![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
269 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
This systems protects a person by detecting changes in the environment?
|
The sensory system
|
|
|
An environment change becomes a?
|
Stimulus
|
|
|
The stimulus from the environment initiates a nerve ____?
|
Impulse
|
|
|
The external stimulus from sensory organs travel toward the CNS by way of what?
|
Afferent neuron, ascending tract
|
|
|
A stimulus becomes a sensation only when the cerebral cortex ________the nerve impulse it generates?
|
Interprets
|
|
|
Types of stimulus are?
|
Internal (visceral)
External (skeletal, integumentary, Ears, nose, eyes) |
|
|
Type of stimulus that arrive from the external and are detected at or near the body surface?
|
External
|
|
|
Type of stimulus that originates internally to maintain homeostasis?
|
Internal (visceral)
|
|
|
The part of the nervous system that detects a stimulus?
|
Sensory receptor
|
|
|
A free dendrite of a sensory neuron, such as the receptors for pain is what type receptor?
|
Sensory
|
|
|
Type of Receptor? A modified ending, or end-organ, on the dendrite of an afferent neuron, such as those for touch and temperature?
|
Sensory
|
|
|
Type of receptor? A specialized cell associated with an afferent neuron, such as the rods and cones of the retina of the eye and the receptors in the other special sense organs?
|
Sensory
|
|
|
Receptors can be classified according to the type of _________ to which they respond?
|
Stimulus
|
|
|
Type of Sensory receptor such as the receptors for taste and smell, detect chemicals in solution?
|
Chemoreceptors
|
|
|
Type of Sensory receptor located in the retina of the eye, responds to light?
|
Photoreceptors
|
|
|
Type of Sensory receptor that detect change in temperature, many of these located in skin?
|
Thermoreceptors
|
|
|
Type of Sensory receptor that respond to movement such as stretch, pressure, or vibrations?
|
Mechanoreceptors
|
|
|
Any receptor must recieve a stimulus of adequate intensity called?
|
Threshold stimulus (must meet a certain level to activate sensory recpetors)
|
|
|
Type of sense that is localized in a special sense organ?
|
Special sense
|
|
|
Type of sense that is widely distributed throughout the body?
|
Generalized sense
|
|
|
Special senses include what senses?
|
Vision, hearing, equilibrium, taste, smell
|
|
|
General senses include what senses?
|
Pressure, temperature, pain, and touch, also sense of position (muscles, joints, tendons)
|
|
|
What structures protect the eye?
|
Skull bones, eyelids, eyelashes, eyebrow, conjuctiva (covers sclera, lacrimal glands, nasolacrimal duct.
|
|
|
The upper and lower eyelids anatomical name?
|
Superior Palpabrea levator, Inferior Palpabrea levator
|
|
|
Cells within the _______produce mucus that aids in lubricating the eye?
|
Conjunctiva
|
|
|
Tears from the lacrimal glands lubricate the eye and contain an ________that protects against infection?
|
Enzyme
|
|
|
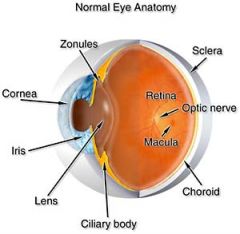
The eyeball has three coats or tunics, what are they?
|
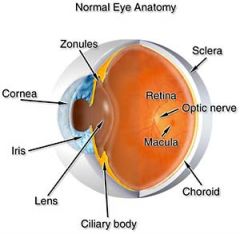
Sclera, Choroid, retina
|
|
|
Type tunic that is made of tough connective tissue, also referred to the "white of the eye"?
|
Sclera
|
|
|
Appears white because of the collagen it contains and has no blood vessel to add color?
|
Sclera
|
|
|
Tunic composed of a delicate network of connective tissue interlaced with many blood vessels?
|
Choroid
|
|
|
Tunic that contains dark brown pigment, prevents incoming light rays from scattering and reflecting the inner surface of the eye?
|
Choroid
|
|
|
The tunic that is the actual receptor layer of the eye?
