![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
172 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
1/3 |
.33 |
|
|
|
1/5 |
.2 |
|
|
|
1/6 |
.166 |
|
|
|
1/7 |
.14 |
|
|
|
1/8 |
.125 |
|
|
|
1/9 |
.11 |
|
|
|
2/3 |
.66 |
|
|

|
R |
|
|
|
Giga |
10^9 |
|
|
|
Mega |
10^6 |
|
|
|
Kilo |
10^3 |
|
|
|
Centi |
10^-2 |
|
|
|
Mili |
10^-3 |
|
|
|
Convert Kg to g |
.001 |
|
|

Speed of sound formula |
|
|
|
|
Acceleration formula |
A=🔺C/t
🔺C =C2-C1 answer usually in m/s |
|
|
|
Frequency time formula |

F=1/t |
|
|
|
Mass Reactance formula |

|
|
|
|
Log of 1 |
0 |
|
|
|
Log of 2 |
.3 |
|
|
|
Log of 3 |
.48 |
|
|
|
Log of 7 |
.85 |
|
|
|
Angular velocity |

|
|
|
|
Force formula |
F=ma |
|
|
|
Frequency formula |
F=1/t |
|
|
|
Hooks law |
F=-kx |
|
|
|
Mass Reactance formula |
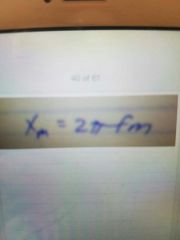
|
|
|
|
Momentum |
M=m•c |
|
|
|
Pressure equation |

|
|
|
|
Rectifier average full wave |

A signifies amplitude Peak |
|
|
Rectifier average half wave |
🐮 |
|
|
|
Speed formula |
S=d/t |
|
|
|
Speed of sound formula |

|
|
|
|
Wavelength formula |

The speed of sound divided by frequency |
|
|
|
Hecto |
10^3 |
|
|
|
Deci |
10^-1 |
|
|
|
Micro |
10^-6 |
|
|
|
Nano |
10^-9 |
|
|
|
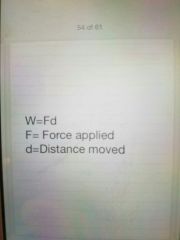
Work formula |
|
|
|
|
Pendulum formula |

It's f not t |
Assume it's the natural frequency |
|
|
Radius mean formula |
Look this up |
|
|
|
Amplitude Root mean Square |
.7(A peak) - A is amplitude Peak |
|
|
|
Speed formula |

|
|
|
|
Newton's to dynes |

|
|
|
|
Pascals to dynes & newtons |

|
|
|
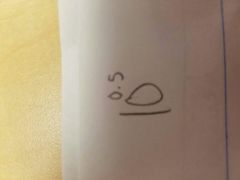
|
3 |
|
|
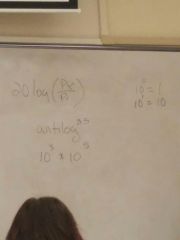
Antilog trick |
C sdh |
|
|
|
10^.5 |
3 |
|
|
|
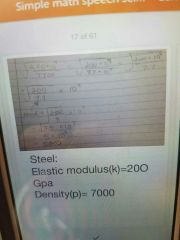
Elasticity (property of matter) |
Ratio of stress to strain |
|
|
|
Youngs model |
Long skinny objects |
|
|
|
Bulk modulus |
More bulky shapeless objects |
|
|
|
The speed of sound depends on |
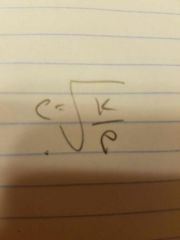
Elasticity of medium and density of medium |
|
|
|
Transverse wave |
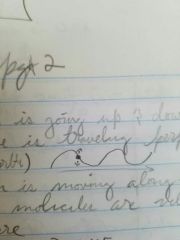
Medium is going up and down but the wave is traveling perpendicular |
|
|
|
Longitudinal wave |
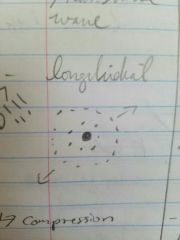
Medium is moving along the way if all the molecules are vibrating along the sphere |
|
|
|
compression |
What all the atoms are pressed together |
|
|
|
Refraction |
Where all the atoms are not compressed |
|
|
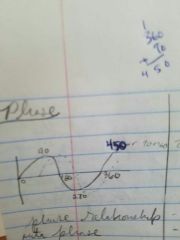
Phase |
At t=0 where is the wave? How much of it is out of phase Standard form starts at zero |
|
|
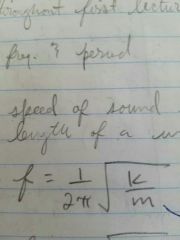
Mass spring |
? Assume it's a natural frequency of vibration |
|
|

