![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
159 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Basic Concepts
What is a hydrocarbon? |
An organic compound consisting of carbon and hydrogen only |
|
|
Basic Concepts
Why can carbon atoms form so many compounds? |
- It can form bonds with other carbon atoms to make chains and rings - Can form single, double or triple bonds to other carbons - Can bond with atoms of other elements - O,H,N,P,Cl,Br,Fl, I etc |
|
|
Basic Concepts
How many electrons in the outer shell of carbon? Thus how many bonds can it make? |
4 |
|
|
Basic Concepts
Define saturated hydrocarbon |
Hydrocarbons with single bonds only |
|
|
Basic Concepts
Define unsaturated hydrocarbon |
Hydrocarbons with one or more double bonds |
|
|
Basic Concepts
Define aliphatic hydrocarbon |
A hydrocarbon with carbon atoms joined together in straight or branched chains |
|
|
Basic Concepts
Define alicyclic hydrocarbon |
A hydrocarbon with carbon atoms arranged in a ring structure |
|
|
Basic Concepts
Define functional group |
The part of an organic molecule responsible for its chemical reactions |
|
|
Basic Concepts
Define homologous series |
A series of organic compounds with the same functional group but with each successive member differing by CH2 |
|
|
Basic Concepts
Define Alkane |
The homologous series with the general formula CnH2n+2 |
|
|
Basic Concepts
What is nomenclature? |
A system of naming compounds |
|
|
Basic Concepts
What is an alkyl group? |
An alkane with a hydrogen atom removed, eg. CH2, C2H5 |
|
|
Basic Concepts
Draw 2,3,3-trimethylpentane |
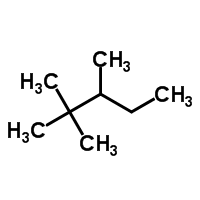
|
|
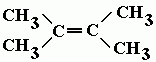
Basic Concepts
Name |
2,3,-dimethylbut-2-ene |
|
|
Basic Concepts
Draw 2,3,4-trimethylhexane |
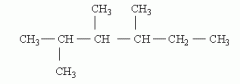
|
|
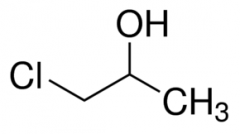
Basic Concepts
Name |
2-chloropropanol |
|
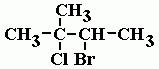
Basic Concepts
Name |
3-bromo, 2-chloro, 2-methylbutane |
|
|
Basic Concepts
What is empirical formula? |
The simplest whole-number ratio of atoms of each element present in a compound |
|
|
Basic Concepts
A hydrocarbon contains 85.63% C and 14.37% H, Calculate the empirical formula |
85.63/12 = 7.14 14.37/1 = 14.37 1:2 CH2 |
|
|
Basic Concepts
What is molecular formula? |
The actual number of atoms of each element in a molecule |
|
|
Basic Concepts
A compound has an Empirical formula of CH2O and relative molecular mass of 60.
Find the molecular formula. |
CH2O = (12+1+1+16) = (30) 60/30 = 2 C2H4O2 |
|
|
Basic Concepts
What is general formula? |
The simplest algebraic formula for a member of its homologous series |
|
|
Basic Concepts
What are the general formulas you need to know? |
Alkanes - CnH2n+2 Alkenes - CnH2n Alcohols - CnH2+1OH
|
|
|
Basic Concepts
What is displayed formula? |
The formula that shows the relative positioning of all the atoms in a molecule and the bonds between them H H-C-H H |
|
|
Basic Concepts
What is structural formula? |
Formula that shows the minimal detail for the arrangement of atoms in a molecule. CH3CH2CH3 |
|
|
Basic Concepts
What is skeletal formula?
|
A simplified organic formula, with hydrogen atoms removed from alkyl chains, leaving just a carbon skeleton with associated functional groups |
|
|
Isomerism
What are structural isomers? give the three ways in which they can occur |
Structural isomers are molecules with the same molecular formula but different structural arrangement of atoms
1) Differing functional group position 2) Different functional groups entirely (Ex aldehyde/ketone) 3) Branching!
