![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
28 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What does measuring the rate and extent of binding provides information |
1. Number of binding sites 2. Their affinity 3. Accessibility for various drugs |
|
|
What can radioligand binding be used to do |
Characterise receptions in their natural environments as well as receptors transferred into cell lines Study receptor subtypes and their expression in different tissues Identify novel agonists and antagonists that interact with receptors Define receptors in normal and disease tissues |
|
|
What is a radioligand |
It is a Ligand that is made radioactive |
|
|
Why do we measure receptor coupling to different second messenger systems |
Test agonist and antagonists Link receptor functional responses Identify G protein vs beta arrestin pathways Identify bias agonist and antagonists |
|
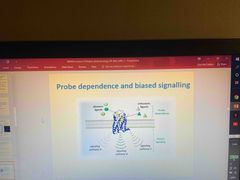
Describe this image |
Allosteric modulators can affect how strong or weak a signal down a pathway is eg. A could be strong but B and C weaker. Or B and C moderately strong and A weak |
|
|
Describe these graphs |
A) slightly biased towards IP B) blocks the pathways creating no response C) bias towards by sending activation towards beta arrestin pathway |
|
|
Why express the receptors in cells |
See which pathways are linked Test agonists and antagonists Make mutations in the receptor at different points to see what happens |
|
|
What are biochem/biophysical measurements |
Tagging receptors Immuno precipitate the receptor- what it’s bound to Hydrophobicity plots |
|
|
What is a tag |
A sequence that allows us to bind to the receptors |
|
|
What is hydrophobicity |
Look at a receptor and see what parts do better in an aqueous solution or lipids |
|
|
Where is beta arrestin located |
C terminus |
|
|
How do we to we measure heterotrimeric G protein dissociation |
By use of bioluminescence resonance energy transfer BRET |
|
|
How do we get decreased BRET signals in TRUPATH |
Within binding of the drug. The alpha and beta subunits dissociate resulting in the decrease |
|
|
What happens with increased concentration of drugs in TRUPATH |
The BRET2 signal decreases |
|
|
What can a TRUPATH assay tell us |
Distinguish between agonist potencies very easily Show differences in efficacy between drugs Show antagonism Inverse agonist m signal should go up |
|
|
What can pig ileum not distinguish between |
Cant easily distinguish between Agonists and antagonists |
|
|
What was required to resolve the structure of GPCRs |
Engineering to stabilise the receptor |
|
|
Where is the largest conformational change in inactive and active GPCR crystal structures |
At the extracellular side is depicted as an inward movement of TM6 |
|
|
Where do different ligands bind on different regions |
Different ligands will bind to regions within the receptor |
|
|
Is there a shift at TM6 with an antagonist |
No shift |
|
|
What direction does the inverse agonist shift go |
Left |
|
|
What kind of agonist is salmeterol |
Partial agonist at beta 2 adrenergic receptor |
|
|
What are the two binding sites of ligands called |
orthostatic or allosteric |
|
|
What does biotopic mean |
Two parts |
|
|
Where have the majority of biotopic GpCR ligands been found |
Muscarinic Adenosine Dopamine receptors |
|
|
How were biotopic ligands were first demonstrated |
By biased muscarinic mAChR partial agonist, McN-A-343 |
|
|
What function does McN-A-343 have |
Has functional selectivity by engaging both an orthosteric and allosteric site at the M2 mAChR |
|
|
What does McN-A-343 display |
Mixed modes of orthosteric or allosteric pharmacology depending on the experimental assay conditions |