|
Retina
|
|
|
Tunic contains light-sensitive cells known as rods and cones?
|
Retina
|
|
|
Generate the nerve impulses associated with vision?
|
Rods and cones
|
|
|
The process which is the bending of light rays as they pass from one substance to another substance of different density?
|
Refraction
|
|
|
Because of this light from a very large area can be focused on a very small area of the retina?
|
Refraction
|
|
|
An anterior continuation of the sclera, but it is transparent, colorless, whereas the rest of sclera is opaque and white?
|
Cornea
|
|
|
Referred to as "the window of the eye"?
|
Cornea
|
|
|
Bulges forward slightly and is the main refracting structure of the eye?
|
Cornea
|
|
|
Has no blood vessels, is nourished by the fluid that constantly wash over it?
|
Cornea
|
|
|
A watery fluid that fills much of the eyeball anterior to the lens, helps maintain the slight forward curve of the cornea?
|
Aqueous Humor
|
|
|
Constantly produce and drained from the eye?
|
Aqueous Humor
|
|
|
Technically called the "CRYSTALLINE LENS"?
|
Lens
|
|
|
A clear, circular structure made of a firm elastic material?
|
Lens
|
|
|
Has two bulging surfaces and is considered biconvex?
|
Lens
|
|
|
Important in light refraction because it is elastic and its thickness can be adjusted to focus light for near or far vision?
|
Lens
|
|
|
A soft jelly like substance that fill the entire space posterior to the lens?
|
Vitreous Body
|
|
|
Important in maintaining the shape of the eyeball as well as in aiding in refraction?
|
Vitreous Body
|
|
|
What are the structures that refract light as it passes through the eye?
|
Cornea, aqueous humor, lens, vitreous body
|
|
|
The receptor cells of the eye, named for their shape?
|
Rods and cones
|
|
|
Part of the retina that are highly sensitive to light, thus function in dim light but do not provide a sharp image?
|
Rods
|
|
|
Are more numerous than cones and are distributed more toward the periphery (anterior portion)of the retina?
|
Rods
|
|
|
Responsible for dark adaptation, from more light to less light?
|
Rods
|
|
|
Rods are unable to differentiate what?
|
Color
|
|
|
Function in bright light, sensitive to color, and give sharp images?
|
Cones
|
|
|
Are localized at the center of the retina?
|
Cones
|
|
|
A tiny depressed area near the optic nerve is?
|
Fovea centralis
|
|
|
Point of the sharpest vision and contains a high density of cones?
|
Fovea centralis
|
|
|
The fovea is contained within a yellow spot called?
|
The macula lutea
|
|
|
An area that may show degenerative changes with age and contains the fovea?
|
The macula lutea
|
|
|
Cones have specific colors they are sensitive to, what are the colors?
|
Red, green, and blue light
|
|
|
The absence of retinal cones results in?
|
Color blindness
|
|
|
The ______ and ____ function by means of pigments that are sensitive to light?
|
Rods and cones
|
|
|
The rod pigment is known as?
|
rhodopsin or visual purple
|
|
|
What vitamin is needed to manufacture rhodopsin?
|
Vitamin A
|
|
|
A lack of Vitamin A results in?
|
Night Blindness
|
|
|
Nerve impulses from the rods and cones flow into sensory neurons that merge to form what?
|
The optic nerve
|
|
|
The optic nerve is also labelled the ?
|
Cranial nerve II
|
|
|
Impulses from the optic nerve travel to the center of the?
|
Occipital cortex of the brain
|
|
|
Two groups of muscle in the eye are?
|
Intrinsic and Extrinsic muscles
|
|
|
How many extrinsic muscles are connected with each eye?
|
Six (6)
|
|
|
Muscle of the eye Originates of the bones of the orbit and inserts?
|
On the surface of the sclera
|
|
|
The muscle in the eye are named for their?
|
Location
|
|
|
Eye muscle that pull on the eyeball in a coordinated fashion so that both eyes center on one visual field?
