![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
193 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
The 2008 physical activity guidelines for Americans just attention to the growing problem of |
Physical inactivity among adults, & the little progress that has been made to reverse the trend. |
|
|
|
As little as 2.5 hours a week of Moderate aerobic physical activity can substantially reduce |
Chances for chronic diseases, leading to significant health benefits. |
|
|
|
What is one of the most important goals of the 2008 physical activity guidelines for Americans? What percentage of US adults engage in regular leisure time physical activity |
Small doses of regular physical activity can help prevent, treat, & cure more than 40 of the most common chronic health conditions. |
|
|
|
What percentage of US adults engage in regular leisure time physical activity? |
30% |
(3x/week of vigorous 20+ min workouts or 5x/week of light-to-moderate 30+ min workouts) |
|
|
A comprehensive fitness assessment |
A series of measurements that help to determine the current health/fitness level of clients. |
|
|
|
Health & fitness assessments are not designed to |
Diagnose medical/health conditions. |
|
|
|
Instead health & fitness assessments are designed to |
Serve as a way of observing/documenting a clients individual structural & functional status. |
|
|
|
Health & fitness professionals do not |
Diagnose medical conditions Prescribe treatment or diets Provide treatment of any kind for injury/disease Provide rehabilitation services for clients. Provide counseling services for clients |
There are 5 |
|
|
A comprehensive fitness assessment provides a variety of |
Subjective & objective information, a pre-participation health screening, resting physiological measurements (HR, BP, ht, & wt) , & hey series of measurements to help determine their fitness level. |
|
|
|
Fitness assessment subjective information |
General & medical history : Lifestyle, occupation, medical & personal info |
|
|
|
Fitness assessment objective information |
Physiological assess Body composition testing Cardiorespiratory assess Static & dynamic posture assess Performance assess |
There are 5 |
|
|
Subjective information is gathered from a prospective client to give |
the health & fitness professional feedback regarding personal history. |
|
|
|
A pre-participation health screening includes a |
Medical history questionnaire (PAR-Q), a review of their chronic disease risk factors, & presence of any signs/symptoms of disease. |
|
|
|
What are the 3 classifications after a pre-participation health screening has taking place? |
Low risk Moderate risk High risk |
|
|
|
Those who are considered low risk after the Pre-participation health screening |
Don’t have any signs/symptoms of cardiovascular, pulmonary, or metabolic disease & have = 1 cardiovascular disease risk factor. |
|
|
|
Those who are considered moderate risk after the Pre-participation health screening |
Don’t have any signs/symptoms of cardiovascular, pulmonary, or metabolic disease but have >/= 2 cardiovascular disease risk factors. |
|
|
|
Those who are considered high risk after the Pre-participation health screening |
Have 1 or more signs/symptoms of cardiovascular, pulmonary, or metabolic disease. |
|
|
|
After the pre-participation health screening information has been collected/reviewed/stratified |
Personal trainers can now to proceed with fitness testing/refer the client for further medical evaluation. |
|
|
|
Physical activity readiness questionnaire (PAR-Q) |
Determines the safety/possible risk of exercising for a client based on answers to specific health questions. |
Usually for individuals who require further medical evaluation (high risk) before they’re allowed to exercise. |
|
|
Answering yes to one or more questions on the PAR-Q, The personal trainers should |
Refer them to a physician for further medical screening before starting an exercise program. |
|
|
|
PAR-Q sample question |
In the past month, have you had chest pain when you were not performing any physical activity? |
|
|
|
A health history is a collection of information that is generally part of a medical physical/ medical health history, including |
Biographic, demographic, occupational, general lifestyle (physical, mental, emotional, sociocultural, sexual, spiritual) |
|
|
|
Occupation General |
Occupation General |
|
|
|
