![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
25 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What is the initial thyroid precursor? Source? |
Thyroid Diverticulum - arises from floor of primitive pharynx
|
|
|
What happens to the Thyroid Diverticulum? What is it connected to?
|
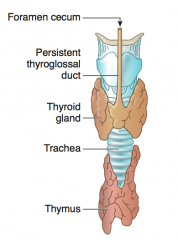
- Descends into neck from origin in floor of primitive pharynx |
|
|
How is the Thyroid initially connected to the Tongue? What happens to this connection?
|
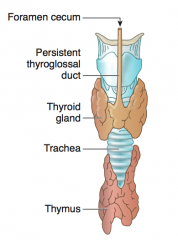
- Thyroid diverticulum is connected to the tongue by the Thyroglossal Duct
- Normally disappears, but may persist as pyramidal lobe of thyroid - Foramen cecum is a normal remnant of the thyroglossal duct |
|
|
What is the normal remnant of the thyroglossal duct (connects tongue to thyroid diverticulum)?
|
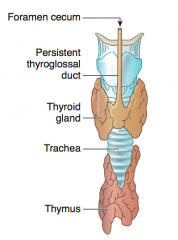
Foramen Cecum |
|
|
What is the most common ectopic thyroid tissue site?
|
Tongue
|
|
|
What diagnosis should you consider in a patient presenting with an anterior midline neck mass that moves with swallowing or protrusion of the tongue?
|
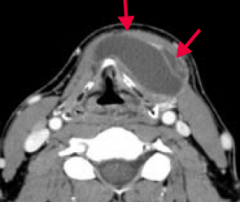
Thyroglossal Duct Cyst |
|
|
What diagnosis should you consider if your patient presents with a mass in their lateral neck?
|
Branchial Cleft Cyst - persistent cervical sinus
|
|
|
What are the adrenal cortex and medulla derived from?
|
- Adrenal cortex: mesoderm |
|
|
What are the layers of the adrenal cortex from external to internal?
|
- Zona Glomerulosa
- Zona Fasiculata - Zona Reticularis |
|
|
What is the primary regulatory control of the Zona Glomerulosa? Secretory product?
|
- Controlled by Renin-Angiotensin
- Secretes Aldosterone |
|
|
What is the primary regulatory control of the Zona Fasiculata? Secretory product?
|
- Controlled by ACTH and CRH |
|
|
What is the primary regulatory control of the Zona Reticularis? Secretory product?
|
- Controlled by ACTH and CRH
- Secretes sex hormones (eg, androgens) |
|
|
What kind of cells are in the Adrenal Medulla?
|
Chromaffin cells
|
|
|
What is the primary regulatory control of the Adrenal Medulla? Secretory product?
|
- Controlled by preganglionic sympathetic fibers |
|
|
What is the most common tumor of the adrenal medulla in adults? What does it characteristically cause?
|
Pheochromocytoma
- Episodic hypertension |
|
|
What is the most common tumor of the adrenal medulla in children? What does it characteristically cause?
|
Neuroblastoma |
|
|
How is the adrenal gland drained on the left side?
|
Left adrenal gland → Left adrenal vein → Left renal vein → IVC
|
|
|
How is the adrenal gland drained on the right side?
|
Right adrenal gland → Right adrenal vein → IVC
|
|
|
What tissue are the anterior and posterior pituitary made from?
|
- Anterior Pituitary: oral ectoderm (Rathke pouch)
- Posterior Pituitary: neuroectoderm |
|
|
What is the other name for the posterior pituitary? What does it secrete?
|
Neurohypophysis
- Vasopressin / ADH - Oxytocin |
|
|
What is the source of ADH and Oxytocin?
|
They are both made in the hypothalamus and shipped to the posterior pituitary via the neurophysins (carrier proteins)
|
|
|
What is the other name for the anterior pituitary? What does it secrete?
|
Adenohypophysis
Think FLAT PiGs eat MuSH: - FSH - LH - ACTH - TSH - Prolactin - GH - MSH (Melanotropin) |
|
|
What kind of cells are there in the anterior pituitary? Functions?
|
- Acidophils: secretes Prolactin and GH
- Basophils: FSH, LH, ACTH, and TSH |
|
|
What are the subunits of the hormones released from the anterior pituitary? Functions?
|
- α subunit: hormone subunit common to TSH, LH, FSH, and hCG
- β subunit: determines hormone specificity |
|
|
Which hormones have the same α subunit?
|
- TSH
- LH - FSH - hCG |