|
muscles of the eye
|
|
|
Process by which muscles pull on the eyeball in a coordinated fashion so that both eyes center on one visual field?
|
convergence
|
|
|
Necessary for a clear image on the retina?
|
convergence
|
|
|
Three dimensional vision or stereoscopic vision is a characteristic of?
|
Primates
|
|
|
The involuntary muscles located within the eye are known as?
|
Intrinsic muscles
|
|
|
Form two circular structures within the eye, the iris and the ciliary muscle?
|
Intrinsic muscles
|
|
|
The colored or pigmented part of the eye?
|
Iris
|
|
|
Composed of two sets of muscle fibers that the size of the central opening (pupil)?
|
Iris
|
|
|
Central opening of the iris?
|
Pupil
|
|
|
Regulates the amount of light that enters the eye?
|
Iris
|
|
|
In bright light the muscles of the iris?
|
Contract
|
|
|
The narrowing of the piris is termed?
|
Constriction
|
|
|
In dim light the radial muscles of the iris do what?
|
Dilate
|
|
|
The enlargment of the pupil is known as?
|
Dilation
|
|
|
Shaped like a flattened ring with a central hole the size of the outer edge of the iris?
|
Ciliary muscle
|
|
|
This muscle holds the lens in place by means of filaments?
|
Ciliary muscle
|
|
|
The filaments or ligaments of the ciliary muscle are called?
|
suspensory Ligaments
|
|
|
These ligaments project from the ciliary muscle to the edge of the lens around its entire circumference?
|
suspensory Ligaments
|
|
|
This intrinsic muscle of the eye controls the shape of the lens to allow for vision at near and far distances?
|
Ciliary muscle
|
|
|
This process changes the lens shape for better viewing?
|
Accomodation
|
|
|
A common cause of farsightedness in the aging process, is due to a loss of elasticity in this eye muscle?
|
Ciliary muscle
|
|
|
What is the function of the Iris?
|
To control the amount of light entering the eye
|
|
|
What is the function of the ciliary muscle?
|
Holds the lens in place contorting it by suspensory ligaments to accommodate near and far vision
|
|
|
Carries visual impulses from the retinal rods and cods to the brain?
|
Optice nerve
|
|
|
Known as the Cranial Nerve II?
|
Optic nerve
|
|
|
Carries impulses of pain, touch, and temperature from the eye and surrounding parts of the brain?
|
opHthalmic branch of the trigeminal nerve
|
|
|
There are no rods and cones in the area of the optic nerve causing?
|
Blind spot
|
|
|
What is the pathway for transmitting external information from the eye to the brain?
|
External stimulus - outer layer - retina - rods and cones - optic nerve - thalamus-occipital of brain
|
|
|
The image that falls on the retina is overfracted causing the image to be?
|
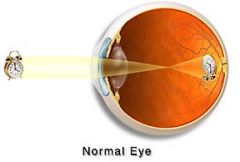
Upside down
|
|
|
Which part of the brain reverses the upside down image?
|
visual centers of the brain
|
|
|
Three nerves that caryy impulses to the eyeball muscle?
|
Oculomotor nerve, trochlear nerve, abducens nerve
|
|
|
Also known as cranial nerve III (3)?
|
Oculomotor nerve
|
|
|
Also known as cranial nerve V (5)?
|
Trochlear nerve
|
|
|
Also known as cranial nerve VI (6)?
|
Abducens nerve
|
|
|
The largest of the three motor nerves to the eye?
|
Oculomotor nerve
|
|
|
Supplies voluntary and involuntary motor impulses to all but two eye muscles?
|
Oculomotor nerve
|
|
|
Supplies the superior oblique extrinsic eye muscle?
|
Trochlear nerve
|
|
|
Supplies the lateral rectus extrinsic eye muscle?
|
Abducens nerve
|
|
|
What are the seven steps of vision? LICESOL (LYSOL:)
|
L= Light refracts
I= Iris adjusts the pupil C=Ciliary adjusts the lens E=Extrinsic convergence S=Stimulates rods/cones (retina) O=Optic nerve transmits impulse 2 brain L=Lobe (occipital) interprets impulse |
|
|
What is the cranial nerve II and what does it do?
