![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
32 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Metabolism |
They are the chemical reactions within an organism |
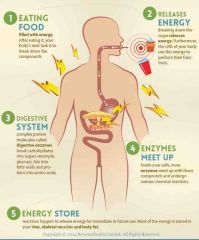
There's 2 types of _____ |
|
|
Biosynthesis |
The production of the complex molecules within living cells and organisms |
Carbon skeletons are needed in this |
|
|
Decomposition |
Reactions that break down the organic food molecules into simpler forms so they release energy |

A type of metabolic process which is similar to food breaking down/ rotting |
|
|
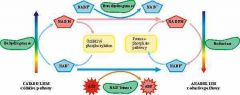
Cell Respiration |
A pathway for the energy released by decomposition to the cells so they can function |
Also has two types depending on oxygen use |
|
|
Aerobic |
Respiration that occurs when oxygen is present |
A type of cellular respiration |
|
|
Anaerobic |
Respiration that occurs when there is no oxygen present |
Another type of cellular respiration |
|
|
Fermentation |
What a pyruvate undergoes when oxygen is absent |
Used to create alcohol |
|
|
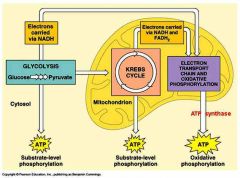
Glycosis |
The process in which enzymes partially oxidize the glucose and split the glucose into 2 3-carbon molecules |
First stage of aerobic respiration |
|
|
Glucose |
Simple carbohydrate |
Divided into 3 stages of use |
|
|
Krebs Cycle |
The 2-carbon molecules resulting from the end of glycosis are completely oxidized into carbon dioxide. |
ATP molecules to conserve energy released from this reaction |
|
|
NAD+/NADH |
Electrons and protons lost from glycosis and the Krebs cycle go to the NAD+. Hydrogen atoms also lost in those stages reduce NAD+ into NADH. NAD+ is an easily reduced molecule |
Similar to the NADP+ and the NADPH in photosynthesis |
|
|
Electron Transport System |
Where the protons and electrons from the oxidize NADH go |
Third stage of aerobic respiration |
|
|
FAD/FADH2 |
Two hydrogen atoms, in the Krebs Cycle, that comes from glucose reduces to a second hydrogen carrier molecule known as FAD. FADH2 is created and carries hydrogen in cells |
NADH, NADPH, and ____ carry hydrogen |
|
|
ATP |
Energy from the protons and electrons in the ETS release energy when being passed to oxygen and the energy is used to form ATP |
Mostly synthesized by the ETS |
|
|
Pyruvate |
Key ingredient in several anaerobic pathways |
It's kind of like the "flour" to the ____ you could say because flour is the main ingredient in a lot of our daily foods |
|
|
Lactate |
Is a 3-carbon acid made when NADH and pyruvate convert to it |
Happens when insufficient oxygen is present at the end of glycosis |
|
|
Lactic Acid Fermentation |
The anaerobic pathway that converts NADH and pyruvate into NAD+ and lactate. The NAD+ goes back to the beginning of glycosis and the glycosis increases the ATP until more oxygen is available |
Technical name for the process that happens at the end of glycosis when the oxygen isn't sufficient |
|
|
Cristae |
The inner membrane that has many folds which extend to the inside of the mitochondrion |
Enzymes of the ETS are organized here |
|
|
Mitochondrion |
The Krebs cycle and the ETS occurs in this organelle. It also provides efficiency and organization to cell respiration |
The ____ is similar to the chloroplast in photosynthesis |
|
|
Matrix |
Fluid filled interior space of the mitochondrion |
Most enzymes of the Krebs cycle are found here |
|
|
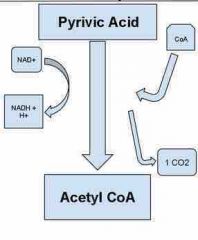
Acetate |
A 2-carbon organic acid left from the enzymes releasing CO2 from each 3-carbon pyruvate |
Step one of the Krebs cycle produces this |
|
|
Coenzyme A/ acetyl CoA |
Coenzyme A is a carrier molecule which binds to the acetate and delivers it to the Krebs cycle. The resulting complex when the coenzyme A and the acetate combine is called acetyl CoA |
Partners with acetate |
|
|
Citrate |
This 6-carbon acid if formed when an enzyme combines acetyl CoA with a 4 carbon acid known an oxalocetate |
Second step of the Krebs cycle |
|
|
Cytochromes |
The series of easily reduced and oxidized enzymes and other proteins in the ETS |
These are embedded in the inner membrane of the mitochondria |
|
|
Facultative anaerobe |
Bacteria that can survive long periods of time with or without oxygen |
Staphylococci; Gram positive |
|
|
Obligate anaerobes |
These are bacteria that are poisoned by oxygen and instead generate ATP from fermentation or anaerobic respiration |
|
|
|
Obligate aerobes |
Organisms such as plants and animals which cannot survive without oxygen |
Dogs and tulips |
|
|
Hydrolysis |
When the components of water are used to break a bond |
Digestion |
|
|
Reduce |
To break something down into smaller pieces |
When NAD+ is reduced to NADH |
|
|
Oxidize |
When another molecule is chemically combined with oxygen |
Happens in glycosis |
|
|
ATP Synthase |
Important enzyme which provides energy for cells |
Important for synthesis of ATP |
|
|
Glucose |
Simple carbohydrate |
Divided into three stages of use |

