![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
31 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What are the advantages of panoramic radiography?
|
1. Broad anatomic coverage
2. Low radiation dose 3. Convenience of examination 4. Can be used on patients who cannot open their mouth 5. The time required to take the radiographs is 3-4 minutes in comparison to 15-20 minutes for a FMRS 6. The panoramic radiograph is an excellent patient education tool and is readily accepted by patients |
|
|
What are the disadvantages of panoramic radiography?
|
1. The resultant image does not resolve the fine anatomical structures (caries, periodontal disease)
2. There is also some magnification, geometric distortion and overlapped images of teeth in the molar region, however the angular relationships are accurate 3. The cost of a panoramic x-ray machine is 2-4 times the cost of an intraoral machine |
|
|
What part of a panoramic x-ray machine allows only a thin part of the x-ray beam to pass, that is used to capture the image?
|
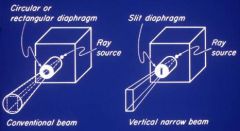
Slit diaphragm in panoramic x-rays
|
|
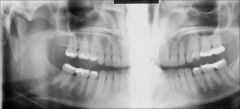
What type of radiograph is this?
|
Panorex
|
|
|
In a panoramic radiograph, how does the film movement compare to the beam movement and source movement?
|
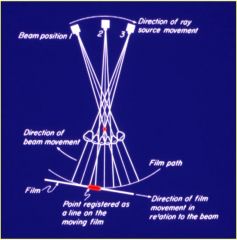
Source and Film movement are in the same direction. Beam movement is opposite direction.
|
|
|
How is the zone of focus, in a panoramic machine, affected by the rotational center?
|
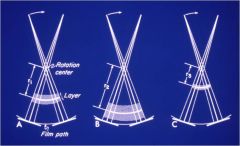
You can have different rotational centers
A) there is a layer with a width and length B) The layer is moved closer to the film, and as you move it closer to the film, you get more width C) If you move the layer closer to the rotational center its length and width get shorter |
|
|
What happens as you get closer to the rotational center?
|
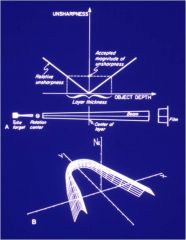
As you come closer to the rotational center this produces the maximal sharpness and image.
|
|
|
As you move away from the rotational center what happens?
|
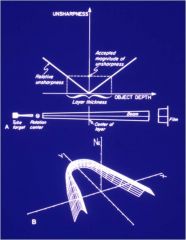
You get the focal trough. It is in the shape of the arch that we want to obtain. (when we select the shape of the jaw on the machine this determines the best path of trajectory)
|
|
|
What is the magnification level that we should take into account, when measuring panoramic radiographs?
|
1.3x
|
|
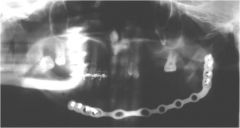
What is the bright J bend on the Patient's Right?
|
Ghost of the metal plate on the patient's left side.
GHOSTS 1. Shape is similar to original object 2. It will be magnified (Larger than actual counter part) 3. Found on opposite side and slightly raised |
|
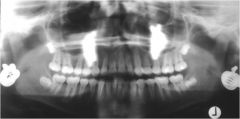
What is the source of these 4 artifacts?
|
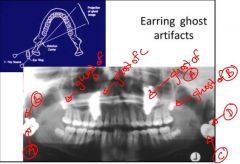
Earrings
|
|
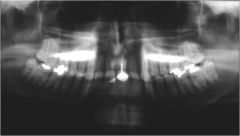
What are these Artifacts?
|
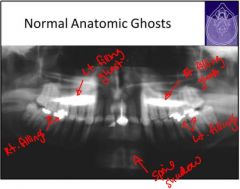
Left Filling Ghost
Right Filling Ghost Shadow of Spine - spine is normally found on R & L sides, but the ghost is centered and blurred. Ghost of ramus - increased radiopactiy Ghost of palate - slightly higher up, blurred on opposite side |
|
|
What happens if you position the patient incorrectly when taking a panoramic x-ray?
|
Jaw slightly anterior - anterior teeth become smaller (posterior teeth look normal)
Jaw slightly posterior - Anterior teeth larger, posterior teeth smaller Rotate patient left or right - One side is larger, other side is smaller |
|
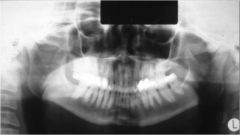
What is wrong with this radiograph?
|
Anteriorly Positioned Patient
Anterior teeth are small Posterior teeth are much larger |
|
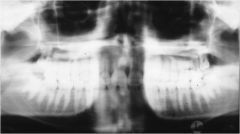
What is wrong with this image?
