![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
38 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Cell Cycle |
Series of stages that represents the process of eukaryotic cell division. |
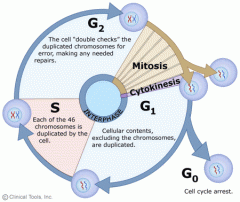
1. After completing ____, a cell becomes two new daughter cells. 2. image |
|
|
Mitosis |
A process of sorting and distributing the chromosomes during cell division. |
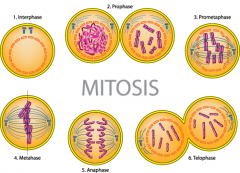
1. The individual chromosomes become visible during ____. 2. image |
|
|
Interphase |
The period between cell divisions which is mostly cell regular growing. |
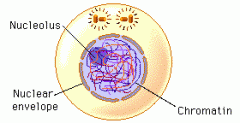
1. ____ takes place in cells most of the time. 2. image |
|
|
G1/G0 |
The first stage of cell cycle where cell enlarges and makes new protein. |
1. Most cells in adult multicellular organisms are in ____. 2. ____represents Gap 1/Gap 0. |
|
|
S |
The second stage of cell cycle. |
1. ____ represents synthesis. 2. The DNA of each chromosome replicates to form a new identical set of chromosomes during____. |
|
|
G2 |
The third stage of cell cycle. |
1. During____, the cell prepares for mitosis by synthesizing specific types of RNA and proteins. 2. The product of ____ will be required for mitosis during the upcoming M phase. |
|
|
M |
The last stage of cell cycle, include mitosis and cytokinesis. |
1. the chromosomes are condensed and visible during this stage. 2. After ____, the daughter cells enters G1 again. |
|
|
Restriction point |
A point between G1/G0 and S in which a cell that pass it commits to a full round of the cell cycle. |
1. ____ is the "point of no return" 2. When a cell in G0/G1 receives these signals, it passes through the ____. |
|
|
Cytokinesis |
Division of the whole cell. |
1. takes place after mitosis. 2. ____ happens very quick. |
|
|
Daughter cell |
Two cells that are formed after one cell's division. |
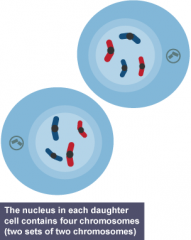
1. The ____ enters the cell cycle after it's formed. 2. image |
|
|
Nucleotide base pairing |
A pairing rule in DNA replication that depends on how many hydrogen bonds each nitrogen base can form with its counterpart. |
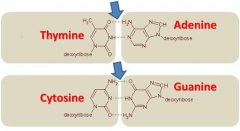
1. Adenine pairs with thymine; guanine pairs with cytosine. 2. image |
|
|
Hydrogen bond |
The electrostatic attraction between polar groups that occurs when a hydrogen atom bound to a highly electronegative atom(N). |
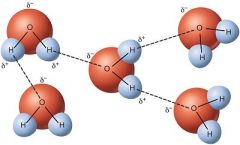
1. ____ is the factor that nucleotide base pairing is based on. 2. image |
|
|
Antiparallel |
To describe two biopolymers run parallel to each other with opposite alignments. |
1. The two strands of DNA are parallel but run in opposite directions. 2. ____ is like a divided highway. |
|
|
DNA polymerase |
The enzyme that catalyzes the formation of the new DNA strands. |
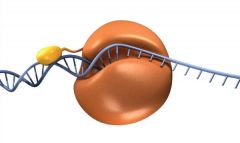
1. ____ can add nucleotides only to the end of an existing nucleic-acid strand. 2. image |
|
|
Semiconservative replication |
Referring the process of DNA replication contain half of the strands from an old DNA and half new. |
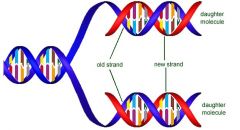
1. ____ is a characteristic of DNA replication. 2. image |
|
|
Histone |
Highly alkaline proteins found in eukaryotic cell nuclei that package and order the DNA into structural units called nucleosomes. |
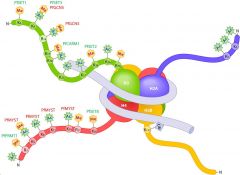
1. ____ are the chief protein components of chromatin. 2. image |
|
|
Chromosome |
Thread-like structures made of protein and a single molecule of DNA. |
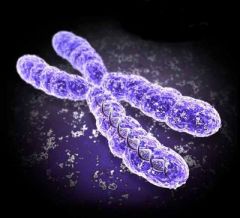
1. ____ is passed from parent cell to daughter cells. 2. image |
|
|
Chromatin |
DNA bound to nucleosomes. |
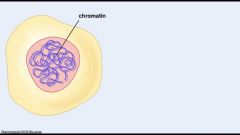
1. Eukaryotic DNA exists in this form most of the time. 2. image |
|
|
Mutation |
Any change in the sequence of a cell's DNA. |
1. most of the ____ are harmful. 2. ____ that persist to the next cell division are inherited by the daughter cells.` |
|
|
Mutagen |
Chemicals in forms of radiation that cause mutations. |

