndrome) |
|
|
What are the three classes of natriuretic diuretics and their sites of action?
|
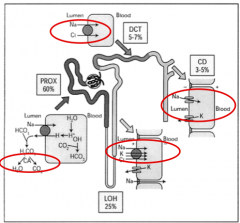
Loop diuretics (Loop of Henle)
Thiazides diuretics (Distal tubule) K-sparing diuretics (Collecting Tubule) |
|
|
Give an example of a loop diuretic.
|
Furosemide,
Bumetanide, Ethacrynic acid |
|
|
Give an example of a thiazide diuretic.
|
Hydrochlorothiazide,
Metolazone, Indapamide, Chlorthalidone |
|
|
Give an example of a potassium-sparing diuretic.
|
Amiloride,
Triamterine, Spironolactone (note: has a different target than the other two) |
|
|
What types of electrolyte disturbances can patients develop while on diuretics? (give 3)
|
Hypokalemia (except K-sparing),
Hypomagnesemia, Hyponatremia, Metabolic alkalosis, Altered calciuresis (e.g. hypercalcuria -> stone formation) hypercalcemia (thiazide) |
|
|
What are the four principals of renal dosing? (ADME)
|
Absorption
Distribution Metabolism Elimination |
|
|
drugs that accumulate in renal failure
|
benzodiazepines (most)
allopurinol chlorpropamide gentamicin insulin meperidine morphine gabapentin glyburide lithium metformin |

