![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
75 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
T/F
X-rays are a form of electromagnetic energy |
True
|
|
|
What is Radiography?
|
The process of making radiographs
|
|
|
What do we use dental radiographs to view and assess as an adjunct to clinical examination?
|
1. Teeth, bone and jaws
2. Bone loss 3. Caries 4. Pathology 5. Follow-up |
|
|
What type of films are used for direct exposure?
|
Intraoral films
|
|
|
What type of films are used for indirect exposure
|
Panoramic films Indirect exposure
|
|
|
What are some types of Intra-ral films?
|
Periapicals (PAs)
Bitewings (BWs) Occlusal |
|
|
What are some types of Extra-oral films?
|
Panoramic
Cephalometric Skull Projections |
|
|
What differentiates conventional films from each other?
|
Different speed types
D-Speed E-Speed F-Speed |
|
|
What are different Digital (receptors) film types?
|
PSP (photostimulable phosphor)
CCD CMOS |
|
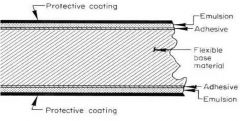
What is the flexible base material?
|
Cellulose acetate (semi-clear) 0.2 mm thick
|
|
|
What are the different film sizes?
|

Size 0-4
|
|
|
Which film size is used on children?
|

0
|
|
|
Which film size is used for anterior periapicals?
|

1
|
|
|
Which film size is used for bitewings, but we don't use it here at CWRU?
|

3
|
|
|
Which film size is used for occlusal radiographs?
|

4
|
|
|
What color are the double xray packets?
|

Gold
|
|
|
What should we keep in mind with double xray packets?
|

They require slightly more radiation exposure
|
|
|
What is the order and content of dental film packets?
|
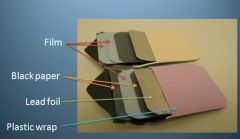
Plastic Wrap
Lead Foil Black Paper Film (1 or 2) Black Paper Platic Wrap |
|
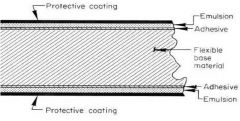
Why is the emulsion placed on both sides?
|
1. To reduce the radiation needed for an x-ray radiograph
2. The film can be read from both sides |
|
|
Why do we use lead foil?
|
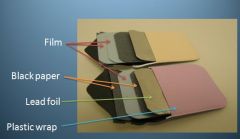
1. Absorbs unused radiation and scattered secondary radiation which reduces dose to patient and helps prevent film fogging
2. Back exposure can be detected (pattern) |
|
|
On the xray packet, where is the dot supposed to go?
|

The dot is always close to the occlusal plane
|
|
|
How do radiolucent objects manifest on an x-ray?
|
Radiolucent = Black
|
|
|
How do radiopaque objects manifest on an xray?
|
Radiopaque = White
|
|
|
T/F
Whe x-ray photons hit the emulsion the energy is stored by the emulsion and will darken the film after chemical processing. |
True
|
|
|
What happens to the emulsion, that has not been hit by x-ray, during processing?
|
The emulsion that has not been hit by x-ray will be washed away during chemical processing
|
|
|
What happens to x-rays when they come into contact with radiolucent objects?
|
Transmits x-rays
|
|
|
What happens to x-rays when they come into contact with radiopaque objects?
|
Radiopaque objects Absorb x-rays
|
|
|
What is the formula for optical density?
|
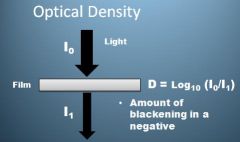
D = Log (Io/I1)
|
|
|
What are the 3 regions on the Film Response Curve?
|
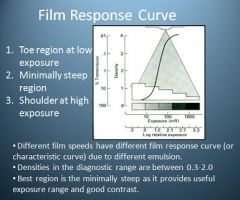
1. Toe region at low exposure
2. Minimally Steep Region 3. Shoulder at High exposure |
|
|
What are the densities in the diagnostic range when referring to the Film Response Curve?
|
0.3-2.0
|
|
|
What are the densities in the diagnostic range when referring to the Film Response Curve?
|
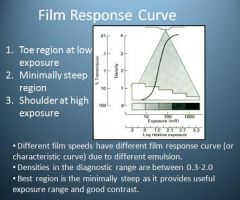
0.3-2.0
|
|
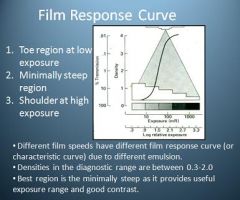
Where is the best region on the film response curve?
|
Minimally Steep Region
Good contrast and useful exposure range |
|
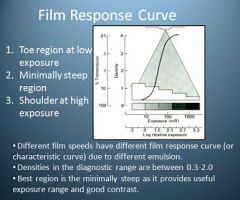
How does the shoulder region of the film response curve manifest?
|
Shoulder region will be more black (Darker Image), which is indicative of over exposure
|
|
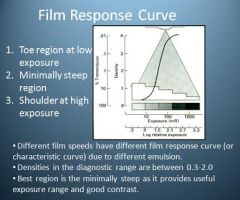
How does the toe region of the film response curve manifest?
|
The toe region will be whiter (Lighter Image) indicates under exposure
|
|
|
What is a useful technique in caries detection or calculus detection, when using Digital Xrays?
|
Adjusting the contrast
|
|
|
What type of contrast is a small gradual change among the different optical densities?
|