Pendulum look this up |
Figure out with g nlr... Assume it's the natural frequency of vibration |
|
|
|
Phase relationship |
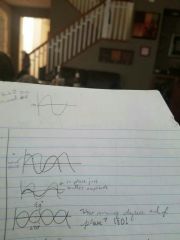
- a different sound can still be in phase when it has a different amplitude - wheres one wave phase in relation to another |
|
|
|
Amplitude |
- height of the sine wave - insinuates magnitude |
|
|
|
Peak amplitude |

What is the amplitude at its peak |
|
|
|
Peak to Peak amplitude |
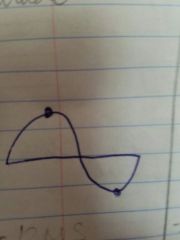
Peak to lowest Peak - x 2 because they are mirror images of each other |
|
|
|
Root mean Square amplitude |
Arms=0.7 (peak) |
|
|
|
Friction |
Is a force that opposes the motion of two objects in contact - friction results in the transfer of kinetic energy to thermal energy |
|
|
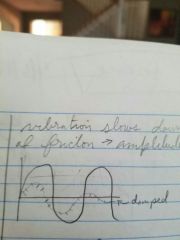
Damping |
Vibration slows down and stops because of friction... Amplitude gets less and less |
|
|
|
Forced vibration |
Not natural frequency an outside force is driving it to its desired frequency |
|
|
|
Resonance |
Driving a vibration that matches its natural frequency so it amplifies the vibration |
|
|
|
Impedance= Z |
Overall opposition to motion or flow of energy in a system - measured in omhs (♎) |
|
|
|
Resistance= R |
energy loss |
|
|
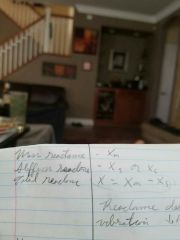
Reactance =X |
Energy storage, temporarily impedes to store then gives it back |
|
|
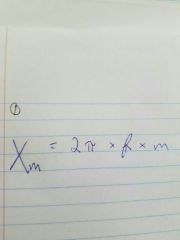
Mass Reactance |
- f is the frequency of the driving force - m is the mass of the system - driving frequency NOT!!!!! the natural frequency |
|
|
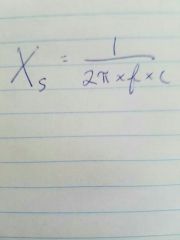
Stiffness reactance |
F is the frequency of the driving force - she is the compliance |
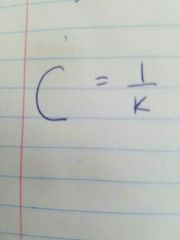
|
|
|
Total impedance |
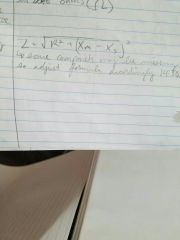
|
|
|
|
Resonance |
Definition at 20:00 on lecture 2a |
|
|
|
Nominal scale of measurement |
Quality or type no quantity (same/diff) categories |
|
|
|
Ordinal |
Categorize a shin and quantification ( greater or lesser) - cannot perform any other mathematical operations on the scale - uses for comparison , ranking but not |
|
|
|
Interval scale |
Quantification with equal intervals - numerical comparison for voting - we need to make sure that the intervals are equidistant |
|
|
|
Ratio scale |
Can be exponential or log scale - a reference Baseline - the rest of the scale multiple of the base |
|
|
|
Laws of exponents |