|
|
|
Isomerism What are stereoisomers? |
Compounds with the same structural formula, but with a different arrangement of the atoms in space |
|
|
Isomerism What criteria is required for E/Z isomerism ? |
- C=C bond must be present - Each carbon must be attached to two different groups |
|
|
Isomerism Define E/Z isomerism |
A type of stereoisomerism in which different groups attached to each carbon of a C=C double bond may be arranged differently in space due to restricted rotation of the C=C bond. |
|
|
Isomerism
Define Cis- Trans isomerism |
A special type of E/Z isomerism in which there is a non-hydrogen group and a hydrogen group on each C of a C=C double bond. Cis/Z = H atoms on the same side Trans/E = Atoms on different sides |
|
|
Organic Reagents
In what two ways can bonds be broken ?
|
Heterolytic or Homolytic fission |
|
|
Organic Reagents
Define homolytic fission
|
The breaking of a covalent bond with one of the bonded electrons going to each atom, forming two radicals. |
|
|
Organic Reagents
Define heterolytic fission |
The breaking of a covalent bond with both of the bonded electrons going to one of the atoms forming a cation and an anion |
|
|
Organic Reagents
What is a radical? |
A species with an unpaired electron |
|
|
Organic Reagents
Define nucleophile |
An atom or group of atoms that is attracted to an electron deficient centre or atom where it donates a pair of electrons to form a covalent bond |
|
|
Organic Reagents
Define electrophile |
An atom or group of atoms that is attracted to an electron rich centre or atom where it accepts a pair of electrons to form a covalent bond. |
|
|
Organic Reagents
Define addition reaction |
A reaction in which a reactant is added to an unsaturated molecule to make a saturated molecule
2 Reactants ---> 1 Product |
|
|
Organic Reagents
Draw the reaction between Ethene + Br 2 |

|
|
|
Organic Reagents
Define substitution reaction |
A reaction in which an atom or group of atoms is replaced with a different atom or group of atoms
2 Reactants ----> 2 Products
|
|
|
Organic Reagents
Draw the reaction between Bromoethane and OH- |

|
|
|
Organic Reagents
What is an elimination reaction? |
The removal of a molecule from a saturated molecule to make an unsaturated molecule |
|
|
Organic Reagents
Draw the elimination of ethanol. Include the conditions. |

|
|
|
Organic Reagents
What does % yeild measure? |
The proportion of products formed in a reaction. |
|
|
FUEL N' POOP
What is crude oil? |
A fossil fuel made from naturally decaying plants and animals - a mixture of different hydrocarbons (mostly unbranched) |
|
|
FUEL N' POOP
Why do we like crude oil? |
Some of its components are valuable and are used in petrol, kerosene and heating and lubricating oils |
|
|
FUEL N' POOP
What is fractional distillation ? |
The separation of components in a liquid mixture into fractions which differ in boiling point (and hence chemical composition by means of distillation, typically using a fractionating column |
|
|
FUEL N'POOP How can you obtain a pure hydrocarbon? |
1) Separate the complex mixture of hydrocarbons into fractions - each consisting of a mixture of hydrocarbons with similar boiling points
2) Further distillation of a crude oil fraction can be used to obtain a pure hydrocarbon |
|
|
FUEL N' POOP
Describe the process of fractional distillation |
1) Fractional distillation takes place in a fractionating column 2) First, the crude oil is vaporised by heating 3) It is then passed into the fractionating column 4) The column is hotter at the bottom than at the top and the gases pass up the column through a series of bubble caps 5) Eventually, as they rise, the gases reach a temperature that is lower than their boiling point so the vapour condenses to a liquid 6) The liquid fractions are then tapped off in storage containers |
|
|
FUEL N' POOP
Draw and annotate a fractionating column |
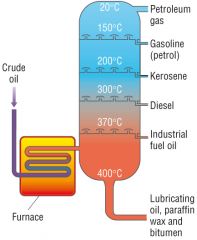
|
|
|
FUEL N' POOP