1. As many mutations can cause cancer, ____ are therefore also likely to be carcinogens. 2. image |
|
|
Excision repair |
The process by which mismatches mutation are repaired. |
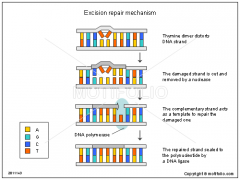
1. In ___, enzymes remove part of one strand from the mismatched section, synthesize a replacement that matches the strand, and bond the new nucleotides to the rest of strand. 2. |
|
|
Leading strand/Lagging strand |
Two strands of DNA. DNA replication occurs continuously on one strand and discontinuous on the other strand. |
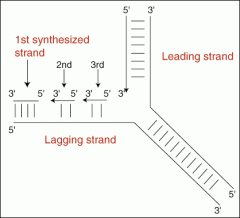
1. They occurs because the DNA strand is antiparallel. 2. image |
|
|
Sister chromatids |
The two copies of each chromosome made during the S phase. |
1. ____ are ready to be separated and delivered to each new nucleus. 2. image |
|
|
Centromere |
Proteins at a narrow point that attaches the sister chromatids as a cell enters the M phase. |
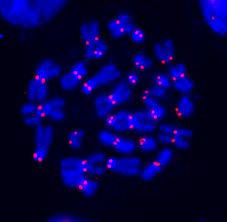
1. ____ usually are near the center of the chromosome. 2. image(red dots) |
|
|
Aneuploid |
Daughter cells with abnormal numbers of chromosomes. |
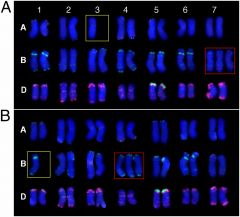
1. A mistake at chromosome segregation will result ____. 2. image |
|
|
Prophase |
the first phase of mitosis |
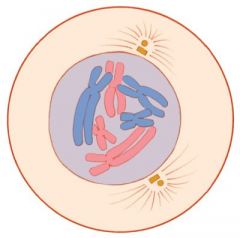
1. chromatin condenses during ____. 2. image |
|
|
Metaphase |
the second phase of mitosis |
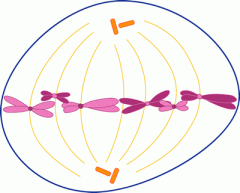
1. in ____, motor proteins in the kinetochores have pulled the chromosomes into a ring between the two poles. 2. image |
|
|
Anaphase |
the third phase of mitosis |
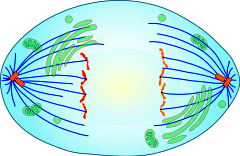
1. in ____, enzymes break down the protein holding sister chromatids together. 2. image |
|
|
Telophase |
the fourth phase of mitosis |
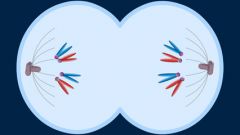
1. in ____, two new nuclei are produced. 2. image |
|
|
Centrioles |
A small set of microtubules arranged in a specific way. |

1. ____ are found in pairs and move towards the poles of the nucleus during cell division. 2. image |
|
|
(Mitotic) spindle (fibers) |
Spindle fibers form a protein structure that divides the genetic material in a cell. |
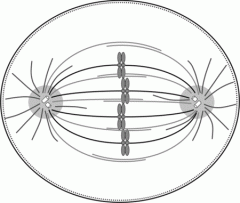
1. During prophase, microtubules begin to form around the nucleus and join to form ____. 2. image |
|
|
Spindle poles |
The site at which the microtubules at the ends of the spindle are anchored protein structures that surround the centrioles at each end of the cell. |
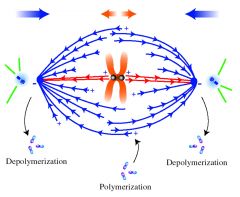
1.____ form around the centrioles. 2. image |
|
|
Kinetochore |
A protein complex within each centromere. |
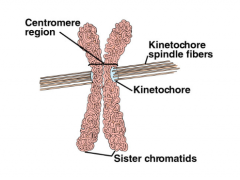
1. Some of the microtubules in the spindle bind to the ____ of each chromatid. 2. image |
|
|
Cyclins |
Proteins within the cell begin to accumulate and then rapidly disappear as the cell cycle progresses. |
1. they are called ____ because they regulate progresses. 2. the most important ____ are the G1____ and the mitotic ____. |
|
|
Kinases |
Enzymes that transfer a phosphate group from ATP to other enzymes. |
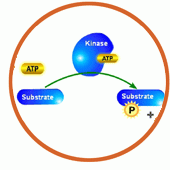
1. Cyclins act by binding to various ____. 2. image |
|
|
Cell-cycle arrest |
A state in which checkpoint controls consist of proteins that detect mistakes and damage and quickly halt the cell cycle until repairs are made. |
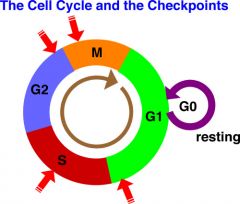
1. without ____, mitosis could produce daughter cells with damaged or missing chromosomes. 2. image |
|
|
Cancer |
Uncontrolled cell growth and reproduction. |

1. Research on mismatched genes is critically important in the detection and prevention of ____. 2. image |
|
|
Checkpoints |
Eukaryotic cells have checkpoints at several stages in the cell cycle where they arrest the process when a problem is detected. |
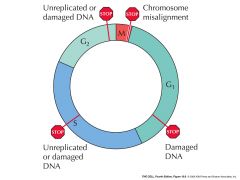
1. ____ prevents production of daughter cells with genetic damage. 2. image |

