![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
51 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Herpes -> HSV-2
|
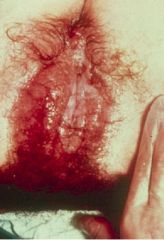
Produces small vesicles and shallow ulcers that can involve the vulva, cervix, vagina, etc
MNGC's with eosinophilic intranuclear inclusions |
|
|
Herpes Simplex Virus 2
Seen in males as ulcers |
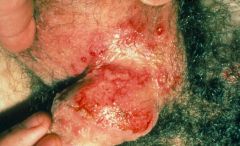
What causes this?
|
|
|
Herpes
MNGC's with viral inclusions in the nucleus |
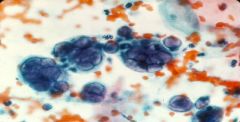
What is this?
Describe what you see |
|
|
HPV:
-Sexually transmitted __1__ virus -virus is located in the __2__ of affected cells -affected cells are called __3__ |
1. DNA
2. nucleus 3. Koilocytes |
|
|
What is HPV associated with an increased risk of?
|
Dysplasia
Carcinoma |
|
|
What 2 ways does HPV stimulate the proliferation of Squamous epithelium?
|
Exphytic = condyloma
Flat |
|
|
Condylomata acuminata
HPV |
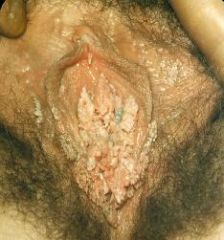
What is this called?
What is the cause? |
|
|
Condyloma caused by HPV
|
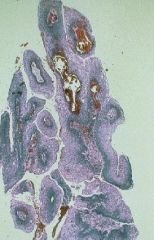
What is this showing?
|
|
|
Koilocytes
HPV |
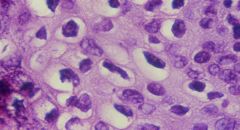
What are these cells called?
What causes them? |
|
|
Pruritic vaginitis with a white discharge and a fiery red mucosa
|
Candida
|
|
|
Candidiasis
|
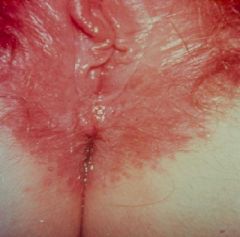
What is this?
|
|
|
What are 4 risk factors for Candidiasis?
|
1. Diabetes
2. Broad-spectrum Antibiotics 3. Oral Contraceptives 4. Pregnancy |
|
|
Wet mount of Candida
|
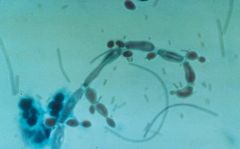
What is this?
|
|
|
Tuberculosis
Non-caseating granulomas in histology |
What is the cause of this?
How would your suspicion be confirmed? |
|
|
Describe the pathophysiology of Bartholin's Gland Cyst
|
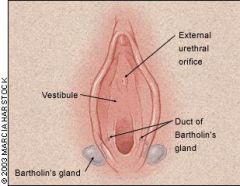
Duct obstruction that leads to cyst formation -> edema and swelling
|
|
|
What is the most common cause of Bartholin's Gland cyst?
|
N. gonorrhoeae
|
|
|
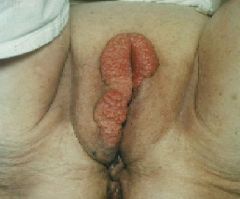
Bartholins Gland cyst
|
What is shown at the right?
|
|
|
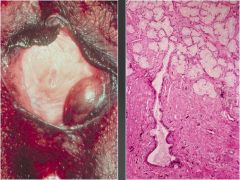
-Abnormal growth of the Vulvar skin with white plaques and skin atrophy
-Histologically there is Hyperkeratosis, loss of Rete Ridges, an Acellular Zone, and Chronic inflammation |
Lichen Sclerosus
|
|
|
Lichen Sclerosus
Itching or Painful sex |
What is this called?
How can it present clinically? |
|
|
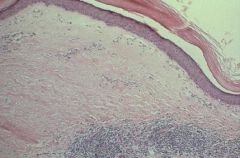
Lichen Sclerosus
-Hyperkeratosis -Loss of Rete ridges = undulation between dermis and epidermis -Acellular zone -Chronic Inflammation |
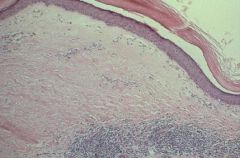
What is this?
How do you know? |
|
|
Squamous Hyperplasia
- thickened epithelium - hyperkeratosis - epidermal dipping |
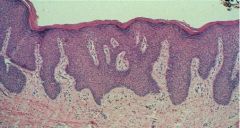
What is this and how do you know?
|
|
|
Is a spectrum of neoplastic changes in the vulva, ranging from koilocytic changes to mild/moderate/severe dysplasia to Carcinoma in situ
|
Vulvar Intraepithelial Neoplasia
|
|
|
What is Vulvar Intraepithelial Neoplasia associated with?
