![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
35 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Nutrients |
Components in food that are necessary for organisms' survival or growth. |
1. Vitamins, proteins, carbohydrates. 2. ____is for provide energy or support metabolism. |
|
|
Heterotrophs |
Organisms that cannot produce organic nutrients by itself. |
1. Animals, fungi, many bacteria. 2. Ninety-five percent or more of all types of living organisms are____. |
|
|
Autotrophs |
Organisms that can produce nutrients out of it's surrounding. |
1. Most of the plants are____. 2. Photoautotrophs and chemoautotrophs. |
|
|
Photoautotrophs |
Autotrophs that use the energy from light to produce nutrients for themselves. |
1. Green plants and photosynthetic bacteria are____. 2. ____can fix carbon. |
|
|
Photosynthesis |
A chemical process that organisms use to turn light energy into organic energy. |
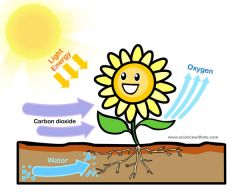
1. 6CO2 + 12H2O ------>C6H12O6 + 6H2O + 6O2 |
|
|
Chemoautotrophs |
Organisms that gain energy during chemical processes. |
1. The ____ designation is in contrast to phototrophs. 2. nitrifying bacteria |
|
|
Chemosynthesis |
A process that help chemoautotrophs to convert carbon molecules into energy. |
1. Venenivibrio stagnispumantis gains energy by oxidizing hydrogen gas. 2. Using the oxidation of inorganic molecules or methane as a source of energy, rather than sunlight, as in photosynthesis. |
|
|
Cell respiration |
A series of reactions happen in the cells to support their metabolism. |
1. ____is one of the key ways a cell gains useful energy to fuel cellular activity. 2. ____releases heat. |
|
|
Producers |
Organisms that synthesis organic compounds in a food chain/web. |

1. Grass. |
|
|
Consumers |
Organisms that consumes other produces or consumers and obtain energy. |

1. Lion |
|
|
Decomposers |
Organisms that live by decompose other dead or decaying organisms and obtain energy from it.
|

1. Fungi |
|
|
Food Web |
A natural form of a system of what-eats-what in the biosphere. |
1. a consumer-resource system 2. ____is more complicated than a food chain. |
|
|
Biotic |
A describe of a living thing. |

1. Human |
|
|
Abiotic |
A description of Nonliving things |

1. Stones |
|
|
Ecosystem |
A system that biotic and abiotic things connected with each other and interacting each other. |
1. ____encompass specific, limited spaces 2. Energy, water, nitrogen and soil minerals are other essential abiotic components of an____. |
|
|
Habitats |
A place where living things lives. |
1. Coral reef is a rich____ for sea life. 2. For a parasitic organism, ____ is the body of its host. |
|
|
Biosphere |
The sum of all of the ecosystems on earth. |
1. ____can also be termed as the zone of life on Earth. |
|
|
Energy |
It's a property of organisms that supports living. It cannot be destroyed or created but can be converted. |
1. ____ has many different forms. 2. In the food chain, lots of ____ are lost as heat. |
|
|
Chemical energy |
Potential energy in a chemical substance, can be released during chemical reactions. |
1. batteries, light bulbs, cells, nuclear weapons 2. ____related to the structural arrangement of atoms or molecules. |
|
|
Free energy |
The amount of energy that are usable in a thermodynamic system. |
1. ____ is the internal energy of a system minus the amount of energy that cannot be used to perform work. 2. The unusable energy is given by the entropy of a system multiplied by the temperature of the system. |
|
|
Heat energy |
When there's energy that has been released during a chemical reaction, it's in heat form. |
1. Photosynthesis 2. ____refers to a process of transfer between two systems |
|
|
First Law of Thermodynamics |
The total energy of an isolated system is constant. Energy can be transformed, but it cannot be created or destroyed. |
1. The change in the internal energy of a closed system is equal to the amount of heat supplied to the system, minus the amount of work done by the system on its surroundings. 2. ____is a version of the law of conservation of energy |
|
|
Second Law of Thermodynamics |
The sum of the entropy is always increased if there's no energy come in. |
1. ____may be expressed in many specific ways. 2. ____is an empirical finding that has been accepted as an axiom of thermodynamic theory. |
|
|
Entropy |
A measure of disorder, always tend to increase. |
1. the ____ of an isolated system never decreases. 2. Systems that are not isolated may decrease in ____. |
|
|
Enzymes |
They are like any catalysts and are not consumed in chemical reaction. |
1. ____remains the same before and after the chemical reaction. 2. Activators are molecules that increase activity. |
|
|
Catalysts |
A matter to make the chemical reaction quicker without having anything happens. |
1. With a ____, reactions occur faster and require less activation energy. 2. Often only tiny amounts of ____ are required |
|
|
Active Site |
A part of an enzyme, including binding site and catalytic site. |
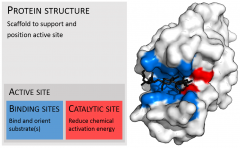
1. ____is usually a groove or pocket of the enzyme which can be located in a deep tunnel within the enzyme. 2. |
|
|
Substrate |
The chemical species that we can observe in a chemical reaction. |
1. An enzyme ____ is the material upon which an enzyme acts. 2. the ____ is the reagent whose concentration is changed. |
|
|
Metabolism |
A process that's done within the cells and allows organisms to reproduce and grow. |
1.____ are enzyme-catalyzed reactions. 2. Metabolism is usually divided into two categories: catabolism, and anabolism. |
|
|
Synthesis |
Creating something out of what we can easily got. |
1. Plants ____ oxygen by photosynthesis. 2. ____has artificial means. |
|
|
Decomposition |
A process that an complex organic matter breaks down into something different. |
1. ____ is essential for recycling the finite matter that occupies physical space in the biome. 2. Decomposers do this. |
|
|
Biosynthesis |
A process that convert substrates into more complicated organic compounds. |
1. ____ occurs due to a series of chemical reactions. 2. The prerequisite elements for ____ include: precursor compounds, chemical energy (e.g. ATP). |
|
|
Oxidation |
One of the reaction of redox. It's the loss of electrons. |
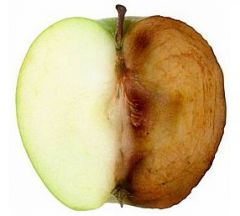
1. ____ reactions are commonly associated with the formation of oxides from oxygen molecules. |
|
|
ATP |
Adenosine-5'-triphosphate, an energy carrier in the cells. |
1.____ is used as a substrate in signal transduction pathways by kinases that phosphorylate proteins and lipids. 2. ____ is continuously recycled in organisms. |
|
|
ADP |
Adenosine diphosphate, an essential organic compound in the energy flow and metabolism. |
1. ____contains two phosphate groups attached to the 5’ position. 2.____ is continuously recycled in organisms as ATP |