What can you do with the fractions obtained from crude oil? |
- Used as fuels - Can be further processed to make petrochemicals (chemicals from natural gas and oil) - Can be distilled further to form pure liquids in other fractionating columns, operating over a narrower range of temperatures - Bitumen can be used in road surfacing or roof coverings |
|
|
FUEL N' POOP
Describe the bonding between alkane molecules |
Weak intermolecular forces of attraction between molecules -> Van Der Waals. |
|
|
FUEL N' POOP
Describe the effect of chain length on the boiling points of alkanes |
As the chain length increases, boiling point increases. This is because the intermolecular forces between the molecules get stronger. A longer chained alkane has more points of contact between the molecules = more VDW forces between the molecules. It takes more energy and thus a higher temperature to separate the molecules |
|
|
FUEL N'POOP
Describe the effect of branching on the boiling points of alkanes. |
Branched isomers have lower boiling points because there are fewer points of contact = fewer VDWs. Also, branched molecules cannot get as close to eachother as unbranched ones, thus decreasing intermolecular forces. Therefore, less energy is required to separate the molecule. |
|
|
FUEL N' POOP
Write the equation for the combustion of methane |
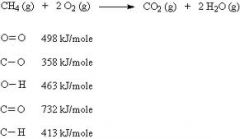
|
|
|
FUEL N' POOP
What is the function of propane and butane? |
They are easily liquefied and are commonly known as liquefied petroleum gas or LPG. They are used as fuels in barbecues, patio heaters, and portable cooking appliances such as those used in camping. |
|
|
FUEL N' POOP
Write the equation for the complete combustion of Octane. |
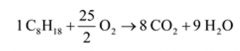
|
|
|
FUEL N' POOP
Why will octane undergo incomplete combustion? |
Most cars have a limited supply of oxygen |
|
|
FUEL N' POOP
Write the equation for the incomplete combustion of octane |
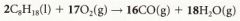
|
|
|
FUEL N' POOP
Describe the properties of CO, how it is formed, its effects and why it is produced |
- Colourless, odourless gas - poisonous - at home, it can be formed from faulty domestic heating systems, blocked fuels/chimneys or inadequate ventilation - prevents haemoglobin in red blood cells from binding with oxygen and the body's tissues become starved of oxygen - CO is produced when any fossil fuel is burned with an insufficient supply of Oxygen |
|
|
FUEL N' POOP
What is cracking? |
The breaking down of long-chained saturated hydrocarbons to form a mixture of shorter-chained alkanes and alkenes. |
|
|
FUEL N' POOP
Why would you need to make short chained alkenes from longer chained ones? |
After the fractional distillation of crude oil there is a surplus of long-chained hydrocarbons. You want short-chained hydrocarbons for use of fuels and for polymer production |
|
|
FUEL N' POOP
What are the conditions for Cracking? |
Zeolite catalyst 450 degrees
|
|
|
FUEL N' POOP Define catalyst |
A substance that increases the rate of a chemical reaction without being used up |
|
|
FUEL N' POOP
Draw one possible cracking reaction of dodecane, C12H26 |
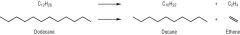
|
|
|
FUEL N' POOP
How can you produce branched alkanes from unbranched alkanes? |
ISOMERISATION |
|
|
FUEL N' POOP
Draw the isomerisation of pentane |
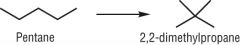
|
|
|
FUEL N' POOP
How can you produce alicyclic/aromatic hydrocarbons from aliphatic hydrocarbons |
REFORMING |
|
|
FUEL N' POOP
Draw the reforming process for pentane |
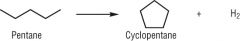
|
|
|
FUEL N' POOP
Draw the reforming process for heptane |
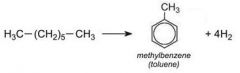
|
|
|
FUEL N' POOP
What does an octane rating close to 100 indicate? |
That the fuel burns efficiently |
|
|
FUEL N' POOP
Why are branched alkanes used in fuels for car engines? |
Branched and cyclic alkanes promote more efficient combustion than straight chained alkanes |