|
Posteriorly positioned patient
Anterior teeth are very big Posterior teeth are smaller |
|
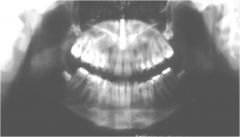
What is wrong with this image?
|
Excessive Downward Chin Tip
(Large Smile) |
|
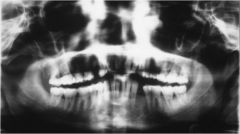
What is wrong with this image?
|
Excessive Upward Chin Tip
(FROWN) |
|
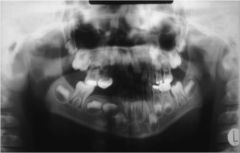
What is wrong with this image?
|
Rotation and lateral displacement of patient midline
|
|
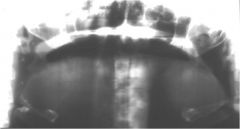
What ghosts do you see?
|
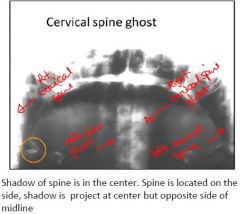
Right and left Cervical Spine Ghosts
|
|

What causes this type of image?
|
Slumped Spine Artifact
If patient is slumped, you will get more shadow of spine in anterior midline region of film therefore difficult to diagnose anterior region. |
|
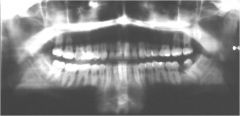
What type of artifact is seen here?
|
Oral Airspace Artifact
Recall in clinic exercise that it was important to ask the patient to touch their tongue to the roof of their mouth. If not, the airway space superimposes on roots of anterior and posterior maxillary space. Very dark in max. |
|
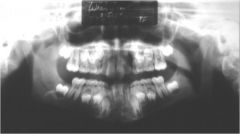
What is this problem that can mimic disease?
|
Assymetric Airspace
|
|
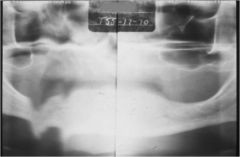
What type of artifact is this?
|
Motion artifact - Vertical
Unit hit patient while scanning, which produces distortion. |
|
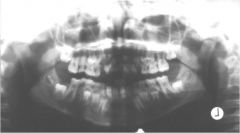
What type of artifact is this?
|
Motion Artifact Horizontal
You can get duplication or deletion of structure. If the patient was scanned and they move in the same direction of the scan then the structures will be scanned twice (duplication) If the patient is standing still and then suddenly moved away while scanning, this will produce some missing structures. |
|
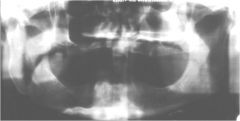
What artifact is occuring here?
|
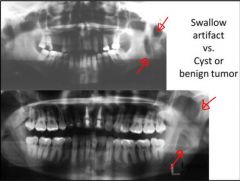
Patient motion artifact: Swallow
Swallow during scan causing the hyoid bone to move up. this causes distortion at the botton of the film. A swallow artifact could look like a cyst |
|
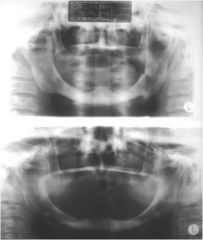
What type of artifact is this?
|
Motion simulating fracture
The patient moved during the scan, causing a discontinuity at the inferior border of the mandible. Looks like a fracture, but it is just an artifact. |
|
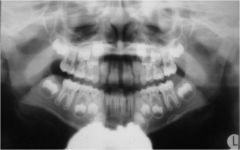
What type of artifact is this?
|
Apron artifact
X-ray source comes from lower, sometimes captures the apron. |
|
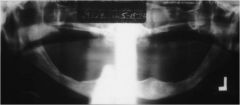
What type of artifact is this?
|
Apron artifact
Sometimes you get the shadow on center |
|
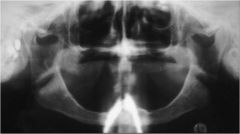
What kind of artifact is this?
|
Necklace artifact
Also Hearing aid |
|
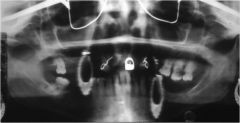
What type of artifact is found here?
|
Removable appliances
earrings (ghost in center) eyeglasses |
|
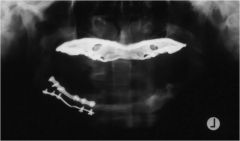
What is making this Lepidoptera Panormicus?
|
Metal Denture in Maxilla
Panoramic butterfly - Lepidoptera means scale wing |