|
Optic nerve, transmits impulses received from the retina (rods/cones) to the brain
|
|
|
The sense organ for both hearing and euqilibrium?
|
The ear
|
|
|
Outer Ear
|
Includes an outer projection and a canal ending at the membrane? (Ear)
|
|
|
An airspace containing three small bones in the ear?
|
Middle Ear
|
|
|
The most complex and contains the sensory receptors for hearing and equlibrium?
|
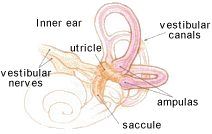
The inner ear
|
|
|
The portion of the ear that is visiible?
|
Pinna or auricle
|
|
|
The canal that leads from the pinna or auricle to deeper parts of the ear?
|
External auditory canal or meatus (audi=sound, meatus, hole)
|
|
|
Part of the external portion of the ear that directs sound into the ear?
|
Pinna
|
|
|
Contains many wax (ceruminous glands)?
|
External auditory canal
|
|
|
The wax in the ears is known as?
|
cerumen
|
|
|
The eardrum is also known as?
|
Tympanic membrane
|
|
|
Vibrates freely and is the boundary between the canal and the middle ear cavity?
|
Typanic membrane (ear drum)
|
|
|
Three small bones of the ear are known as?
|
ossicles
|
|
|
Ear bone shaped like a hammer?
|
Malleus
|
|
|
Ear bone shaped like an ANVIL?
|
Incus
|
|
|
Ear bone shaped like a stirrup or saddle?
|
Stapes
|
|
|
What are the functions of the ossicle in the ear?
|
To amplify sound waves from the eardrum to the inner ear
|
|
|
Connects the middle ear cavity with the throat (pharynx)?
|
Eustachian Tube
|
|
|
The most important part of the ear is the internal portion or?
|
Labyrinth
|
|
|
The skeleton the the inner ear is called?
|
Bony Labyrinth
|
|
|
What are the three divisions of the bony labyrinth?
|
Vestibule, semicircular canals, cochlea
|
|
|
Conists of two bony chambers that contain some of the receptors for equilibrium?
|
Vestibule
|
|
|
Three projecting tubes located toward the posterior?
|
Semicircular canals
|
|
|
Coiled like a snail shell and located twoard the anterior and contains the receptors for hearing?
|
Cochlea (coc shell)
|
|
|
The fluid of the bony labyrinth?
|
Perilymph (peri-around)
|
|
|
Whithin the bony labyrinth an exact replica of shell is made of?
|
Membrane
|
|
|
The tubes and chamers in the membrane within the bony labyrinth are?
|
Membraneous labyrinth
|
|
|
The membraneous labyrinth are filled with what type of fluid?
|
Endolymph (Endo-within, inside)
|
|
|
What is the structure of the fluids in the bony labyrinth?
|
Endolympth (inside)
Perilympth (around) |
|
|
The organ of hearing (inner ear)?
|
Organ of Corti
|
|
|
Consists of ciliated receptor cells located inside the cochlea?
|
organ of Corti
|
|
|
The memraneous cochlea is also known as ?
|
Cochlear duct
|
|
|
Soundwaves enter the external ear canal and cause vibrations in the?
|
Tympanic Membrane
|
|
|
Ossicles amplify the vibrations from the tympanic membrane and finally transmit them from the stapes to?
|
Oval window of the inner ear
|
|
|
The cilia move back and forth against what membrane?
|
Tectorial membrane
|
|
|
The motion of the tectorial membrane sets up nerve impulses that travel to the brain in the?
|
Cochlear nerve (branch of the eighth cranial nerve)
|
|
|
Soundwaves leave the ear through another membrane-covered space in the bony labyrinth called?
|
The Round Windoe
|
|
|
Hearing receptors respond to what aspects of sound?
|
Pitch (tone) and intensity (loudness)
|
|
|
The organ of Corti's receptors in this area detect high pitch sounds?
