![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
36 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What is the first step in production of adrenal steroids?
|
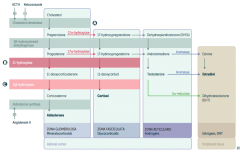
Conversion of Cholesterol → Pregnenolone via Cholesterol Desmolase
|
|
|
How do you produce Aldosterone?
|
1. Cholesterol → Pregnenolone (Cholesterol Desmolase)
2. Pregnenolone → Progesterone (3β-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase) 3. Progesterone → 11-deoxycorticosterone (21-hydroxylase) 4. 11-deoxycorticosterone → Corticosterone (11β-hydroxylase) 5. Corticosterone → Aldosterone (Aldosterone Synthase) |
|
|
What are the molecules on the way from Cholesterol to Aldosterone?
|
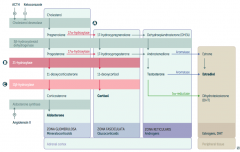
1. Cholesterol
2. Pregnenolone 3. Progesterone 4. 11-deoxycorticosterone 5. Corticosterone 6. Aldosterone |
|
|
What are the enzymes on the way from Cholesterol to Aldosterone?
|
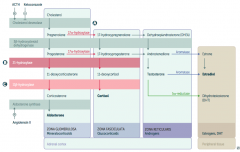
1. Cholesterol Desmolase
2. 3β-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase 3. 21-hydroxylase 4. 11β-hydroxylase 5. Aldosterone Synthase |
|
|
How do you produce Cortisol?
|
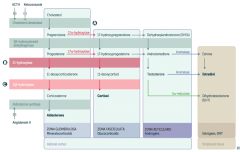
1. Cholesterol → Pregnenolone (Cholesterol Desmolase)
2. Pregnenolone → 17-hydroxypregnenolone (17α-hydroxylase) 3. 17-hydroxypregnenolone → 17-hydroxyprogesterone (3β-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase) 4. 17-hydroxyprogesterone → 11-deoxycortisol (21-hydroxylase) 5. 11-deoxycortisol → Cortisol (11β-hydroxylase) Steps 2 and 3 can be switched around, but need both enzymes |
|
|
What are the molecules on the way from Cholesterol to Cortisol?
|
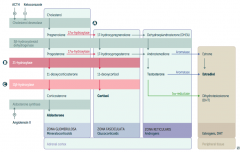
1. Cholesterol
2. Pregnenolone 3. 17-hydroxypregnenolone 4. 17-hydroxyprogesterone 5. 11-deoxycortisol 6. Cortisol OR 3. Progesterone (depending on order of enzymes) |
|
|
What are the enzymes on the way from Cholesterol to Aldosterone?
|
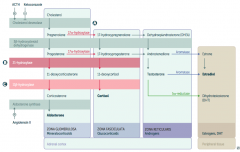
1. Cholesterol desmolase
2. 17α-hydroxylase 3. 3β-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase 4. 21-hydroxylase 5. 11β-hydroxylase (Enzymes 2 and 3 can be done in either order) |
|
|
How do you produce Estradiol?
|
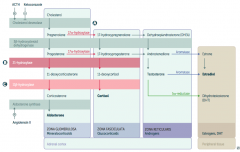
1. Cholesterol → Pregnenolone (Cholesterol Desmolase)
2. Pregnenolone → 17-hydroxypregnenolone (17α-hydroxylase) 3. 17-hydroxypregnenolone → Dehydroepiandrosterone (DHEA) 4. DHEA → Androstenedione 5. Androstenedione → Estrone (Aromatase) 6. Estrone → Estradiol OR 5. Androstenedione → Testosterone 6. Testosterone → Estradiol (Aromatase) |
|
|
What are the actions of Aromatase?
|
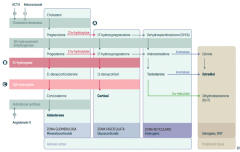
- Androstenedione → Estrone
- Testosterone → Estradiol |
|
|
What are the actions of 5α-Reductase?
|
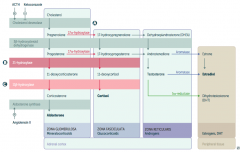
Testosterone → Dihydrotestosterone (DHT)
|
|
|
Which enzyme deficiency would cause:
- Mineralocorticoids: ↑ - Cortisol: ↓ - Sex Hormones: ↓ |
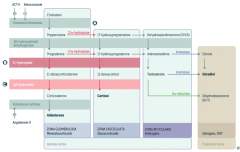
17α-Hydroxylase (A)
Glucocorticoid and Androgen/Estrogen precursors cannot be produced, which shuttles more Pregnenolone / Progesterone substrate through the Aldosterone pathway |
|
|
Which enzyme deficiency would cause:
- Mineralocorticoids: ↓ - Cortisol: ↓ - Sex Hormones: ↑ |
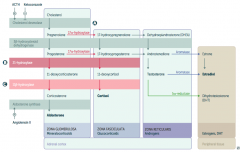
21-Hydroxylase (B)
Progesterone and 17-Hydroxyprogesterone cannot continue towards formation of Aldosterone and Cortisol, so they get shuttled to the sex hormone pathway |
|
|
Which enzyme deficiency would cause:
- Mineralocorticoids: ↓ / ↑ - Cortisol: ↓ - Sex Hormones: ↑ |
11β-Hydroxylase (C)
- ↓ Aldosterone - ↑ 11-deoxycorticosterone (results in ↑ BP) - Cortisol can't be made - Sex hormones increased due to extra substrate |
|
|
What is similar about 17α-hydroxylase, 21-hydroxylase, and 11β-hydroxylase deficiencies?