Long Scale or Low Contrast
|
|
|
What type of contrast is large or abrupt differences among optical densities?
|

Short Scale or High Contrast
|
|
|
What are different affectors of Subject Contrast?
|
1. Thicknes
2. Density 3. Atomic Number 4. KVP 5. Presence of Contrast Medium 6. Scattered Radiation |
|
|
What are different affectors of Film Contrast?
|
1. The characteristic curve of the film
2. Film Density 3. Use of intensifying screens or direct exposure 4. Film processing |
|
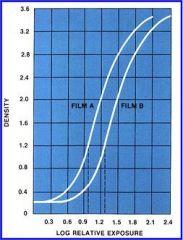
What regulates film speed?
|
Size of the crystals in the emulsion regulates film speed
|
|
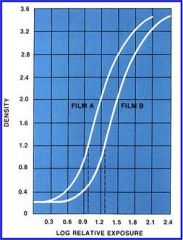
What are the 3 film speeds used in dentistry?
|
D-speed film (Ultraspeed)
E-speed film (Ektaspeed) F-speed film (Insight) |
|
|
Which speed film provides the highest speed film with the greatest reduction in radiation dose to the patient?
|
F-speed film (InSight)
60% less exposure time than D-speed & 20% less than E-speed |
|
|
What speed film do most dentists and why?
|
Many dentists still use D-speed films, ignoring the benefits of F-speed films. Dentists are resistant to change.
|
|
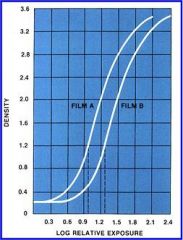
Which film has faster response and why?
|
Film A has a faster response because it requires less exposure time to produce the same level of optical density.
|
|
|
How many x-rays do we take for a Full Mouth Radiographic Series?
|
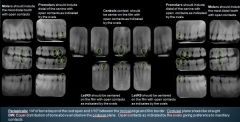
20 films
16 PAs + 4 BWs |
|
|
Where are the key interproximal spaces for Molar Bitewings?
|
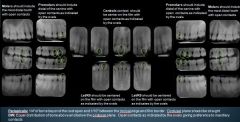
Between the 1st & 2nd Molars
|
|
|
Where are the key interproximal spaces for Premolar Bitewings?
|
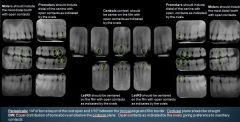
Between the Canine and 1st PM
Between the 1st & 2nd PM |
|
|
Where are the key interproximal spaces for Premolar PAs?
|
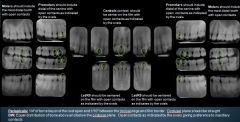
Between the canine and the 1st Premolar
|
|
|
Where are the key interproximal spaces for Central Incisor PAs?
|
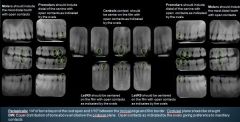
Between the CIs
|
|
|
Where are the key interproximal spaces for Lateral Incisors?
|
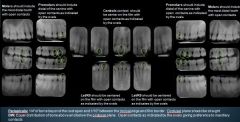
Between LI & Canine
|
|
|
When taking Molar Radiographs, what should be included?
|
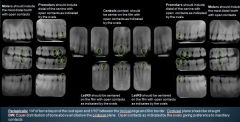
The most distal tooth
|
|
|
When taking Premolar Radiographs, what should be included?
|
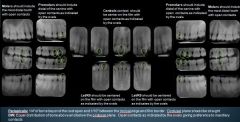
The Distal of the Canine
|
|
|
What are the boundary guidelines for Periapicals?
|
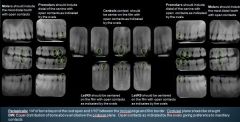
PA = 1/4" of bone beyond the root apex and 1/10" between the incisal edge & film border. Occlusal plane should be straight
|
|
|
What are the guidelines for bitewing radiographs?
|
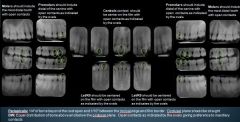
BW: Equal distribution of bone above and below the occlusal plane. Open contacts as indicated by the ovals giving preference to maxillary contacts.
|
|
|
What are Periapical radiographs used for?
|
1. Interproximal Anteriors for Caries
2. Marginal Integrity of Anterior restorations 3. Periapical structures & crowns of teeth for pathology 4. Presence of calculus |
|
|
T/F
Periapical radiographs are used for evaluating crestal bone height |
FALSE
PAs are NOT suitable for evaluating crestal bone height. |
|
|
What are Bitewing radiographs used for?
|
1. Interproximal Caries
2. Crestal bone height level 3. Interproximal calculus 4. Crowns of teeth & marginal integrity of restorations |
|
|
What is the best way to evaluate crestal bone height in patients with periodontitis?
|
Vertical Bitewings
|
|
|
What is the selection criteria for the amount and type of radiographs to take?
|
1. What the dentist needs to view on a radiograph
2. Number of teeth in the oral cavity 3. Conditions that may interfere with film placement 4. Patient ability to cooperate |
|
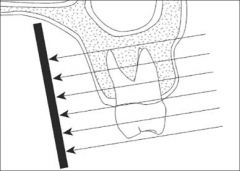
What Projection Technique is this?
|
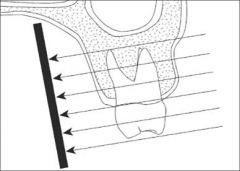
Parallel Technique
The central x-ray beam is perpendicular to tooth and the x-ray film |
|
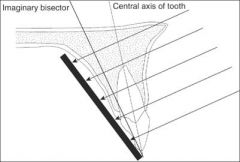
What projection technique is this?
|
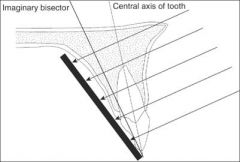
Bisecting Angle Technique
The central x-ray beam is perpendicular to the line that bisects the angle formed between the tip of the tooth and the x-ray film |
|
|
What type of Collimator reduces the radiation dose a patient is exposed to?
|
Rectangular Collimator cuts the radiation dose to the patient up to 60%
|
|
|
What is the Blue Rinn film holder for?
|

