![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
73 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What epithelium covers the Exocervix?
|
Squamous epithelium
|
|
|
Mucus-secreting Columnar Cells
|
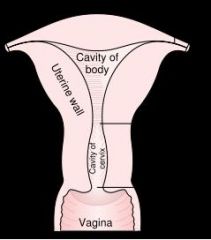
What epithelium covers the Endocervix?
|
|
|
Squamo-Columnar Jxn = Transition Zone in the Cervix
|
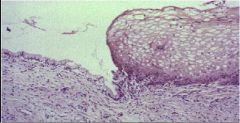
What is this?
|
|
|
Normal Squamous Epithelium of the Exocervix
|
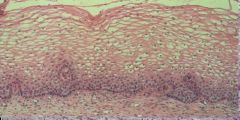
WHat is this?
|
|
|
Normal Endocervical Columnar epithelium that secretes mucus
|
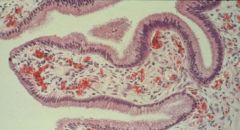
What is this?
|
|
|
Pap Smear
-Left = normal Squamous cells -Right = normal Endocervical cells |
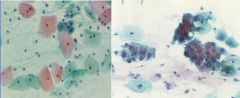
What are these?
|
|
|
Chronic Cervicitis
|
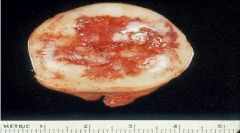
What is this picture showing?
|
|
|
Endocervical Polyp
|
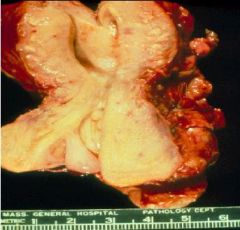
What is this picture showing?
|
|
|
Cervical Intraepithelial Neoplasia:
1. CIN I = ? 2. CIN II = ? 3. CIN III = ? |
1. Mild dysplasia = lower 1/3
2. Moderate dysplasia = lower 2/3 3. Severe Dysplasia / Carcinoma In situ = full thickness |
|
|
Mild Squamous Dysplasia = CIN I
*basal layer is at the top |
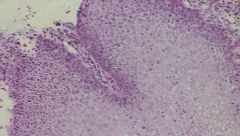
Cervix biopsy...what is it showing?
|
|
|
Moderate Squamous Dysplasia = CIN II
|
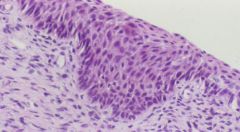
Cervix biopsy...what is the diagnosis?
|
|
|
Sever Squamous Dysplasia = CIN
|
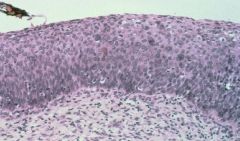
Cervical biopsy...what is the diagnosis
|
|
|
Glandular epithelium has turned into Squamous epithelium which then turned into Dysplasia
|
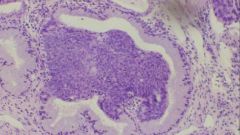
Endocervix biopsy - what has happened?
|
|
|
Mild Squamous Dysplasia
- somewhat enlarged nuclei |
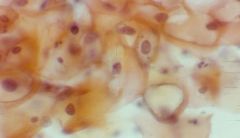
Pap smear showing Cervical cells - what is the diagnosis?
|
|
|
Moderate Squamous Dysplasia
-nuclei:cytoplasm ratio is increased |
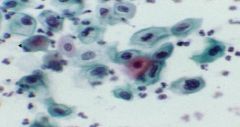
Pap smear with Cervix cells...what is the diagnosis?
|
|
|
Severe Squamous Dysplasia = CIN III
|
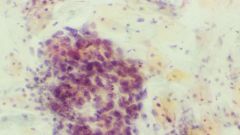
Pap smear showing Cervix cells...what is the diagnosis?