|
|
FUEL N' POOP
What is the hydrogen produced during reforming used for? |
Other chemical processes such as ammonia production and margarine production |
|
|
FUEL N' POOP
How have we come to rely on the chemicals produced by crude oil? |
Over 90% of crude oil produced is used as a fuel source . Petrochemicals (plastics, pharmaceuticals, cosmetics, dyes and inks) are made indirectly from crude oil
|
|
|
FUEL N' POOP
What does a good fuel need? |
- to be readily available - to be easily transported - to be inexpensive
|
|
|
FUEL N' POOP
What are the disadvantages of burning hydrocarbons? |
It produced pollutants: - CO - a toxic gas formed by incomplete combustion in the internal combustion engine - CO2 - Contributes to global warming via the greenhouse effect - Nitrogen Oxides - Contributes to acid rain and destruction of forests - Sulfur Dioxide - Contributes to acid rain |
|
|
FUEL N' POOP
Explain Global warming |
Burning fuels to generate energy releases CO2 and other greenhouse gases into the atmosphere. These greenhouse gases prevent heat from escaping the atmosphere, and hence lead to increased temperatures on Earth |
|
|
FUEL N' POOP
What is the effect of increased temperatures on Earth? |
A change in climate - heavier rain, more frequent, violent storms, polar ice caps could melt, sea levels rise, flooding etc |
|
|
FUEL N' POOP
What is a biofuel? |
A fuel that is derived from living material such as plants, or from animal waste |
|
|
FUEL N' POOP
Give two examples of crops specifically grown for energy use |
Sugar cane Oilseed Rape |
|
|
POOP How is ethanol utilised + made? |
Ethanol can be made by fermenting sugar and other carbohydrates. It burns efficiently in plentiful supply of oxygen to give CO2 and H2O. Ethanol can be blended with petroleum causing fuel to burn more efficiently. This also reduces harmful exhaust emissions. |
|
|
FUEL N' POOP
What is bioethanol? |
A fuel oil derived from natural sources such as plants - the most popular source of biodeisel is Rapeseed. It is normally blended with normal diesel.
|
|
|
ALKANES AND SUBSTITUTION REACTIONS
What are the conditions for the halogenation of alkanes? |
Alkanes react with halogens in the presence of UV LIGHT or a temp of 300 degrees |
|
|
ALKANES AND SUBSTITUTION REACTIONS
Write the reaction between methane and chlorine |
CH4 + Cl2 ---> CH3Cl +HCl |
|
|
ALKANES AND SUBSTITUTION REACTIONS
What kind of reaction is this? Define this reaction :3 |
It is a RADICAL SUBSTITUTION REACTION - a type of substitution reaction in which a radical replaces a different atom or group of atoms. |
|
|
ALKANES AND SUBSTITUTION REACTIONS
Explain what occurs in radical substitution |
- Covalent bonds are broken by homolytic fission to form radicals with an unpaired electron - A hydrogen atom in the alkane is substituted by a halogen atom |
|
|
ALKANES AND SUBSTITUTION REACTIONS
What is a reaction mechanism? |
A sequence of steps showing the path taken by electrons in a reaction |
|
|
ALKANES AND SUBSTITUTION REACTIONS
What are the three stages of the chlorination of alkanes? |
Initiation Propagation Termination |
|
|
ALKANES AND SUBSTITUTION REACTIONS
Outline the full mechanism of chlorination of alkanes |
Step 1: Initiation Cl-Cl ---> Cl • + Cl • The Cl-Cl bond in a chlorine molecule is broken by homolytic fission, forming two chlorine radicals. UV Radiation provides energy for this fission Step 2: Propagation 1) CH4 + Cl • ----> • CH3 + HCl 2) • CH3 + Cl2 -----> CH3Cl + Cl • 1) Chlorine radicals attack methane : a single C-H bond is broken by homolytic fission, forming a methyl radical, • CH3. HCl is also formed. 2) The • CH3 radical reacts with Cl2 forming CH3Cl and another chlorine radical. This can then be used for the first propagation step. Step 3: Termination Two radicals combine to form a molecule - • Cl + • Cl ---> Cl2 - • Cl + • CH3 ---> CH3Cl - • CH3 + • CH3 ---> C2H6 The termination stage removes radicals, stopping the reaction,.