|
The base of the cochlea
|
|
|
The organ of Corti's receptors in this area detect lower pitched sounds?
|
The top of the cochlea
|
|
|
Loud sounds stimulate more _____ and produce more________, sending more nerve impulses to the brain?
|
Cells, vibrations
|
|
|
What are the 8 steps in hearing?
|
1=Soundwaves enter ear
2=tympanic membrane vibrates 3=ossicles transmit vibrations across the middle ear cavity. 4=stapes transmits the vibrations to the inner ear fluid. 5=vibrations move cilia on hair cells of the organ of Corti in the cochlear duct. 6=movement against tectorial membrane generates nerve impulses. 7=impulses travel to the brain in the 8th cranial nerve. 8=temporal lobe cortex interprets the impulses. |
|
|
Sensory receptors located in the vestibule and semicircular canal of the inner ear are responsible for?
|
Equilibrium
|
|
|
Receptors for the sense of equilibrium are also?
|
ciliated cells
|
|
|
Type of equilibrium with receptors in two small chambers of the vestibule, tilting head, moving in straight line, and in motorvehicle?
|
Static equilibrium (Static means still)
|
|
|
Receptor for equilibrium is called?
|
Macula
|
|
|
The fluid above the cilitated cells contain calcium carbonate crystalls called?
|
Otoliths (oto=ear) (lith=stone)
|
|
|
These receptors function when the body is spinning or moving in different directions?
|
Cristae
|
|
|
Type of equilibrium when the body is moving or spinning in different directions?
|
Dynamic equilibrium
|
|
|
Type of crystals located at the bases of the semi circular canals?
|
Cristae
|
|
|
Nerve fibers from the vestibule and semicircular canals form?
|
The vestibular nerve
|
|
|
This nerve joins the cochlear nerve to form the vestibulocochlear nerve, the 8th cranial nerve?
|
Vestibular nerve
|
|
|
Where are the receptors for equilibrium located?
|
The vestibule and semicircular canals
|
|
|
What are two types of equilibrium?
|
Static and dynamic
|
|
|
The sense of taste is also known as?
|
Gustation
|
|
|
This sense involves receptors in the tongue and two different nerves that carry impulses to the brain?
|
Tast or Gustation
|
|
|
Taste receptors are known as?
|
Taste Buds
|
|
|
Taste Buds are located along the edges of the small depressed areas of the tongue called?
|
Fissures
|
|
|
What are the four different regions of the tongue taste map?
|
Sweet, Salty, Sour, Bitter
|
|
|
Sweet tastes are most acutely experienced in what region of the tongue?
|
Tip of the tongue
|
|
|
Salty tastes are most acute in what region of the tongue?
|
Anterior sides (front)
|
|
|
Sour tastes are most acute in what region of the tongue?
|
Laterally on the tongue
|
|
|
Bitter tastes are detected on what part of the tongue?
|
Posterior part (Back)
|
|
|
Water taste receptors are located where?
|
In the back of the throat
|
|
|
Nerves of taste are include what two cranial nerves?
|
Facial VII (7) and glossopharyngeal IX (9)
|
|
|
The sense of smell is called?
|
Olfaction
|
|
|
The receptors for smell are located in?
|
The epithelium of the superor region of the nasal cavity
|
|
|
Which nerve are the impulses for smell carried by?
|
The olfactory nerve (I)
|
|
|
The olfactory nerve travels to the?
|
Olfactory center in the brains temporal cortex
|
|
|
What are the special senses that respond to chemical stimuli?
|
gustation and olfaction
|
|
|
Type of senses located within specific sense organs, limited to a relatively small area?
|
Special senses
|
|
|
Type of general sense with receptors called tactile corpuscles?
|
Touch
|
|
|
Type of touch receptor found mostly in the dermins of the skin and around the hair line?
|
Tactile corpuscles
|
|
|
Tactile corpuscles are the most dense on what part of the body?
|
Tips of fingers, lips and tongue
|
|
|
Tactile corpuscles are least dense on what part of the body?