|
|
|
Severe Squamous Dysplasia
|
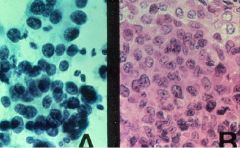
The left is pap smear and the right is histology...what is the diagnosis?
|
|
|
What are the risk factors for Cervical Intraepithelial Neoplasia?
|
1. HPV infection (higher #'s)
2. multiple sex partners 3. Early age of first intercourse |
|
|
What does Squamous Cell Carcinoma of the Cervix usually evolve from?
|
CIN
|
|
|
What is the histology of Squamous Cell Carcinoma of the Cervix?
|
Invasive Squamous cells in the Stroma
|
|
|
What are the clinical presentations of Squamous Cell Carcinoma of the Cervix?
|
1. Post-coital bleeding
2. painful intercourse 3. Malodorous discharge |
|
|
Where does Cervical Carcinoma most typically occur?
|
Squamo-Columnar Jxn = Transition zone
|
|
|
What are the 3 treatment options for Cervical Carcinoma?
|
Conization
Radical hysterectomy Radiation therapy |
|
|
Cervical Cancer at the Squamocolumnar jxn
|
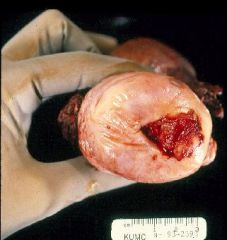
What is this showing?
|
|
|
Cervical Carcinoma
|
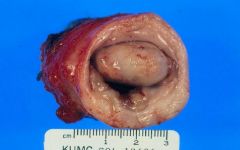
What is this showing?
|
|
|
Non-invasive Carcinoma In-situ = CIN III
|
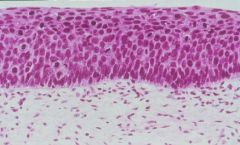
What is this showing?
|
|
|
Cervical carcinoma that only invades < 3 mm with no vascular or lymphatic invasion
|
Microinvasive Squamous Cell Carcinoma
|
|
|
This comprises 10% of Cervical Carcinomas and is related to HPV 16 and 18
|
Adenocarcinoma
|
|
|
Cancer that has a 75% decrease in incidence and mortality over the past 50 years
However, it is the 2nd most common cause of cancer related morbidity and mortality among women in developing countries |
Adenocarcinoma of the Cervix
**85% of cervical cancers are Squamous Cell Carcinoma |
|
|
Types of HPV that account for 80% of Cervical Cancers?
|
16 & 18
|
|
|
Endocervical Adenocarcinoma
-back to back glands -stromal invasion -Anaplastic nuclei |
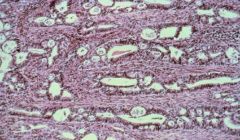
What is this showing?
|
|
|
What affects the Proliferative Phase of the Menstrual Cycle?
|
Estrogen
|
|
|
What is the most variable phase of the Menstrual Cycle?
|
Proliferative phase
|
|
|
Describe the histology of the Proliferative Phase of the menstrual cycle
|
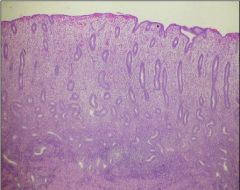
Tubular glands
Monomorphic stroma |
|
|
What affects the Secretory Phase of the Menstrual Cycle?
|
Progesterone
|
|
|
Describe the histology of the Secretory phase of the Menstrual Cycle
|
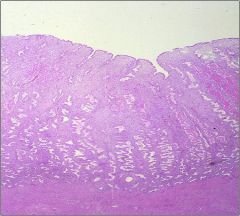
Coiled Glands
Edematous Stroma |
|
|
What are the causes of Dysfunctional Uterine Bleeding in:
1. New borns 2. Childhood 3. Adolescents 4. Reproductive age 5. Menopause |
1. maternal withdraw of estrogen
2. tumors secreting estrogen 3. psychogenic, stress, nutritional, tumor 4. same as 3 5. Estrogen secreting tumors |
|
|
What is the definition of Dysfunctional Uterine Bleeding?