|
|
|
ALKANES AND SUBSTITUTION REACTIONS
Describe the speed at which propagation occurs and what type of reaction it is |
Propagation reactions are rapid: the reactions continue until no reactants remain. It is a CHAIN reaction: Although a Cl • is used in the first step, another is generated in the second step. This can now react with another CH4 molecule. This continues until the Cl2 is used up or the termination stage removes all the radicals. |
|
|
ALKANES AND SUBSTITUTION REACTIONS
What further reactions can occur?
|
Chloromethane may react with further Chlorine radicals until all Hydrogens have been replaced. This results in a mixture of CH3Cl CH2Cl2 CHCl3 CCl4 |
|
|
Alkenes
What are alkenes? |
Unsaturated hydrocarbons with at least one C=C double bond |
|
|
Alkenes
What is the general formula for an aliphatic alkene? |
CnH2n |
|
|
Alkenes
What reactions do they typically take part in? |
Addition
|
|
|
Alkenes
How is ethene obtained? |
From the catalytic breakdown of crude oil fractions |
|
|
Alkenes
What are alkenes used to make? |
Polymers for the plastic industry |
|
|
Alkenes
Explain and draw the formation of a Pi bond. |
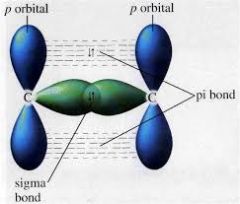
A sigma bond is formed directly between two carbon atoms between two carbon atoms by the overlap of orbitals. Each carbon atom contributes one electron to the electron pair in the sigma bond. A pi bond is formed above and below the plane of carbon atoms by sideways overlap of p orbitals. Each carbon atoms contributes one electron from a p orbital to the electron pair in the pi bond.
|
|
|
Alkenes
Explain how fixed rotation occurs |
The pi bond fixes the carbon atoms in position, at either end of the double bond |
|
|
Alkenes
In alkanes, each carbon involved in the double bond.... |
Uses 3 e-s in the formation of 3 sigma bonds Uses 1 e- in the formation of 1 pi bond. |
|
|
Alkenes
Explain the shape of an alkane molecule |
3 regions of electron density surround each carbon atom in the double bond Parts of electrons repel eachother as far apart as possible to minimise repulsions This gives a trigonal planar shape, with 120 degree bond angles Ethene is a FLAT PLANAR MOLECULE - all atoms are in the same plane |
|
|
Alkenes
Define pi bond |
The reactive part of a double bond formed above and bellow the plane of the bonded atoms by sideways overlap of p orbitals |
|
|
Alkenes
Describe cyclic alkenes |
-Cyclic alkenes have a closed ring o carbon atoms containing one or more double bonds -Most common is cyclohexene -They do not have the same general formula as aliphatic alkenes |
|
|
Alkenes (reactions)
Why are alkenes more reactive than alkanes? |
Because of the C=C double bond |
|
|
Alkenes (reactions)
Which is stronger? A C-C or C=C bond? |
C=C is stronger. |
|
|
Alkenes (reactions)
What does the following information tell you? Average bond enthalpy C-C +347 kJmol-1 C=C +612 kJmol-1 |
A double bond is stronger than a single bond but a pi bond is weaker than a sigma bond (612-347 = 265)
|
|
|
Alkenes (reactions)
Describe and draw the typical addition reactions of alkenes |
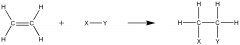
|
|
|
Alkenes (reactions)
Draw and explain the addition of hydrogen to ethene (with conditions pls) (hydrogenation/reduction) |
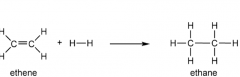
Nickel catalyst 150°
|
|
|
Alkenes (reactions)
Draw and explain the addition of a halogen to ethene |
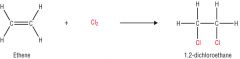
Alkenes react rapidly with halogens such as chlorine, bromine and iodine at room temperature
|
|
|
Alkenes (reactions)
Draw and explain the bromination of alkenes
|

When bromine is added to a sample containing an alkene, the colour changes from orange to colourless. This is used as a test for unsaturation.
