![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
35 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What is the source of Parathyroid Hormone (PTH)? |
Chief cells of parathyroid gland
|
|
|
What are the effects of PTH?
|
- ↑ Bone resorption of Ca2+ and PO4(3-)
- ↑ Kidney reabsorption of Ca2+ in distal convoluted tubule - ↓ Reabsorption of PO4(3-) in proximal convoluted tubule - ↑ 1,25-(OH)2-D3 (Calcitriol) production by stimulating kidney 1α-hydroxylase |
|
|
How does PTH affect the nephron? Which parts?
|
- ↑ Kidney reabsorption of Ca2+ in distal convoluted tubule
- ↓ Reabsorption of PO4(3-) in proximal convoluted tubule |
|
|
How does PTH affect the bones?
|
↑ Bone resorption of Ca2+ and PO4(3-)
- ↑ Production of macrophage colony-stimulating factor and RANK-L (receptor activator of NF-κB ligand) - RANK-L secreted by osteoblasts and osteocytes binds RANK (receptor) on osteoclasts and their precursors → stimulates osteoclasts and ↑ Ca2+ |
|
|
How does PTH affect the kidney, besides its action on the nephron?
|
↑ 1,25-(OH)2-D3 (Calcitriol) production by stimulating kidney 1α-hydroxylase
|
|
|
Which enzyme produces 1,25-(OH)2-D3 (calcitriol) in the kidney?
|
1α-Hydroxylase
|
|
|
What is the net effect of PTH on Ca2+ and PO4(3-) in the serum and urine?
|
- ↑ Serum Ca2+
- ↓ Urine Ca2+ - ↓ Serum PO4(3-) - ↑ Urine PO4(3-) (Phosphate Trashing Hormone = PTH) |
|
|
What peptide is similar to PTH? Source?
|
PTH-related peptide (PTHrP) |
|
|
How is PTH regulated?
|
- ↓ Serum Ca2+ → ↑ PTH
- ↓ Serum Mg2+ → ↑ PTH - ↓↓ Serum Mg2+ → ↓ PTH |
|
|
What are common causes of ↓ Mg2+?
|
- Diarrhea
- Aminoglycosides - Diuretics - Alcohol abuse |
|
|
What is the effect of PTH on the intestine?
|
- Increases intestinal Ca2+ absorption |
|
|
What are the forms of calcium in the plasma? What percent is in each form?
|
- Ionized (~45%)
- Bound to albumin (~40%) - Bound to anions (~15%) |
|
|
How does pH affect calcium homeostasis in the plasma?
|
↑ in pH → ↑ affinity of albumin (negative charge) to bind Ca2+ |
|
|
What are the sources of Vitamin D? Activation?
|
- D3 from sun exposure in skin
- D2 ingested from plants - Both converted to 25-OH in liver and to 1,25-(OH)2 (active form) in kidney - 24,25-(OH)2-D3 is an inactive form |
|
|
What is the function of Vitamin D (Cholecalciferol)?
|
- ↑ Absorption of dietary Ca2+ and PO4(3-)
- ↑ Bone resorption → ↑ Ca2+ and PO4(3-) |
|
|
How is Vitamin D regulated?
|
- Increased 1,25-(OH)2-D production by: ↑ PTH, ↓ [Ca2+], ↓ [PO4(3-)]
- 1,25-(OH)2 feedback inhibits its own production |
|
|
What are the implications of a deficiency of Vitamin D?
|
- Rickets in kids
- Osteomalacia in adults |
|
|
What can cause a Vitamin D deficiency?
|
- Malabsorption
- ↓ Sunlight - Poor diet - Chronic kidney failure |
|
|
What is the source of Calcitonin?
|
Parafollicular cells (C cells) of Thyroid
|
|
|
What is the function of Calcitonin?
|
↓ Bone resorption of Ca2+ → Tones down Ca2+ levels
|
|
|
What regulates Calcitonin?
|
↑ Serum Ca2+ causes Calcitonin secretion (to tone down Ca2+ levels in serum)
|
|
|
How do PTH and Calcitonin relate?
|
- Calcitonin opposes actions of PTH
- Calcitonin is not important in normal Ca2+ homeostasis |
|
|
Which endocrine hormones signal via "cAMP"?
|
FLAT ChAMP + CGG:
- FSH - LH - ACTH - TSH - CRH - hCG - ADH (V2 receptor) - MSH - PTH - Calcitonin - GHRH - Glucagon |
|
|
Which endocrine hormones signal via "cGMP"?
|
Think vasodilators:
- ANP - NO (EDRF) |
|
|
Which endocrine hormones signal via "IP3"?
|
GOAT HAG:
- GnRH - Oxytocin - ADH (V1 receptor) - TRH - Histamine (H1 receptor) - Angiotensin II - Gastrin |
|
|
Which endocrine hormones signal via "steroid receptors"?
|
VETTT CAP:
- Vitamin D - Estrogen - Testosterone - T3 and T4 - Cortisol - Aldosterone - Progesterone |
|
|
Which endocrine hormones signal via "intrinsic tyrosine kinase"?
|
MAP kinase pathway, think growth factors
- Insulin - IGF-1 - FGF - PDGF - EGF |
|
|
Which endocrine hormones signal via "receptor-associated tyrosine kinase"?
|
JAK/STAT pathway, think acidophiles and cytokines (PIG)
- Prolactin - Immunomodulators: IL-2, IL-6, IL-8, IFN - GH |
|
|
What kind of signaling pathway is important for the MAP kinase pathway?
|
Intrinsic tyrosine kinase
|
|
|
What kind of signaling pathway is important for the JAK?STAT kinase pathway?
|
Receptor-associated tyrosine kinase
|
|
|
What is the signaling pathway of steroid hormones?
|
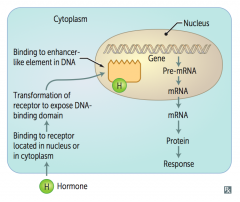
- Steroid hormone binds to receptor located in nucleus or cytoplasm
- Transformation of receptor to expose DNA-binding domain - Enters cell and binds to enhancer-like element in DNA - Affects gene transcription: pre-mRNA → mRNA → protein → response |
|
|
What happens to steroid hormones in the serum? Why?
|
Steroid hormones are lipophilic and therefore must circulate bound to specific binding globulins, which ↑ their solubility
|
|
|
What happens to men with increased sex-hormone binding globulin (SHBG)?
|
Gynecomastia
|
|
|
What happens to women with increased sex-hormone binding globulin (SHBG)?
|
Hirsutism
|
|
|
What can increase the amount of sex-hormone binding globulin (SHBG)?
|
- OCPs
- Pregnancy (Free estrogen levels remain unchanged) |