|
Back of hand and back of neck
|
|
|
The sensory end organs for pressure are located where?
|
subcutaneous tissues beneath the skin, also near joints, muscles, and other deep tissues
|
|
|
Sensory end organs for pressure are sometimes referred to as?
|
Receptors for deep touch
|
|
|
Temperature nerve endings are?
|
Free nerve endings
|
|
|
Receptors that are not enclosed in capsules, but are merely branchings of nerve fiber?
|
Free nerve endings
|
|
|
Free nerve endings are widely distributed in the?
|
Skin
|
|
|
Name the types of temperature receptors in the skin?
|
Heat and cold receptors
|
|
|
Receptors located in the muscles, tendons, and joints which relay impulses that aid in judging one's position and changes in loaction of body parts in relation to each other are?
|
Proprioceptors
|
|
|
Type of receptors aided in function by the equilibrium receptors of the internal ear?
|
Proprioceptors
|
|
|
Sense of movement is known as?
|
Kinesthesia
|
|
|
Cerebellum is the main coordinating center for this type of general sense receptor?
|
Proprioceptors
|
|
|
Is the most important protective sense?
|
Pain
|
|
|
Pain receptors are widely distributed?
|
Free nerve endings
|
|
|
How many pathways tranmit pain to the CNS?
|
Two
|
|
|
What type of pain does each pathway transmit?
|
One is for acute, sharp pain
The other is for slow chronic pain |
|
|
Drugs that relieve pain?
|
Analgesic drugs
|
|
|
Two main categories of analgesic drugs?
|
Nonnarcotic, Narcotics
|
|
|
This type of analgesic drug acts locally to reduce inflammation and are effective for mile to moderate pain?
|
Nonnarcotic drugs
|
|
|
This type of analgesic drug act on the CNS to alter perception and response to pain?
|
Narcotic drugs
|
|
|
Type of analgesic drug commonly known as NSAIDS non-steroidal antiinflammatory drugs?
|
Nonnarcotic drugs
|
|
|
Examples of nonnarcotic drugs are?
|
Ibuprofin and naproxen
|
|
|
Type of analgesic drug effective for severe pain, usually orally or IM?
|
Narcotic drugs
|
|
|
Morphine is an axample of what type of analgesic drug?
|
Narcotic
|
|
|
Although most commonly used to prevent pain during surgery, can also be used to relieve types of chronic pain?
|
Anasthetics
|
|
|
Natural pain relief associated with the control of pain, Internally released from the brain?
|
Endorphins
|
|
|
Other types of pain relief?
|
Heat and cold therapy, and relaxation or distraction techniques
|
|
|
The phenomenon when sensory receptors are exposed to continuous stimulus, receptors often adjust themselves so that the sensation becomes less acute?
|
Sensory adaptation Ex: putting your hand in hot water, after your hand is acclimated the water feels less hot even if it not
|
|
|
In sensory adaptation these receptors adapt rapidly?
|
warmth, cold, and light pressure
|
|
|
In sensory adaptation these receptors DO NOT adapt?
|
Pain receptors
|
|
|
The vasular pigmented middle tunic of the eyeball?
|
Choroid
|
|
|
A vision receptor that is sensitive to color?
|
Cone
|
|
|
The part of the eye that light rays pass through first as they enter the eye?
|
Cornea
|
|
|
The membrane that lines the eyelids?
|
Conjuctiva
|
|
|
Another name for the blind spot, the region where the optic nerve connects with the eyeball?
|
Optic disk
|
|
|
The innermost coat of the eyeball, the nervous tissue layer that includes the receptors for the sense of vision?
|
Retina
|
|
|
A vision receptor that function well in dim light?
|
Rod
|
|
|
The structure that alters the shape of the lens for accomodation?
|
Ciliary muscle
|
|
|
The watery fluid that fills much of the eyeball in front of the crystalline lens?
|
Aqueous humor
|
|
|
Two sets of muscle fibers that regulate the amount of light entering the eye?
|
Iris
|
|
|
The jelly-like material located behind the crystalline lens that maintains the spherical shape of the eyeball?
