![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
30 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What are the benefits of digital x-rays?
|
1. Allows faster image access, open image just by searching pt's neame, can send image to colleague, etc
2. No chemical processing. Once you capture the image you are done 3. Dose reduction 4. Digital image processing - zoom in, enhance contrast, brightness 5. Image database - archive all your patients images 6. Professional image - Pt senses that you are up to date, latest technology 7. Dental marketing 8. Novelty |
|
|
What is data stored as in digital imaging?
|
Bits
BInary digiT 1's & 0's |
|
|
What is the term for when the continuous signal gets sampled then reconstructed using discrete units?
|
Analogue to Digital Conversion
|
|
|
What are 4 main components that affect digital image quality?
|
1. The imaging system (image capture) - sensors, phosphor plates (PSP)
2. Display system (the monitor that you are using to display image) 3. Viewing condition - want subdued light. When light is on it is harder to see what's going on. Look at images with dim light conditions 4. Viewer - The more experience you have looking at radiographs, the better you are at interpreting what you see. |
|
|
What are the image quality system components that contribute to the image capture?
|
1. Resolution (spatial resolution)
2. Contrast (contrast-resolution) 3. Bit Depth 4. Signal to Noise Ratio (SNR) 5. Field of View |
|
|
What is the difference between Spatial resolution & Contrast resolution?
|
Spatial resolution - Resolving power of any image-forming device
Contrast resolution - ability to distinguish between smallest differences in the intensity of an image. (usually useal for medical imaging) |
|
|
What is used to test resolution?
|

Line pairs per mm
The higher line pairs, the better your sensors are. We can see big black lines, (they are metal lines running from top to bottom) and they converge as you go down. In conventional film we get 20 lines per mm, but when we convert to digital, not all systems are abole to get that resolution. Digital - zoom in, can still distinguish line pairs at 20. At upper portion of graph, we can see lines much easier, but notice, the blackets you can get is at top, as you go down it becomes fuzzy. Once we get to 20 lines per mm, contrast drops significantly, but can still get resolution (can still see lines) |
|
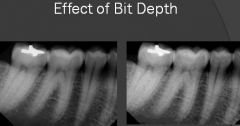
Which image has better bit depth?
|
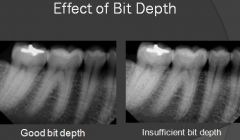
Left image
|
|
|
What is a measure used to quantify how much signal has been corrupted by noise?
|
Signal to Noise Ratio (SNR)
|
|
|
In radiography, the more x-ray photons you have, the better signal to noise ratio. How do you get more photons?
|
1. Increase exposure time, increase mA (current)
2. The higher radiation dose the better image quality |
|
|
What effect does noise have on a radiograph?
|
When you have high noise you cannot tell where root ends or where the PDL space or lamina dura is
|
|
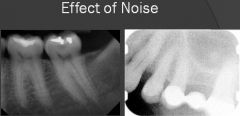
Can short exposure noisy images be useful?
|
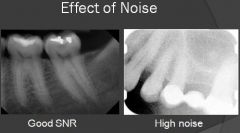
If you are trying to locate impacted teeth or root fragments, you don't need full exposure
|
|
|
What are two ways of acquiring digital dental imaging?
|
1. Sensors or Solid-State detectors (CCD & CMOS)
2. Receptors or Plates (PSP) |
|
|
What is the purpose of a scintillator?
|
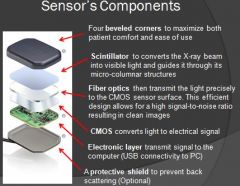
Takes x-ray photon and converts them to light photons
|
|
|
What do the fiber optics do for the sensor?
|
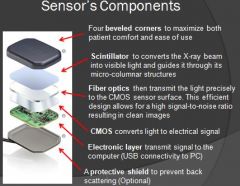
Guide photons to the image detector component
|
|
|
What is the purpose of CMOS on a sensor?
|
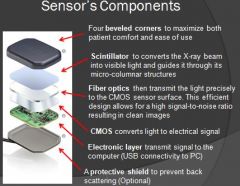
Converts light signal to electrical signal, so computer can process that information
|
|
|
What is the purpose of the electronic layer on a sensor?
|
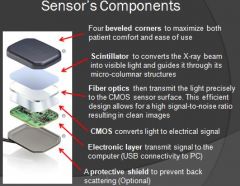
Takes electrical signal and passes the signal to computer through either wireless or usb connector
|
|
|
What is the purpose of a protective shield on a sensor?
|
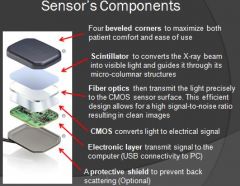
Absorb scattered radiation
|
|
|
What type of sensor resembles film, has a thin profile, base layer just like with film and coated with phosphor layer, and there is a protective coating to reduce film scratching
|

Photostimulable Phosphor (PSP) Plates
|
|
What is the sequence of the PSP cycle?
|
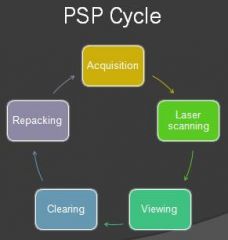
see above
|
|
|
What PSP scanner do we currently use at CWRU?
|
ScanX
Old model - after you put sensor on top, it comes out from bottom, then need to expose light. |
|
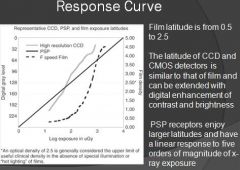
What will the image look like at the foot of the response curve?
|
Underexposed, image will appear white
|
|
|
What are the pros and cons of CCD/CMOS vs PSP?
|
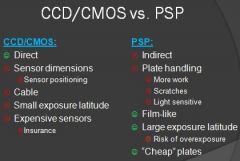
|
|
|
What are the most useful tools for digital image processing?
|
Contrast, Brightness, Gamma adjustment
Zoom Rulers |
|
|
What acts as a graphical representation of the tonal distribution in a digital image?
|
Histogram
It plots the number of pixels for each tonal value |
|
|
What are some toys used for image enhancement?
|
LUT inversion
Color conversion Embossing |
|

What will happen to the line pairs when you sharpen the image with a filter?
|
You lose resolution
|
|
|
What are some things to take into consideration when selecting a Display system?
|
Monitor resolution
Color vs Grayscale - can go color or grayscale. Color is cheaper. Grayscal for professionals, better gray scale value, but no more intraoral image views. Bit depth Contrast Screen size |
|
|
What is the best image display or viewing system?
|
OLED - 1 mm thickness, best contrast, whitest white, and pitch black
|
|
|
What are the best image storage formats?
|
TIFF (compressed/uncompressed)
PNG |