|
Abnormal uterine bleeding due to Extra-Uterine causes
|
|
|
What are the typical causes of Acute Endometritis?
|
1. Ascending infection from Cervix
2. Abortion 3. Instrumentation |
|
|
What are the typical causes fo Chronic Endometritis?
|
Intrauterine devices (IUDs)
Pelvic Inflammatory Disease Abortion |
|
|
How do you differentiate between Acute and Chronic Endometritis?
|
Acute = PMN's
Chronic = Plasma Cells |
|
|
Acute Endometritis
|
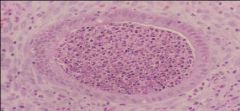
What is this showing?
|
|
|
Chronic Endometritis
presence of Plasma cells |
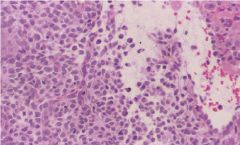
Endometrium biopsy:
What is this showing? How do you know? |
|
|
Where do Endometrial Polyps usually occur?
|
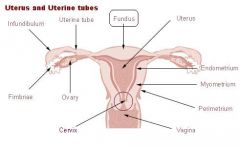
Fundus
|
|
|
What does the histology of an Endometrial Polyp contain?
|
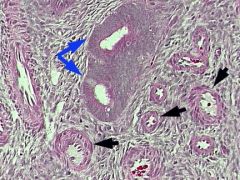
1. Endometrial glands, cysts, hyperplasia
2. Fibromatous stroma 3. Thick-walled blood vessels |
|
|
Endometrial Polyps
Benign Inter-menstrual bleeding |
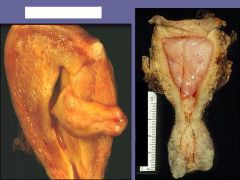
What are these showing?
Are they malignant or benign? How do they typically present clinically? |
|
|
Endometrial Polyp
Menorrhagia / Dysfunctional Uterine bleeding |
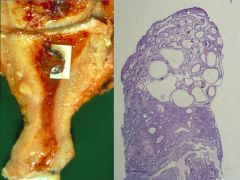
What are these?
What can they result in? |
|
|
Endometrial Polyp -> thick-walled blood vessel
|
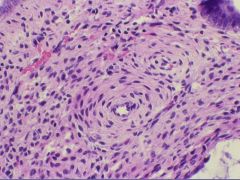
Biopsy taken from the Endometrium...what is the diagnosis?
|
|
|
What is the treatment for Endometrial Polyps
|
Curettage = cutting out the polyp with a spoon-like device
|
|
|
Simple Hyperplasia
|
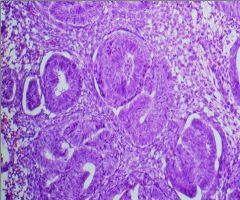
Endometrium biopsy...what is the diagnosis?
|
|
|
Simple Hyperplasia = increased # of dilated glands
|
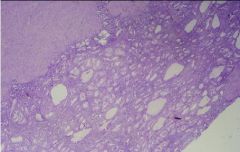
Endometrium biopsy...what is the diagnosis?
|
|
|
Complex Hyperplasia = glands appear crowded and are surrounded by relatively scant stroma
|
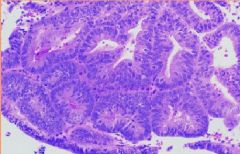
Endometrial biopsy...what is the diagnosis?
|
|
|
Atypical Hyperplasia = glands appear crowded and have an irregular shape, with stratification of cells that often protrude into the lumen
- nuclear atypia |
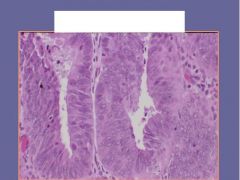
Endometrial biopsy...what is the diagnosis?
|
|
|
Cystic Hyperplasia = Swiss Cheese Hyperplasia
|
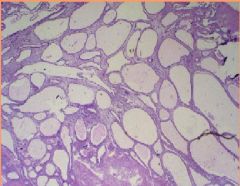
Endometrial biopsy...what is the diagnosis?
