![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
12 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
List the 4 heart valves and what areas they seperate
|
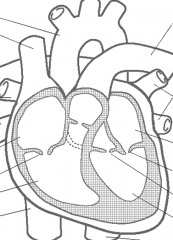
Tricuspid valve - RA and RV
Pulmonary valve - RV and pulmonary artery Mitral valve - LA and LV aortic valve - LV and aorta |
|
|
What are the papillary muscles and what do they do?
|
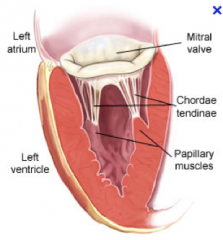
"They are muscles in the ventricle that attach to the atrialventricular valves (tricuspid and mitral).
- 3 attach to tricuspid (each leaflet) - 2 attach to mitral ""bicuspid"" (each leaflet) There function is to keep the valves shut during ventricular contraction thus preventing blood back flow." |
|
|
Explain electrical conduction through the heart.
1. Where it is generated 2. The conduction pathway structures |
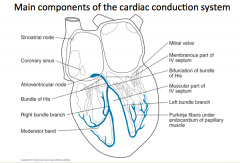
1. SA Node in healthy heart
2. SA Node - passive spread to LA - collection at coronary sinus - AV Node - Bundle of His - R/L Bundle Branch - Purkinje Fibres |
|
|
What are the components of the Right and Left Coronary Arteries?
and what do they supply? |
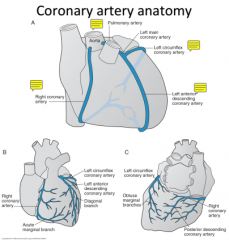
Right Coronary Artery: (supplies the RV and portions of the LV
Right Coronary Artery, Right "Acute" Marginal Artery, Posterior descending Artery Left Coronary Artery: Left main - Circumflex Artery - obtuse marginal branch (lateral and posterior LV) left main - Left anterior descending artery - Diagonal Branch, (LV wall, anterior RV wall anterior intraventricular septum |
|
|
What is the Sacrolemma?
A. Place in myocardial cells where calcium is stored B. Membrane of a muscle cell C. A component in the contraction apparatus D. A part of the electrical conduction pathway |
B. Membrane of a muscle cell
|
|
|
Inside a cardiac muscle cell (cytoplasm) state if the following ions are more or less abundant compared to outside the cell at rest.
Na+ Ca2+ Cl- K+ Bonus: Lab values give you ion concentration where? |
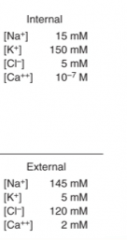
"Na+ - Less abundant inside the cell
Ca2+ - Less abundant inside the cell Cl- - More abundant inside the cell K+ - More abundant inside the cell Bonus: Lab values give you concentrations ouside the cell as they come from blood draws (the plasma). |
|
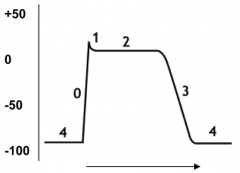
Explain what channels are involved in each step 0-4 of the diagram below.
|
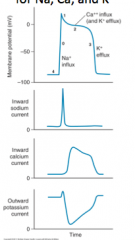
4 - Resting Phase (Maintained By Na+/K+ ATPase)
0 - Depolarization (Opening of Na+ Channels - Na+ In) 1 - Slight Repolarization (Closing of Na+ Cahnnels) 2 - Plateau Phase (Opening of Calcium Channels - Ca2+ In) 3 - Repolarization Phase (Opening of K+ Channels - K+ Out) |
|
|
In respect to ion flux, how does a pacemaker cell (SA Node) depolarize / Repolarize?
|
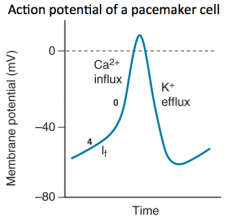
The If (funny current) influxes in calcium and depolarizes the cell and K+ effluxes and repolarizes the cell.
|
|
|
How do the myosin heads gain access to the actin filiments in cardiac muscle contraction?
|
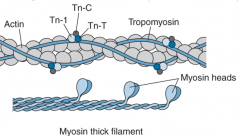
Calcium binds to Tropoinin C which causes a conformational change in the Troponin complex that moves tropomyosin out of the way so the myosin heads can bind actin.
|
|
|
1. What does the SERCA pump do?
2. What protein does sympathetic activation (Beta 1 agonist) indirectly have an effect on to increase the activity of the SERCA pump? |
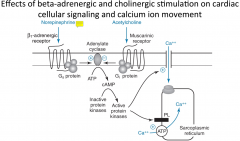
1. It recovers the free calcium and pumps it back into the sarcoplasmic reticulum, so it can be used in the next contraction
2. Phospholamban - (Sympathetic stimulation removes the phospholamban inhibiton via phosphorylation and increased SERCA activity) |
|
|
Acetylcholine activates muscarinic receptors in the heart. this ________ (increase/decreases) Heart Rate.
|
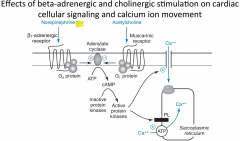
Decreases
|
|
|
ATP binding to the (myosin head - actin complex) causes __________ (the bond to break / contraction).
ATP hydrolysation on the myosin head to ADP + P causes __________ (muscle contraction / myosin head to rest after ATP is bound) The disassociation of ADP from the myosin head when attached to actin causes _________ (muscle contraction / muscle relaxation |
"1. The Bond to break
2. Myosin Heads to reset to be ready for next contraction 3. Muscle contraction For more on this look at this video on youtube: ""Muscle Contraction"" https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=gJ309LfHQ3M" |

