![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
37 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What is the difference in treatment in Seminomas and Nonseminomatous Germ-cell tumors (NSGCT)?
|
Seminomas are RADIOSENTITIVE
|
|
|
What is the most common site of Metastases of Seminomas?
|
Para-aortic lymph nodes
|
|
|
Seminoma
|
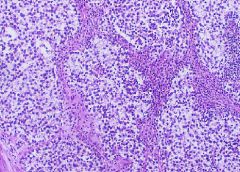
A 30 year old man noticed painless enlargement of the left testicle and after 3 months decided to consult his family physician. The physician palpated the testes and found that the left testicles is enlarged and irregularly nodular and firm. He referred him to a urologist. AFP and hCG were normal
|
|
|
Seminoma
-tumor cells are arranged in lobules surrounded by fibrous strands and infiltrated with lymphocytes |
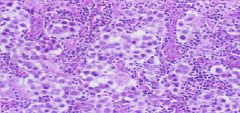
What is this?
How do you know? |
|
|
Intratubular Testicular Germ Cell Neoplasia = carcinoma in situ
|
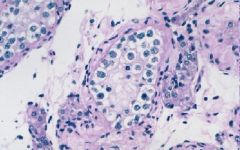
What is this?
|
|
|
Teratoma
- keratin pearls - glands -neural tissue |
What cancer is this?
How do you know? |
|
|
Choriocarcinoma cells
- bulky masses with Hemorrhage and necrosis |
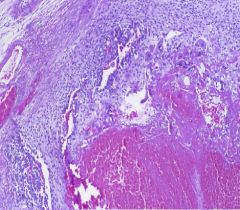
What germ cell tumor is this?
What is the characteristic microscopic feature? |
|
|
Yolk Sac
Schiller-Duval Bodies AFP |
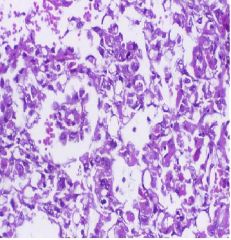
What Germ Cell Tumor?
How do you know? What do they secrete (tumor marker)? |
|
|
Leydig cell tumor
90% are usually benign *androgens secreted from Leydig tumor cells caused precocious puberty |
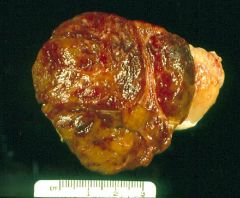
8 year old boy bragged to his friend that his penis has grown during the summer vacation and that he has pubic hair. Had elevated blood androgens.
-What testicular cancer? -Is it most likely to be benign or malignant? |
|
|
Leydig Cell tumor
- Reinke crystalloids - round nuclei with eosinophilic cytoplasm |
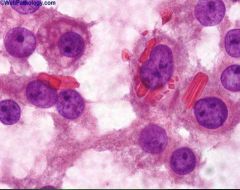
What type of tumor is this?
What are the characteristics of the histology? |
|
|
Yolk Sac Tumor
- 2 year old - Schiller-duval bodies |
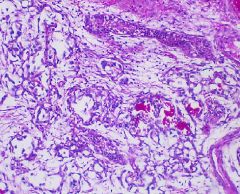
A 2 year old had a tumor mass. This is the histology of the mass.
|
|
|
Yolk Sac tumor
-Schiller-Duval bodies |
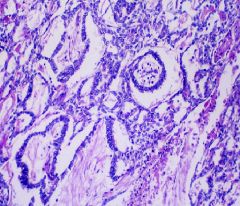
What testicular tumor?
|
|
|
Mumps
- Meningitis - Orchitis = Seminiferous tubule with inflammation - Parotitis |
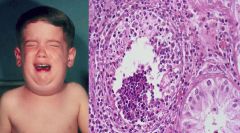
A 3 year old boy developed fever, swelling on both sides of his face. The left testicle was enlarged and sensitive to touching.
|
|
|
A 70 year old man noticed that his right testis is enlarged and slightly painful and sensitive to palpation
What is the MOST LIKELY tumor? |
Metastases from a different site
- Malignant Lymphoma |
|
|
1. Male infertility
2. FSH (b/c loss inhibin made from Sertoli cells) 3. loss of Seminiferous tubules and decreased Testosterone 4. Orchitis, ischemia, toxic injury |
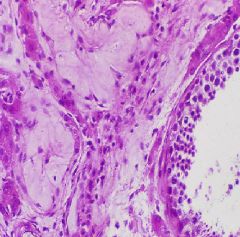
1. What is this condition?
2. What would be elevated? 3. What would cause a decreased sperm count? 4. What are possible causes? |
|
|
1. Leygid Cell tumor
2. Secrete hormones - Androgen = macrogenitosomia - Estrogen = Gynecomastia |
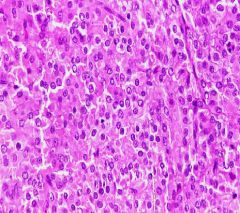
A 50 year old man noticed that his breast have enlarged during the last 6 months. He also noticed slight scrotal discomfort. Physical examination revealed an irregularly enlarge slightly nodular left testicle.