|
Vitreous Body
|
|
|
A pigment needed for vision?
|
Rhodopsin
|
|
|
The depressed are in the retina that is the point of the clearest vision?
|
Fovea centralis
|
|
|
The central opening of the iris?
|
Pupil
|
|
|
The fluid contained within the membraneous labyrinth of the inner ear?
|
Endolympth
|
|
|
The bone that ineracts with the tympanic membrane?
|
Malleus
|
|
|
Another name for the projecting part, auricle, of the ear?
|
Pinna
|
|
|
The channel connecting the middle ear cavity with the pharynx?
|
Eustachian tube
|
|
|
The fluid of the inner ear contained within the bony labyrinth and surroinding the membraneous labyrinth?
|
Perilympth
|
|
|
Ciliated receptor cells that detect sound waves?
|
Organ of Corti
|
|
|
The skeleton of the inner ear?
|
Bony labyrinth
|
|
|
The sense of knowing the position of the head in relation to gravity?
|
Static equilibrium
|
|
|
Small crystals that activate maculae?
|
Otoliths
|
|
|
The sense organ involved in dynamic equilibrium?
|
Semicircular canals
|
|
|
The receptor cells involved in dynamic equilibrium?
|
Cristae
|
|
|
Two small chambers containing maculae
|
Vestibule
|
|
|
The branch of the vestibulocochlear nerve that carries hearing impulses?
|
Cochlear nerve
|
|
|
The nerve that carries visual impulses from the retina to the brain?
|
Optic nerve
|
|
|
The branch of the fifth cranial nerve that carries impulses of pain, touch, and temperature from the eye to the brain?
|
Ophthalmic nerve
|
|
|
The largest of the three cranial nerves that carry motor fibers to the eyeball muscles?
|
Oculomotor nerve
|
|
|
The sense of knowing the position of one's body and the relativ positions of different muscles?
|
Proprioception
|
|
|
The sense of body movement?
|
Kinesthesia
|
|
|
Receptors that detect changes in temperature?
|
Free nerve endings
|
|
|
A person who lacks cones in the retina will experience?
|
Color blindness
|
|
|
The Organ of Corti is the receptor for?
|
Hearing
|
|
|
The transparent portion of the sclera?
|
Cornea
|
|
|
The glands that secrete ear wax are called?
|
ceruminous glands
|
|
|
The nerve endings that aid in judging position and changes in location of body parts are the?
|
Proprioceptors
|
|
|
The sense of position is partially governed by equilibrium receptors in the internal ear, including two small chambers in the vestibule and the three?
|
Semicircular canals
|
|
|
How many semicircular canals are there?
|
Three
|
|
|
The tactile corpuscles are the receptors for the sense of?
|
Touch
|
|
|
Any drug that relieves pain is called?
|
Analgesic
|
|
|
When you enter a darkened room, it takes a while for the rods to begin to function. This interval is known as?
|
Dark adaptation
|
|
|
The receptor tunic layer of the eye is the?
|
retina
|
|
|
These eye muscles control the diameter of the pupil?
|
Intrinsic
|
|
|
There are how many extrinsic muscle connected to each eye?
|
Six 6
|
|
|
The iris is this type of eye muscle?
|
Intrinsic
|
|
|
The sense of temperature is what type of sense?
|
General sense
|
|
|
Soundwaves leave the ear through this type of window?
|
Round
|
|
|
This muscle contracts to thicken the lens?
|
Ciliary muscle
|
|
|
What are the parts of the outer ear?
|
pinna, auditory canal (meatus), tympanic membrane (eardrum)
|
|
|
What are the parts of the middle ear?
|
Ossicles- meallus, incus, stapes
Eustachian tube |
|
|
What are the parts of the inner ear?
|
bony labyrinth, membraneous labyrinth, cochlea (organ of Corti), vestibule (2) maculae, Semicircular canals, cilia, vestibulocochlear (auditory) nerve 8th
|
|
|
The receptor that senses static equilibrium?
|
Maculea
|