|
|
|
|
Scientific notation |

|
|
|
|
Antilog |
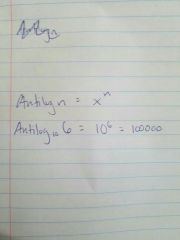
|
|
|
|
Logs |
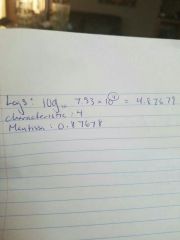
|
|
|
|
Power |
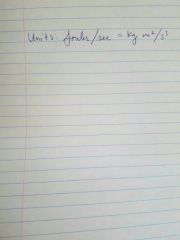
Work done or energy transferred per unit time |
|
|
|
Absolute power of sound |
Is very low approximately 10^-8 W |
|
|
|
Relative power |
Comparing the power of one sound to another reference sound - important because we anchor everything to human hearing we use a threshold of what people can barely hear at 50% of the time |
|
|
|
Level of power |
Px/Pr |
|
|
|
Intensity definition |
Intensity=power÷area - power per unit area -units: w/m^2 |
|
|
|
Level of intensity |
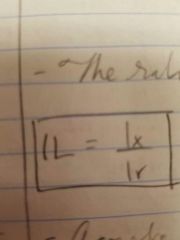
The ratio of one sound to another |
|
|
|
Power vs intensity |
Acoustic power of a source remains constant no matter where the listener sits ( the tree falls in the forest and it makes a sound) - what intensity drops off as I/r^2 with distance even as total power stays constant |
|
|
|
Intensity equation formula |
# dB= 10×log (Ix/Ir) |
|
|
|
What is the reference intensity level for human hearing |
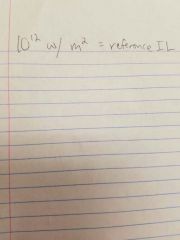
Ir=10^-12 w/m^2 |
|
|
|
Every time you double intensity it increases the decibel by what number |
3 |
|
|
|
If you have the intensity what happens to the decibel number |
It decreases by 3 |
|
|
|
What if we increase the intensity tenfold what is the decibel level |
The decibel level gets increased by 10 |
|
|
|
What if the intensity is less than the standard intensity |
Can you get a negative decimal number |
|
|
|
Sound pressure definition |

Force per unit area
|
|
|
|
Level of pressure |
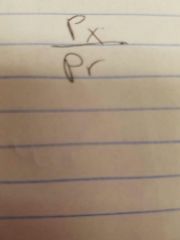
The ratio of one side to another |
|
|
|
Sound pressure level (SPL) reference |
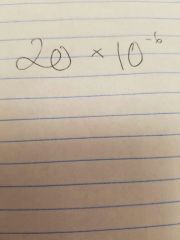
|
|
|
|
SPL decibel formula |
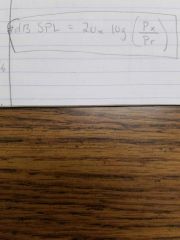
|
|
|

|
Intensity and pressure are proportional to each other because of the square |
|
|
|
dB are a unit less scale |
We just convert these numbers to a manageable scale so we can wrap our heads up them |
|
|
|
When you double the pressure what happens to the decibel number |
It increases by 6 decibels |
|
|
|
What happens to the decibel number when you cut the pressure in half |
You subtract 6 decibel |
|
|
|
What happens to the decibel number when you increase the pressure by a factor of 10 |
You increase the decibel by 20 |
|
|
|
If you double the pressure you quadruple its intensity |
This is due to intensity being proportional to pressure squared |
|
|
|
The intensity level and SPL FOR THE SAME SOUND... |
Are expressed by the same number of decibels |
|
|
|
G |
|
|
|
Combining sound level when sound levels are unequal |

So you have 4 different with different intensity levels Ex: 60 50 30 and 20 dBIL - first you need to find the intensity level for each dBIL - then look at all of the intensity levels and pick the highest one, this number will be the closest to the answer |
The total decibel intensity level can't be lower than the highest IL |
|
|
10^.2 |
1.5 |
|
|
|
10^.6 |
4 |
|
|
|
Mass on a spring |
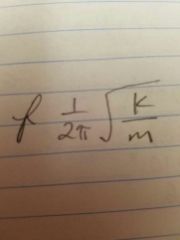
|
|
|
|
Spring constant |
Elasticity |
|
|
|
Circumference formula |
C=2×3.14×r |
|
|
|
Simple wave |
A single sine wave One frequency 1 amplitude |
|
|
|
Complex wave |
Two or more sine waves |
|
|
|
Superposition |
Adding up different sine waves to make a complex wave |
|
|
|
Complex wave analysis |
Waking up the sine wave into small pieces |
|
|
|
Complex wave synthesis |
Putting sine waves together to make a complex wave |
|
|
|
Waveform synthesis |
Using superposition to make a complex |
|
|
|
Fourier series |
The series of sine waves added together from a specific complex wave |
|
|
|
Noise cancellation |
When two sounds are 180 degrees out of phase with each other they cancel each other out |
|
|
|
Periodic waves |
Complex waves that repeat itself |
|
|
|
A periodic waves |
Complex waves that don't repeat themselves |
|
|
|
Complex periodic waves |
A periodic wave that often has a harmonic relation to the lowest frequency component |
|
|
|
Harmonic relation |
Whole number multiples of the lowest frequency component |
|
|
|
Fundamental frequency |
A multiple of the high frequencies the greatest common denominator and usually the lowest frequency component of a complex periodic wave |
|
|
|
Harmonics |
Any frequency that is an integer multiple of the fundamental |
|
|
|
Octave |
A doubling of frequency |
|
|
|
Overtones |
Any of the harmonic other than the fundamental frequency , the first overtone is the second harmonic |
|
|
|
Partials |
Any of the frequency components of a complex wave weather a harmonic or not |
|
|
|
Human speech is usually what kind wave |
Is quasi-periodic not perfectly periodic |
|
|
|
Complex aperiodic waves |
- they have no repetitions - no harmonics, also known as noise - call voicemail, whispering |
|
|
|
White noise |
All of the frequencies with equal amplitude |
|
|
|
Waveform |