|
|
|
Alkenes (reactions)
Draw and explain the addition of hydrogen halides to an alkene |

Hydrogen halides include HCl, HBr and HI. They are gases at room temperature and are bubbled into liquid alkanes. |
|
|
Alkenes (reactions)
Draw and explain the addition of steam to alkenes |
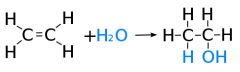
h3PO4 Steam and the gaseous alkene are heated to a high temperature and pressure in the presence of a phosphoric acid catalyst. This is called HYDRATION of an alkene and is a method of preparing alcohols used widely in industry. |
|
|
Alkenes (reactions)
Explain what happens when unsymmetric alkenes undergo addition reactions (use propene + HBr as an example) |
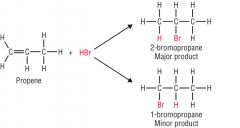
A mixture of organic products is formed.
|
|
|
Alkenes (reactions)
Draw and explain the mechanism for the addition of Br2 to ethene |
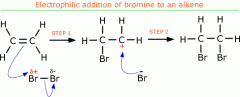
1) When bromine approaches an alkene, the electrons in the pi bond repel the electrons in the Br-Br bond, inducing a dipole: Br∂+ - Br∂- It is now slightly polar. 2) The electron pair in the pi bond is attracted to the partially +ve Br which causes the double bond to break 3) A new bond forms between one C and the Br 4) The Br-Br bond breaks by heterolytic fission - one bromine gets the electron pair 5) A Br- ion and carbocation is formed 6) The +vely charged carbocation is unstable and quickly reacts with the bromide ion to form the final organic product
|
|
|
Alkenes (reactions)
What are Terpenes? |
Alkenes built from whole numbers of Isoprene (C5H8) molecules. The Isoprene molecules can either linked together headd to tail forming chains or can be formed into rings. |
|
|
Alkenes (reactions)
Draw and explain the reaction of C10H16 (Myrcene) with excess hydrogen |

Nickel catalyst |
|
|
Alkenes (reactions)
Draw a full flowchart, with conditions, for alkenes. |
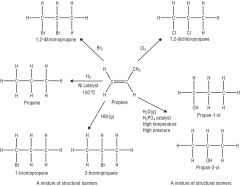
|
|
|
ALKENES AND INDUSTRY
How are unsaturated compounds used in industry? |
They are important starting materials for many common industrial processes - i.e. ethene is polymerised to make plastics |
|
|
ALKENES AND INDUSTRY
What are the 3 things ethene is used to make? |
- 1,2-dichloroethene ClCH2CH2Cl ---> DEGREASER AND PAINT REMOVER -Ethane-1,2- diol HOCH2CH2OH ---> WIDELY USED AS AN ANTIFREEZE AND IS A KEY MATERIAL FOR MAKING POLYESTERS SUCH AS TERYLENE FOR CLOTHING -Ethanoic acid CH3COOH ----> VINEGAR + USED IN ORGANIC SYNTHESIS |
|
|
ALKENES AND INDUSTRY
Describe how margarine is made |
From animal/vegetale fats, mixed with skimmed milk and salt |
|
|
ALKENES AND INDUSTRY
What is the difference between margarines with a high content of mono- or poly-unsaturated fats and butter and other margarines? |
They are said to be healthier and are often made from sunflower or olive oil |
|
|
ALKENES AND INDUSTRY
What are vegetable oils? |
Liquids containing long hydrocarbon chains, often with many double bonds - they are polyunsaturated |
|
|
ALKENES AND INDUSTRY
Why must it be hardened? |
So that is can be spread on bread without soaking into it |
|
|
ALKENES AND INDUSTRY
Describe the process that hardens oils |
HYDROGENATION - Hydrogenation adds hydrogen molecules across double bonds in an addition reaction - It alters the individual molecule in such a way that the oil partially solidifies and hardens - By adding H2 molecules across different numbers of the many double bonds, we can make margarines with different amounts of hardness - thus affecting the spreadibility - Partial hydrogenation of unsaturated fats can transform some CIS double into into TRANS - which are now thought to be bad for health |
