![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
14 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What are amines? |
Compounds derived from ammonia, with one or more H replaced by a carbon chain of ring. |
|
|
How are amines classified? |
Primary, secondary, tertiary. Based on number of R groups on nitrogen. |
|
|
How to name amines: |

Either x-amino... Or ethyl/methyl/propyl...amine Or N substituted see photo |
|
|
How can amines act as bases? |
The N accepts a proton, forming a dative covalent bond. |
|
|
How to form amines and conditions: |
Haloalkane+ NH3➡️ ammonium salt Ammonium salt +NaOH➡️ amine+ NaCl +H2O Ethanol is used as solvent to prevent haloalkanes reacting with water. Excess NH3 is used to prevent further substitution to secondary and tertiary amines. |
|
|
Forming aromatic amines and conditions: |

1Sn/concentrated HCl 2excess NaOH |
|
|
What types of amino acids are there? |
α,β,γ. α is where the R group is bonded to the first C after the COOH. β is the 2nd and γ is the third. |
|
|
What groups do amino acids have? |
Amine and carboxylic acid. |
|
|
What is a chiral centre? |
An atom that holds attachments that can be arranged as 2 non-superimposable mirror images. |
|
|
What is another name for optical isomers? |
Enantiomers |
|
|
Define condensation polymerisation: |
A long chain produced through joining of monomers with loss of a small molecule. |
|
|
What are polyesters formed from? |
Either one monomer with both COOH and OH groups, or two monomers- one with 2 carboxyl groups and one with two alcohol groups. |
|
|
What is an amide linkage? |
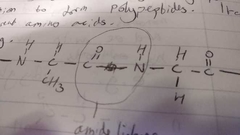
|
|
|
How can polymers be hydrolysed? |
By hot aqueous acid or hot aqueous acid. |