|
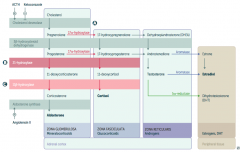
All congenital adrenal enzyme deficiencies → enlargement of both adrenal glands due to ↑ ACTH stimulation (due to ↓ cortisol)
|
|
|
What labs are associated with 17α-hydroxylase deficiency?
|
- ↑ Mineralocorticoids
- ↓ Cortisol - ↓ Sex hormones (↓ DHT) - Hypertension - Hypokalemia |
|
|
How does a patient with 17α-hydroxylase deficiency present?
|
↑ Mineralocorticoids, ↓ Cortisol, and ↓ Sex hormones causes:
- XY: pseudo-hermaphroditism (ambiguous genitalia, undescended testes) - XX: lack secondary sexual development - Both: hypertension, hypokalemia |
|
|
What labs are associated with 21-hydroxylase deficiency?
|
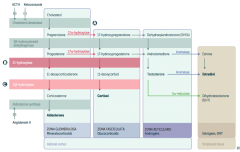
- ↓ Mineralocorticoids
- ↓ Cortisol - ↑ Sex hormones (↑ 17-hydroxy-progesterone) - Hypotension - Hyperkalemia - ↑ Renin activity |
|
|
How does a patient with 21-hydroxylase deficiency present?
|
↓ Mineralocorticoids, ↓ Cortisol, and ↑ Sex Hormones causes:
- Presents in infancy with salt-wasting or in childhood with precocious puberty - XX: virilization - Hypotension, hyperkalemia, ↑ Renin activity |
|
|
What labs are associated with 11β-hydroxylase deficiency?
|
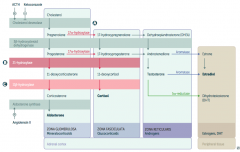
- ↓ Aldosterone
- ↑ 11-deoxycorticosterone (results in ↑ BP) - Hypertension - Low renin - ↓ Cortisol - ↑ Sex hormones |
|
|
How does a patient with 11β-hydroxylase deficiency present?
|
↓ Aldosterone, ↑ 11-deoxycorticosterone, ↓ Cortisol, and ↑ Sex hormones causes:
- XX: virilization - Hypertension |
|
|
What diagnosis should you consider in an XY patient who presents with pseudo-hermaphroditism (ambiguous genitalia, undescended testes)? Other findings?
|
17α-hydroxylase deficiency
- Hypertension - Hypokalemia - ↓ Sex hormones (↓ DHT) - ↓ Cortisol - ↑ Aldosterone |
|
|
What diagnosis should you consider in an XX patient lacking secondary sexual development? Other findings?
|
17α-hydroxylase deficiency
- Hypertension - Hypokalemia - ↓ Sex hormones (↓ DHT) - ↓ Cortisol - ↑ Aldosterone |
|
|
What diagnosis should you consider in an infant presenting with salt wasting? Other findings?
|
21-Hydroxylase deficiency
- Hypotension - Hyperkalemia - ↓ Mineralocorticoids - ↓ Cortisol - ↑ Sex hormones |
|
|
What diagnosis should you consider in an child with precocious puberty? Other findings?
|
21-Hydroxylase deficiency
- Hypotension - Hyperkalemia - ↓ Mineralocorticoids - ↓ Cortisol - ↑ Sex hormones |
|
|
What diagnosis should you consider in an XX patient with virilization? Other findings?
|
21-Hydroxylase deficiency
- Hypotension - Hyperkalemia - ↓ Mineralocorticoids - ↓ Cortisol - ↑ Sex hormones OR 11β-Hydroxylase deficiency - Hypertension (d/t ↑ 11-deoxycorticosterone) - ↓ Aldosterone - ↓ Cortisol |
|
|
What is the source of Cortisol? What does it bind in the blood?
|
- Adrenal Zona Fasciculata
- Binds to corticosteroid-binding globulin |
|
|
What are the effects of Cortisol?
|
Cortisol is a BIG FIB:
- ↑ BP - ↑ Insulin resistance - ↑ Gluconeogenesis, lipolysis, and proteolysis - ↓ Fibroblast activity - ↓ Inflammatory and immune responses - ↓ Bone formation |
|
|
How does cortisol affect BP?
|
↑ BP: upregulates α1-receptors on arterioles → ↑ sensitivity to NE and Epi
|
|
|
How does cortisol affect insulin?
|
↑ Insulin resistance → diabetogenic
|
|
|
How does cortisol affect stored forms of energy?
|
- ↑ Gluconeogenesis
- ↑ Lipolysis - ↑ Proteolysis |
|
|
How does cortisol affect fibroblasts? Effect?
|
↓ Fibroblast activity → causes striae
|
|
|
How does cortisol affect inflammation / immune responses?
|
↓ Inflammatory and Immune responses:
- Inhibits production of leukotrienes and prostaglandins - Inhibits leukocyte adhesion → neutrophilia - Blocks histamine release from mast cells - Reduces eosinophils - Blocks IL-2 production |
|
|
How does cortisol affect bones?
|
↓ Bone formation due to ↓ Osteoblast activity
|
|
|
What infections can be reactivated after administration of exogenous corticosteroids? How?
|
Reactivation of TB and Candidiasis
- Due to blocked IL-2 production |
|
|
How is Cortisol regulated?
|
- CRH (hypothalamus) stimulates ACTH release (pituitary), causing cortisol production in adrenal zona fasciculata
- Excess cortisol ↓ CRH, ACTH, and cortisol secretion |
|
|
What is the effect of chronic stress on cortisol?
|
Chronic stress induces prolonged secretion of Cortisol
|