|
|
|
Endometrial Polyp with Complex Hyperplasia
|
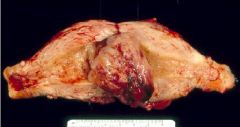
What is this picture showing?
|
|
|
What is Endometrial Hyperplasia a precuror of?
|
Endometrial Carcinoma
|
|
|
What is Endometrial Hyperplasia most often clinically manifested as?
|
Postmenopausal bleeding
|
|
|
What are some things that can cause Endometrial Hyperplasia?
|
1. Estrogen secreting tumor
2. Obesity = fat cells store estrogen 3. Polycystic Ovary disease 4. Estrogen therapy |
|
|
What is the most common cancer of the Female Genital Tract?
|
Endometrial Adenocarcinoma
|
|
|
What is the cause of Endometrial Adenocarcinoma?
|
prolonged Estrogen exposure
|
|
|
What are 7 risk factors for Endometrial Adenocarcinoma?
|
1. Diabetes
2. Nulliparity (no births) 3. Smoking 4. Estrogen secreting tumor 5. HTN 6. Late Menopause = prolonged exposure to estrogen 7. Genetics |
|
|
What is the gross appearance of Endometrial Adenocarcinomas?
|
Polypoid, infiltrative, necrosis and hemorrhage
|
|
|
Endometrial Carcinoma
|
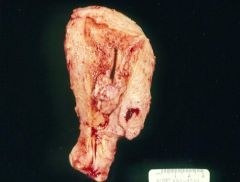
What is this showing?
|
|
|
FIGO I Endometrial Carcinoma
- back to back glands with no stroma |
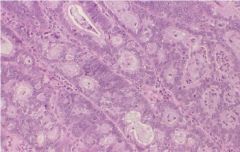
Endometrial biopsy...what is it showing?
|
|
|
FIGO III = poorly differentiated
|
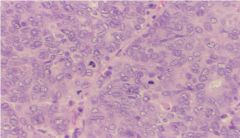
What is the classification of this Endometrial Carcinoma?
|
|
|
FIGO II
|
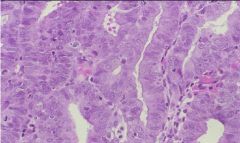
What is the classification of this Endometrial Carcinoma?
|
|
|
Villo-glandular Adenocarcinoma
|
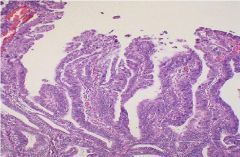
Endometrial biopsy...what is teh diagnosis?
|
|
|
Papillary Serous Adenocarcinoma
|
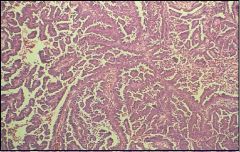
Endometrial biopsy...what is the diagnosis?
|
|
|
Adenocarcinoma with Squamous differentiation
|
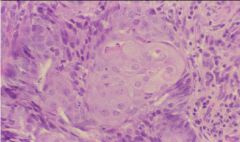
Endometrial biopsy...what is the diagnosis?
|
|
|
Clear cell adenocarcinoma
|
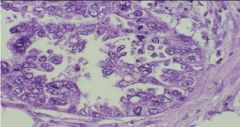
Endometrial biopsy...what is the diagnosis?
|
|
|
Secretory Adenocarcinoma
- could be confused with Secretory Phase BUT there is NO stroma |
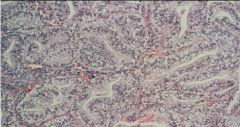
Endometrial biopsy...what is the diagnosis?
|
|
|
How does Endometrial Adenocarcinoma usually present clinically?
|
Abnormal Peri and Post Menopausal bleeding
|
|
|
What is the treatment for Endometrial Adenocarcinoma?
|
Radical Hysterectomy
|