|
|
POLYMERS
What are polymers? |
Long-chain molecules built upon monomer units |
|
|
POLYMERS
What is a monomer? |
A small molecule that combines with many other monomers to form a polymer |
|
|
POLYMERS
What is addition polymerisation? |
The process in which unsaturated alkene molecules (monomers) add on to a growing polymer chain one at a time to form a long saturated molecular chain |
|
|
POLYMERS
How many different types of monomer is used to make an addition polymer? |
One. |
|
|
POLYMERS
Define addition polymer |
A long molecular chain formed by repeated addition reactions of many unsaturated alkene molecules (monomers) |
|
|
POLYMERS
Draw the addition polymerisation of ethene |
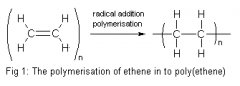
|
|
|
POLYMERS
What are the two industrial processes that involved addition polymerisation? |
- Radical polymerisation - Ziegler-Natta process |
|
|
POLYMERS
Describe radical polymerisation |
- Requires 200 degrees and a high pressure - Reaction leads to branching of the polymer chain and the production of polymer mixtures - Poly(phenylethene), poly(styrene) and branched poly(ethene) is produced in this way |
|
|
POLYMERS
Describe the Ziegler-Natta process |
- Requires TiCl3 + Al(C2H5)2Cl catalysts at 60 degrees - Alkene is passed over the catalyst - conversion is low and any unreacted alkene is recycled and passed over the catalyst repeatedly -Most common method for the manufacture of non-branched poly(ethene)
|
|
|
POLYMERS
What is the general equation for addition polymerisation? |
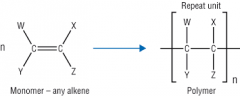
|
|
|
POLYMERS
What is a repeat unit? |
A specific arrangement of atoms that occurs in the structure over and over again. |
|
|
POLYMERS
Draw the general formation of poly(ethene)/polythene |
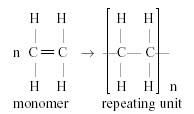
|
|
|
POLYMERS
Draw the general formation of poly(propene)/polypropylene |
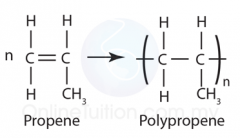
|
|
|
POLYMERS
Draw the general formation of polystyrene (poly(phenylethene)) |
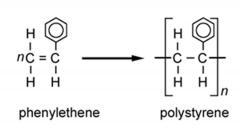
|
|
|
138 POLYMERS
Draw the general formation of PVC (poly(chloroethene)) |
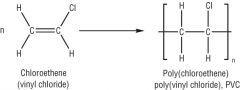
|
|
|
POLYMERS
Draw the general formation of Teflon/PTFE/Poly(tetrafluroethene) |
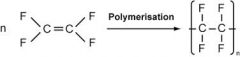
|
|
|
POLYMERS
What is Orlon? |
A polymer used as a synthetic fibre. It is resistant to sunlight and atmospheric gases, making it suitable for outdoor use as a tent materials and sunshades. Repeat unit = H H C C H CN |
|
|
POLYMERS AND GREEN CHEMISTRY POOOP
What are the uses of polystyrene/ poly(phenylethene)? |
- Plastic used in foam packaging - Insulation - Food retail - Model making |
|
|
POLYMERS AND GREEN CHEMISTRY POOOP
What are the uses of poly(ethene)/polyethene? |
-Most widely used plastic - Grocery bags, shampoo bottles, toys etc |
|
|
=POLYMERS AND GREEN CHEMISTRY POOOP
What are the uses of poly(propene)/polyproylene? |
-Food packaging -Containtors that are dishwasher safe - Fibre in carpets - Used in making synthetic ropes - Used as a material for certain lab equipment as it is resistant to chemical attack |
|
|
POLYMERS AND GREEN CHEMISTRY POOOP
What physical properties make polymers good for a broad range of uses |
- They do not react with the substance inside them - Fairly durable - Do not break down easily
|
|
|
POLYMERS AND GREEN CHEMISTRY POOOP
What is a disadvantage to these properties? |
It makes them hard to dispose of |
|
|
POLYMERS AND GREEN CHEMISTRY POOOP