The time of the domain and the amplitude is the range |
|
|
|
Spectrum |

The frequency is the domain and the amplitude is the range |
|
|
|
Amplitude Spectrum |

Also known as a line Spectrum |
|
|
|
Continuous Spectrum |
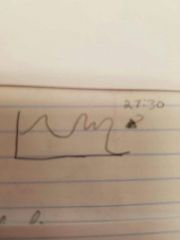
There are too many frequencies so one line would look like a blob so instead they use a curve |
|
|
|
Spectral envelope |
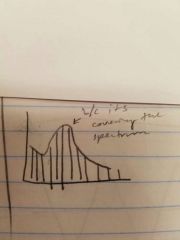
Uses the curve + frequency lines |
|
|
|
Sawtooth wave |
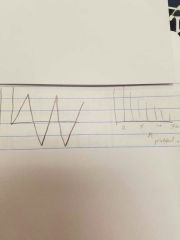
Odd and even harmonics - notice that the amplitude decreases with number of the harmonics - slope of spectral envelope is -6 decibels per octave |
|
|
|
Square wave |

Odd harmonics( even harmonics are missing) - notice that the amplitude decreases with the number of harmonics |
|
|
|
White noise |
A periodic complex wave - all frequencies have equal amplitude - seasons of component frequencies are random |
|
|
|
Signal to noise ratio in decibels SNR in decibels (S/N) |
This concerns background noise Equation-dB S/N=10log (S/N) -If S >N dB S/N is positive -If S<N dB S/N is negative |
|
|
|
Scalar |
Just a number |
|
|
|
Vector |
Both a number and a direction: pressure, velocity, force |
|
|
|
Newton's 1st law (inertia) |
An object will just keep moving in space at a constant speed or stay stationary. ( unless something slows it down and stops it ex: friction,gravity or wind) |
Imagine an object in space |
|
|
Newton's Second Law F=m×a |
If the object moved or changed direction and no longer inert, it is due to a force that is directly related to the direction the force was applied |
|
|
|
Newton's 3rd law |
For every action there is always opposed reaction - so how do we move objects but they don't move us?-think of mass and surface area being incorporated to an acceleration |
Remember F=m×a |
|
|
Natural frequency of vibration |
-the frequency the object prefers to vibrate at - Not a driven frequency!!!! |
|
|
|
Laws of Logs |

|
|
|
|
Single pulse |

|
|
|
|
Pulse train |

|
|
|
|
Micro 10^-6 |
|
|
|
1 radian is approximately equivalent to how many degrees |
60 |
|
|
|
Gravity constant |
9.8 |
|
|
|
What kind of wave is a sound wave |
Longitudinal |
|
|
|
Wave length |
Physical distance in space occupied by one period of a wave |
|
|
|
Frequency |
Cycles per second per unit time |
|
|
|
Period |
Time needed to complete one cycle |
|
|
|

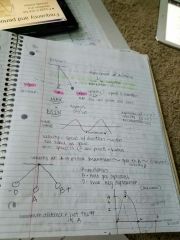
-Displacement: taking it out of the equilibrium - velocity: is zero at b and d -acceleration: movement and direction -Gravity and string: always bringing it back to equilibrium (restoring force)
|
|
|
|
Reactance at low and high frequencies with impedance |

|
|
|
|
Mass and spring concepts |
-Ossolation-simple harmonic , just vibration -Hooks law -F=ma -Has inertia ( no such thing as inertial force!!!) '-Displacement =X and is greatest at the ends -velocity -elasticity=k Acceleration is lowest when |
|
|
|
Characteristic |
The power of 10 |
|
|
|
Mantissa |
Log of the coefficient |
|
|

|
VA e t |
|
|
|
Hdje |
|
|
|
Diff between triangle and square |
Amplitudes decrease at different rates |
|
|
|
Know names of the theroy on last lecture joos Steven's lieberman carol fowler duplex |
Ggghgggt |
|
|
|
Start time on burst and stop at |
Voicing |
|
|
|
Bel equation |
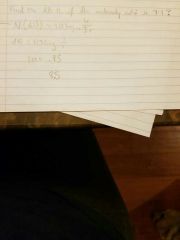
|
|
|
|
Flip equation when we want something that's under tell denominator |
G |
|
|
|
10^-5 |
About 3 |
|

