![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
27 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What x-ray technique aims the central beam at an imaginary line splitting the plane between the central axis of the tooth and the receptor?
|
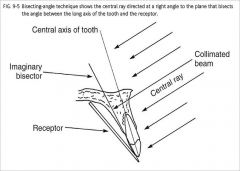
Bisecting Angle Technique
|
|
|
What are other names for the parallel technique?
|
Long cone technique
Right angle technique |
|
What are the benefits of the parallel technique?
|
Minimizes distortion and gives us a better shape of teeth and supporting bone
|
|
What is significant about the focal distance of the parallel technique?
|
Long focal distance, we use a long cone. This reduces effect of large focal spot. Recall that as we go further away, the beam becomes more parallel, reduces magnification and increases sharpness.
|
|
|
T/F
Parallel technique works well for both CMOS, CCD, and PSP. Bisecting technique cannot be used for sensors (thick) and cannot place inside the mouth. |
True
|
|
|
Which x-ray technique has the beam pass perpendicular to the long axis of the tooth and perpendicular to the x-ray film.
|
parallel technique
|
|
|
Where is the best area to place film using the parallel technique?
|
Midline of the palate
When placing fims it needs to be as far as possible from the tooth. We have a curve on the lingual plate. If you bring film closer to the tooth you get film bending. The best way to avoid this is to go further back when you expose film. |
|
|
What are the uses for occlusal radiographs?
|
1. Precisely locate roots & supernumerary, unerupted, & impacted teeth
2. Localize foreign bodies in the jaws and stones in the ducts of sublingual and submandibular glands 3. To evaluate the integrity of the outlines of the maxillary sinus 4. Aid in the examination of patients with trismus, who can open their mouths only a few millimeters; this condition precludes intraoral radiography, which, may be impossible or at least extremely painful for the patient 5. Obtain information about the location, nature, extent, and displacement of fractures of the mandible and maxilla 6. Determine the extent of disease (cysts, osteomyelitis, malignancies) and to detect disease in the palate or floor of the mouth |
|
What is included in the primary field of projection of Anterior Maxillary Occlusal Projections?
|
Anterior Maxilla and its dentition and the anterior floor of the nasal fossa and teeth from canine to canine
|
|
How should the receptor be placed for an anterior occlusal projection?
|
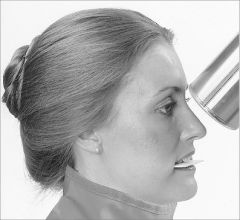
Patient head has sagittal plane perpendicular and occlusal plane is horizontal to the floor.
Exposure side of receptor toward maxilla come in at 45 degrees from the top. Central ray should enter patient's face at tip of nose. |
|
|
T/F
Anterior Maxillary Occlusal Projection is only to look at the anterior region Not the posterior. |
True
|
|
|
T/F
All Occlusal projections produce conecuts |
True
|
|
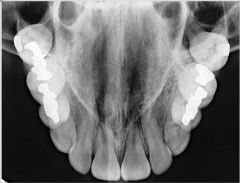
What is seen in a cross-sectional Maxillary Occlusal Projection?
|
Palate
Zygomatic processes of the maxilla Anteroinferior aspects of each antrum Nasolacrimal canals Teeth from second molar to second molar and nasal septum |
|
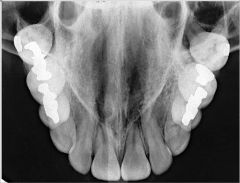
How is the receptor & cone placed in a Cross-sectional Maxillary Occlusal Projection
|
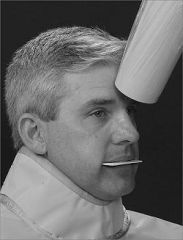
Patient upright w/sagittal plane perpendicular to floor & occlusal plane horizontal.
Come in at 65 degree angulation Center ray enters through bridge of the nose |
|
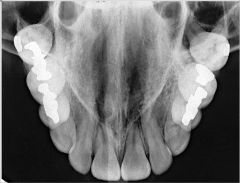
T/F
You can only see anterior structures in a Cross-sectional Maxillary Occlusal Projection |
False
You can see more of posterior structures |
|
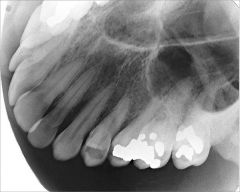
What does a Lateral Maxillary Occlusal Projection show?