1. What is the tumor? 2. What is the cause of the symptoms? |
|
|
Syphillis = Treponema pallidum
|
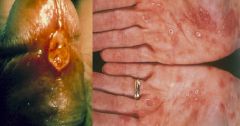
What would be the cause of these 2 symptoms?
|
|
|
Systemic Vasculitis involving small blood vessels in many organs:
1. Recurrent ulcers -mouth -penis/scrotum that are painful -vulva/vagina 2. Skin purpura/ulcerations 3. Arthritis |
Behcet Syndrome
|
|
|
Neisseria gonorrhoea
|
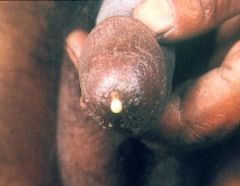
A 28 year old man came back from a weekend in Baltimore and noticed a yellow discharge from his penis, associated with burning pain
|
|
|
N. gonorhoea inside neutrophils
- diplococci |
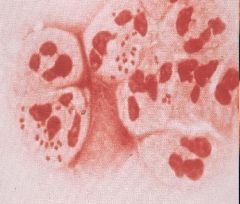
Specimen taken from a urethral discharge
What is the agent? |
|
|
What are the 3 most common microbes causing Urethritis?
|
1. Chlamydia trachomatis
2. N. gonorrhoea 3. Ureaplasma urealyticum |
|
|
Non-infectios Urethritis of unknown etiology preceded by GI or GU infections
Clinical Triad: - Urethritis - Conjunctivitis - Arthritis of weight carrying joints |
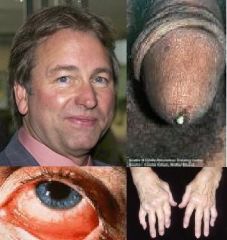
Reiter Syndrome
|
|
|
Fibromatosis of the penis in adults
- curvature of erect penis - pain on erection - painful intercourse |
Peyronie disease
|
|
|
What part of the penis has fibrosis in Peyronie disease?
|
Tunica Albuginea
|
|
|
Indwelling Catheter
|
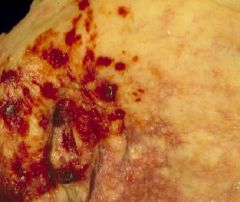
A 60 year old man underwent coronary artery bypass surgery. In the first urine that he voided on his own he noticed blood.
What is this most likely due to? |
|
|
Transitional Cell Carcinoma of the bladder
Smoking |
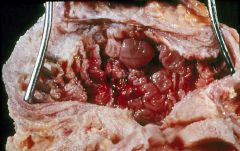
What type of cancer is this?
What is the greatest risk factor? |
|
|
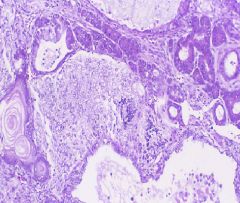
Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia
- median lobe of prostate has formed a valve - trabeculae are on the bladder wall |
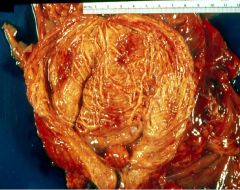
Describe all the findings you see here
|
|
|
Benign prostatic hyperplasia
- trabeculae - stones - diverticulum |
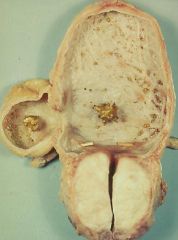
What is the cause of all this?
|
|
|
Prostate cancer
|
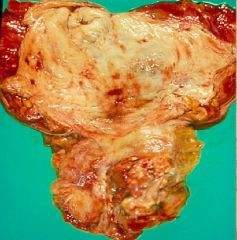
What is this?
|
|
|
Prostate Cancer
Adenocarcinoma |
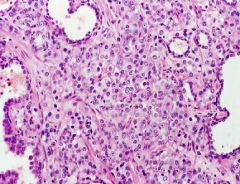
What cancer is this?
What histological cancer is it? |
|
|
Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia
|
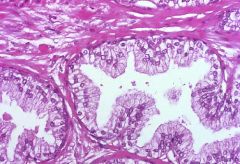
A 62 year old man had a yearly check-up. The only abnormality was elevation of PSA in the blood. Biopsy showed this. What is the diagnosis?
|
|
|
Embryonal Carcinoma Cells in NSGCT
|
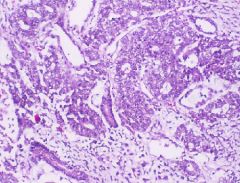
What is this?
|
|
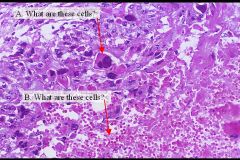
-
|
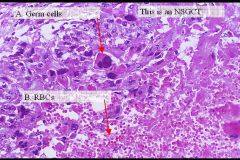
-
|
|
|
Mumps
|
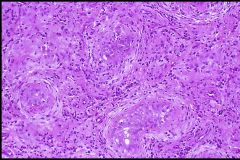
What likely caused this?
|
|
|
Rectum
Urinary Bladder Prostate |
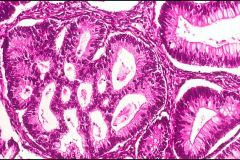
This is metastatic testicular cancer. From where did it most likely originate?
|
|
|
Metastatic Testicular Adenocarcinoma = came from somewhere else
|
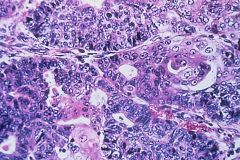
What kind of tumor is this?
|
|
|
Papillary Trasitional cell of the Urinary Bladder
|
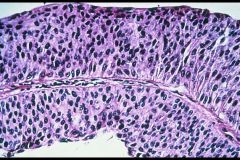
What kind of tumor is this?
|