What is environmentally bad about plastics? |
Much of the plastic waste we create includes additives such as colourants, stabilisers and pasticisers which often contain poisonous heavy metal ions. They are non-biodegradable |
|
|
POLYMERS AND GREEN CHEMISTRY POOOP
What are the two stages to recycling? |
Sorting- polymer indentification codes are used Reclamation - Once sorted, polymers are processed. The polymers are manually chopped into small flakes and washed to remove impurities. This is now sent to manufacturing companies where the pellets are melted and remoulded/ |
|
|
POLYMERS AND GREEN CHEMISTRY POOOP
What happens to a) PET bottles b) HDDE c) LDPE d) LDPE |
a) Converted to carpets, clothing and new bottles b) Reused to make hard plastic materials - boxes, bins, water butts c) Used to make plastic refuse sacks |
|
|
POLYMERS AND GREEN CHEMISTRY POOOP
Describe how polymers can be used as a fuel source |
Burning polymers under controlled conditions produces heat energy which can be harnessed to make electricity. |
|
|
POLYMERS AND GREEN CHEMISTRY POOOP
Describe what feedstock recycling is |
Polymers are converted into synthesis gas - a mixture of H2 + CO
Hydrocarbons and synthesis gas is used as a chemical feedstock for concersion into useful products or as a fuel at oil refineries. |
|
|
POLYMERS AND GREEN CHEMISTRY POOOP
Why is recycling poly(vinyl chloride) PVC problematic? |
It has a high chlorine content. |
|
|
POLYMERS AND GREEN CHEMISTRY POOOP
WWhat is done instead of recycline PVC? What are the disadvantages? |
It is incinerated - it prevents PVC going into landfill sites - but the combustion of PVC produces toxic fumes and may cause corrosion to the PVC plant. Acidic HCl fumes are released. Hence, PVC incinerators are equipped with pollution control apparatus to minimikse thr elease of these harmful emissions |
|
|
POLYMERS AND GREEN CHEMISTRY POOOP
Describe the development of the first commercial PVC recycling plant |
- PVC is seperated from other scrap by dissolving in solvents - High quality PVC is then recovered by precipitaion from the solvent - The solvent is recovered and then used again -This process recycles the PVC coatings of electrical wiring and other PVC waste |
|
|
POLYMERS AND GREEN CHEMISTRY POOOP
What are bioplastics? |
They are biodegradable or compostable plastics derived from renewable raw materials such as starch, cellulose, maize and lactic acid. |
|
|
POLYMERS AND GREEN CHEMISTRY POOOP
How are bioplastics manufactured? |
By non-hazardous processes |
|
|
POLYMERS AND GREEN CHEMISTRY POOOP
What happens when bioplastics are disposed of? |
They degrade naturally into the environment to CO2 + H2O
|
|
|
POLYMERS AND GREEN CHEMISTRY POOOP
How will a biodegradable plastic break down? |
As a result of bacterial activity |
|
|
POLYMERS AND GREEN CHEMISTRY POOOP
What is the criteria for compostable plastics? |
They must break down by a biological process during composting to CO2, H2O, inorganic compounds and biomass |
|
|
POLYMERS AND GREEN CHEMISTRY POOOP
What is currently being used to replace non-degradable plastics? |
- BIOPLASTICS + CORNSTARCH CUTLERY - used to replace oil-derived poly(ethene). Supermarket bags are made out of plant starch and are also used as bin liners that can be compotsted with the waste inside it. - COMPOSTABLE DISPOSABLE TABLEWARE from sugar cane fibre is use to replace polystyrene - although they are less resistant to breakdown, they can withstand temperatures up to 100 degrees. - Poly(lactic) acid is used for cold drink cups - biodegradable in 180 days. |