|
Quadrant of the alveolar ridge of the maxilla
Inferolateral aspect of the antrum Tuberosity Teeth from lateral incisor to the contralateral 3rd molar Zygomatic process of the maxilla superimposes over the roots of the molar teeth |
|
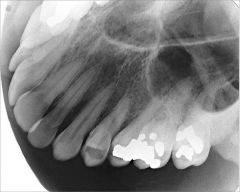
How is Lateral Maxillary Occlusal Projection taken?
|
Coming from one side
Projection of central ray - orient central ray with vertical angulation of 60 degrees 2 cm below lateral canthus of eye directed towards center of receptor (film) |
|
|
What does a Lateral Maxillary Occlusal Projection provide that other occlusals don't?
|
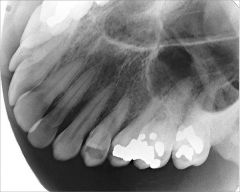
Good image of PM & molars
Roots of PMs Maxillary sinus |
|
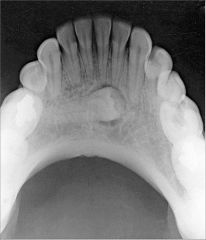
What does an Anterior Mandibular Occlusal Projection show?
|
Anterior portion of mandible
Dentition from canine to canine Inferior cortical border of the mandible |
|
How is patient and cone positioned for an Anterior Mandibular Occlusal Projection?
|
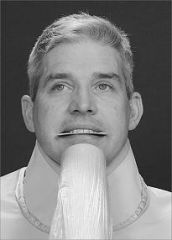
Tilt the chair back so the occlusal plane is 45 degrees above the horizon
Projection of central ray is 10 degrees through point of the chin THIS GIVES THE RAY A TOTAL OF 55 Deg to the plane of the receptor. Point of entry of central ray is in the midline through the tip of the chin |
|
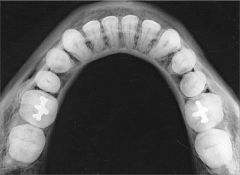
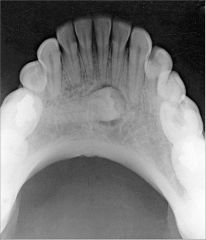
What is a cross-sectional mandibular occlusal projection used to see?
|
Soft tissues of the floor of the mouth
Lingual & Buccal plates of mandible from 2nd molar to 2nd molar When used to check floor of mouth for things like sialoliths, then exposure time should be reduced to half the time used to create an image of the mandible. |
|
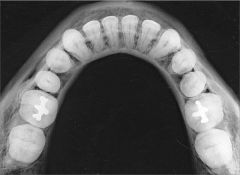
How is the cone and receptor positioned for a Cross-sectional Mandibular Occlusal Projection?
|
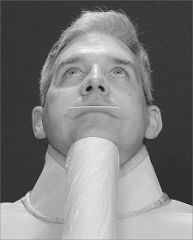
Patient in a semi-reclined position
Central ray at midline 3cm below the chin |
|
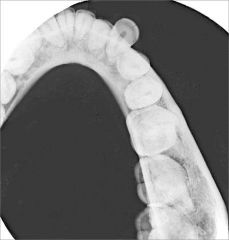
What is covered in the Lateral Mandibular Occlusal Projection?
|
Soft tissues of FOM
Buccal & Lingual cortical plates of 1/2 the mandible Teeth from LI to contralateral 3M |
|
What is the point of entry of the Lateral Mandibular Occlusal Projection?
|
central ray beneath the chin
3 cm posterior to the chin 3 cm lateral to the midline |
|
|
For a lateral mandibular occlusal projection, how far back should a patient be positioned?
|
tilt chair 45 degrees
tilt head 45 degrees Total of 90 degrees |
|
|
What is a brand of mobile radiography?
|
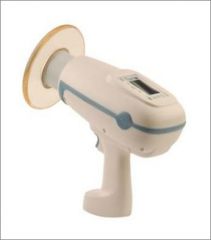
Nomad Pro Portable x-ray (Aribex)
|
|
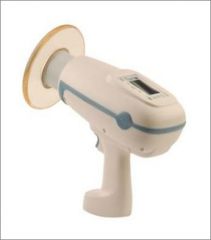
What are the features and limitations of mobile x-ray machines?
|
1. Good image quality
2. Light weight 3. Stable under operation (minimum movement) 4. Battery powered (DC current) 5. KV, mA, time, sensors/film can be adjusted 6. Large number of radiographs can be generated in a single charge cycle 7. Short focal spot 8. Rectangular collimator cannot be used |