Blue = Anterior PAs
|
|
|
What is the Yellow Rinn film holder for?
|

Posterior PAs
|
|
|
What is the Red Rinn film holder for?
|

Bitewings
|
|
|
What is the White Rinn film holder for?
|

RCT
Root Canal Treatment |
|
|
What do you need to leave in your locker when you come to admitting duty?
|
No Jacket, books, backpacks or purses are brought to admitting
|
|
|
What PPE do you bring to admitting?
|
White coat
Gloves Mask |
|
|
What are the only surfaces that you can touch when you are wearing gloves?
|
Only touch surfaces that have barrier coverings when you are wearing gloves.
|
|
|
What is the sequence of injfection control, when setting up your admitting room?
|
1. Wipe room w/caviwipes then place plastic bags on chair & x-ray head
2. Place Allwrap to both light handles & switch & exposure button (anything that you will touch) 3. Tray table outside the room and covered w/napkin 4. place lead apron & thyroid collar over patient 5. Wash hands, don mask then gloves |
|
|
What infection control method should you use for film that is covered by a clear plastic barrier?
|
1. Spray w/Citrace on both sides & pat dry.
2. Replace gloves 3. Pull plastic barrier apart and drop film into clean paper cup Without handling the film |
|
|
What infection control method should you use for film that is NOT covered by a clear plastic barrier?
|
1. Place exposed films on mobile instrument tray w/napkin
2. Spray both sides of film w/Citrace and pat completely dry with paper towel (Remove gloves when you are done. Don't walk around with your gloves on) |
|
|
What is the procedure for getting your film developed?
|
1. Place film in envelopes labeled with: Patient name, Date, # of x-rays, Student name, Do Not mix double & single in same pack
2. Place film on bottom shelf of x-ray window. |
|
|
What is the room cleanup process?
|
1. Remove All plastic coverings
2. Clean all surfaces as follows: wet surfaces w/Caviwipes, Clean & dry with paper towel |
|
|
How do you clean up your Rinn XCP Kit and other autoclavable film holders?
|
Spray & wipe off all parts of film holder then place in sterilization bags. Take to dispensary for sterilization.
|

