![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
19 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Amines
What are amines? |
Ammonia derivatives. |
|
|
Amines
What is a primary amine, a secondary and tertiary amine? |
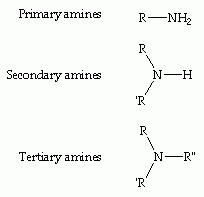
Primary - One H atom replaced
Secondary - Two H atoms replaced
Tertiary - Three H atoms replaced |
|
|
Amines
What are the functions of
a) Amphetamine
b) Phenylephrine
c) Adrenaline |
a) A complex amine used to treat daytime drowsiness and chronic fatigue syndrome
b) Commonly userd as a decongestant. Found in many cold and flu remedies with paracetemol
c) The 'fight or flight' amine that helps the body to deal with sudden stress. |
|
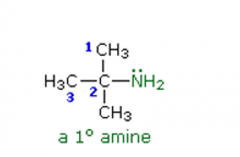
Amines
Name the following amine: |
2-methyl-2-propanamine |
|
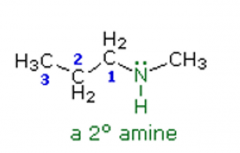
Amines
Name the following amine: |
N-methylpropanamine |
|
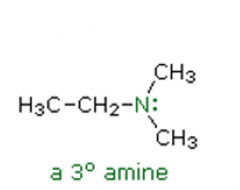
Amines
Name the following amine: |
N,N-dimethylethanamine |
|
|
Amines
What is a base? |
A proton acceptor. |
|
|
Amines
What makes amines weak bases? |
The lone pair of electrons on the Nitrogen atom.
The fact that it can accept a H+ |
|
|
Amines
What happens when an amine accepts a proton? |
A dative covalent bond forms between thelone pair of electrons of the Nitrogen atom and the proton |
|
|
Amines
Draw the reaction between methylamine and a proton. |
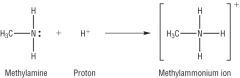
|
|
|
Amines
Base + Acid = ? |
Salt |
|
|
Amines
Draw the reaction of phenylamine and nitric acid |
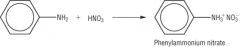
|
|
|
Amines
How are aliphatic amines prepared? |
By warming halogenoalkanes gently with anexcess of ammonia, with ethanol as a solvent. |
|
|
Amines
Write the reaction for the formation of propylamine and the subsequent reactionsthat follows. Describe what happens in each reaction. |
1) CH3CH2CH2Cl + NH3 -> CH3CH2CH2NH2 + HCl
Ammonia reacts with 1-chloropropane by nucleophilic substitution.
Ammonia has a lone pair of electrons that attacks the partially positive carbon atom in the C-Cl bond.
2) NH3 + HCl -> NH4+Cl-
Further ammonia then reacts with the HCl formed.
3) CH3CH2CH2Cl + CH3CH2CH2NH2 -> (CH3CH2CH2)2NH + HCl
The product of the first reaction - propylamine, also has a lone pair of electrons which attacks another molecule of 1-chloropropane, causing further stubstitution.
THE EXCESS AMMONIA IS USED TO MINIMISE THE FURTHER SUBSTITUTION.
|
|
|
Amines
How do you prepare an aromatic amine? |
By reducing nitrobenzen or other nitroarenes using a mixture of tin and concentrated hydrochloric acd, heated under reflux, followed by neutralisation of the excess HCl. |
|
|
Amines
Draw the reduction of nitrobenzene. |
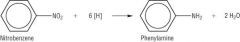
|
|
|
Amines
What are the two steps in the industrial preperation of dyestuffs? |
1) Diazotisation
2) Coupling reactions |
|
|
Amines
Describe the first step in the preperation of azo dyes. |
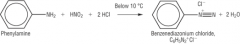
Diazotisation - forms the diazoniun ion When a mixture of phenylamine and nitrous acid is kept below 10°C, a diazonium salt is formed.
1) HNO2 (nitrous acid) is generated by the following reaction:
NaNO2 + HCl -> HNO2 + NaCl
2) The cold nitrous acid then reacts with an aromatic amine to form a diazonium salt. |
|
|
Amines
Describe the second step in the preperation of azo dyes. |
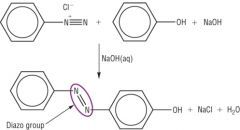
Coupling
A coupling reaction occurs when the diazonium salt, benzenediazonium chloride, is reacted with a phenol/aromatic compound underalkaline conditions.
In the reaction, two benzene rings are linked through an azo functional group -N=N-
The prodct is a brightly coloured compound used as an azo dye. |