What is it a precursor of? |
HPV 16, 6, 11
Squamous Cell Carcinoma |
|
|
What is the most common cancer of the Vulva?
|
Squamous Cell Carcinoma
|
|
|
What are the 3 gross appearances Squamous Cell Carcinoma of the Vulva can be?
|
1. Exophytic (2/3)
2. Ulcerative 3. Endophytic |
|
|
Squamous Cell Carcinoma of the Vulva that has ulcerated through
|
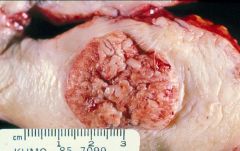
What is the pic showing?
|
|
|
Squamous Cell Carcinoma of the Vulva that is invading the Stroma
|
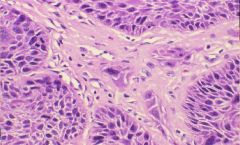
What is this picture showing?
|
|
|
Anaplasia in Vulvar Squamous Cell Carcinoma
|
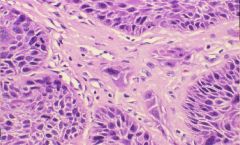
What is this picture showing?
|
|
|
Blood vessel filled with tumor = radical surgery is not enough -> need chemo or radiation as well
|
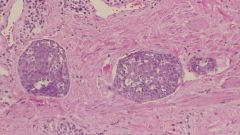
What is this picture showing?
|
|
|
How can Squamous Cell Carcinoma of the Vulva present clinically?
|
1. Pruritis
2. Bleeding 3. Infection 4. Ulcer 5. Mass |
|
|
Where do Squamous Cell Carcinomas of the Vulva metastasize to?
What is the survival rate for this cancer? |
Inguinal and Femoral Lymph Nodes
90% |
|
|
Verrucous Carcinoma = Giant Condyloma
HPV 6 Squamous Cell Carcinoma Good -> invades locally |
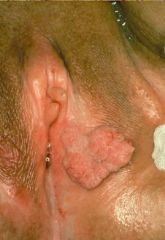
What is this called?
What is the cause? What is it a variant of? What is the prognosis? |
|
|
1. Verrucous Carcinoma
-finger-like projections at bottom 2. HPV 6 |
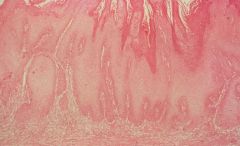
1. What is this?
2. What is most commonly associated with causing this? |
|
|
Red, moist lesion on the labia majora
Often crusts over |
Extramammary Paget's Disease
|
|
|
Extramammary Paget's Disease
|
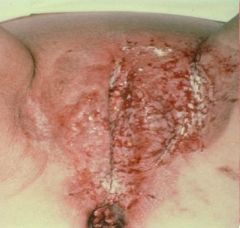
What is this?
|
|
|
Extramammary Paget's Disease
Adenocarcinoma cells |
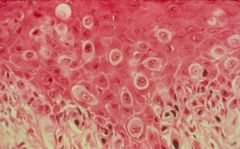
What is this?
What type of cells are they? |
|
|
Melanoma
|
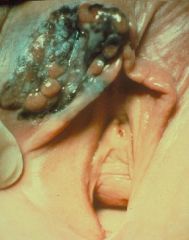
What is this?
|
|
|
Melanoma
|
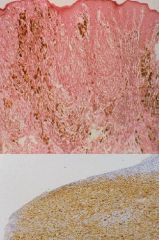
What is this?
|
|
|
Replacement of the Squamous epithelium in the Vagina with Glandular Epithelium
|
Vaginal Adenosis
|
|
|
What is Vaginal Adenosis most commonly the result of?
|
Prenatal DES exposure
|
|
|
Describe the pathophysiology of Vaginal Adenosis (Vulvar Vaginosis)
|
DES inhibits Mullerian differentiation -> see remnants of Mullerian glands -> Adenocarcinoma
|
|
|
Vaginal Adenosis
DES exposure |
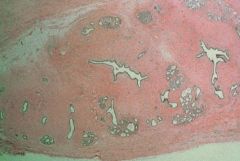
From a vaginal biopsy:
What is it? What is it the result of? |
|
|
Vaginal Adenosis (Vulvar Vaginosis)
|
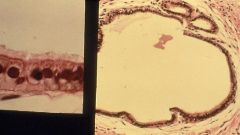
What is this?
|
|
|
Clear cell adenocarcinoma
DES exposure |
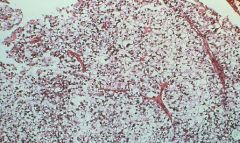
From a vaginal biopsy:
What is it? What causes it? |
|
|
What is the most common cancer of the vagina?
|
Squamous Cell carcinoma
|
|
|
Vaginal Squamous Cell Carcinoma
|
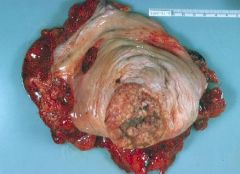
What is this?
|
|
|
Polypoid mass resembling a "bunch of grapes" on vaginal exam in a 3 year old girl
|
Embryonal Rhabdomyosarcoma = Sarcoma Botryoides
|
|
|
Embryonal Rhabdomyosarcoma (Sarcoma Botyroides)
Child < 4 years old |
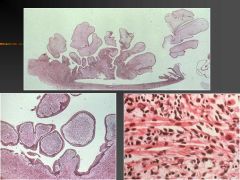
What is this?
How old of a person would have this? |
|
|
Replacement of normal squamous epithelium by a glandular epithelium. History of DES exposure in the early prenatal life
|
VULVAR VAGINOSIS
|
|
|
A rare vulvar neoplasm in which malignant, large, pale vacuolated cells are found scattered throughout the epidermis. Wide local excision is usually curative
|
Extramammary Paget's Disease
|
|
|
A variant of well differentiated squamous cell carcinoma that presents as a large fungating mass resembling a giant condyloma. HPV type 6 is commonly identified in this tumor. The tumor invades locally and typically does not metastasize. Local surgical excision is the treatment of choice
|
Verrucous carcinoma
|