A client’s occupation information helps personal trainer determine |
Common movement patterns & typical energy expenditure levels during the course of an average day. |
|
|
|
Once occupational information is collected trainers can begin to recognize important clues about the client’s |
Muscular skeletal structure/function, potential health/physical limitations, & restrictions that could affect safety & efficacy of the program. |
|
|
|
Examples of occupation questions : Does your occupation require/causeSitting for long periods of time can lead to... |
Extended periods of sitting? Extended periods of repetitive movements? Shoes with heels? You anxiety (mental stress)? |
|
|
|
Sitting for long periods of time can lead to |
Tight hip flexors (rectus femoris, tensor fascia latae, iliopsoas) Postural and balances in the HMS |
|
|
|
Sitting for long periods of time over a computer leads to |
Shoulders and head to fatigue leading to postural imbalances. |
Rounded shoulders Forward head |
|
|
Low energy expenditure and potentially poor cardiorespiratory conditioning can be assumed when individuals |
Sit for prolonged periods of time. |
|
|
|
Repetitive movement is a |
Persistent motion that can cause musculoskeletal injury & dysfunction. |
|
|
|
What can create a pattern overload to muscles & Working with arms overhead for long periods may lead tojoints, which may lead to tissue trauma & eventually kinetic chain dysfunction? |
Repetitive movements |
|
|
|
Working with the arms OH For long periods may lead to |
Shoulder and neck soreness. This may be the result of : tightness in the latissimus dorsi & weakness in the rotator cuff. |
|
|
|
Working OH does not allow for |
Proper shoulder motion/stabilization during activity |
|
|
|
Wearing dress shoes with a puts the ankle complex in a |
A plantarflexed position for extended periods. |
|
|
|
Wearing heels for an extended time can cause tightness in the |
Gastrocnemius Soleus Achilles tendon |
|
|
|
Wearing heels can cause posture imbalances such as |
Decreased dorsiflexion Overpronation at the foot and ankle complex |
This can result in flattening the arch of the foot. |
|
|
Mental stress or anxiety can cause elevated |
Resting heart rate Blood pressure Ventilation at rest & exercise |
|
|
|
Mental stress can lead to abnormal or dysfunctional |
Breathing patterns. |
|
|
|
These abnormal breathing patterns caused by mental stress may cause |
postural or muscular skeletal muscle imbalances in the neck, shoulder, chest, and low back muscles. |
May lead to postural distortion & HMS dysfunction. |
|
|
Lifestyle or personal questions pertains to a clients general lifestyle activities & habits such as... |
Drinking, smoking, exercise, & sleeping habits as well as recreational activities & hobbies. |
|
|
|
Sample questions : client’s lifestyle |
Do you partake in any recreational activities (golf, tennis, skiing)? Do you have any hobbies (reading, gardening, working on cars)? |
|
|
|
Recreation refers to a client’s |
Physical activities outside of the work environment (leisure time). |
|
|
|
Many clients like to golf, ski, play tennis, or perform a variety of other sporting activities in their spare time, proper exercise training must be |
Incorporated to ensure that clients are trained in a matter that optimizes the efficiency of the HMS, without predisposing it to injury. |
|
|
|
Hobbies refer to |
Activities that a client might enjoy participating in on a regular basis. |
Gardening, working on cars, playing cards, reading, watching television, playing video games. |
|
|
Medical history is important because it |
Provides us with info about known/suspected chronic diseases, past/current injuries, health status, or surgeries. |
Coronary heart disease, high blood pressure, diabetes. |
|
|
All past or recent injuries should be recorded and discussed in sufficient enough detail to be able to |
Make decisions about whether exercise is recommended or a medical referral is necessary. |
|
|
|
Previous history of musculoskeletal injury is also a strong predictor of |
Future musculoskeletal injury during physical activity. |
|
|
|
Surgery will cause pain and inflammation that can alterMore than 75% of the American adult population is estimated tonight |
Neural control to the affected muscles/joints if not rehabilitated properly. |
|
|
|
More than 75% of the American adult population is estimated to not engage in |
At least 30 minutes of low-to-moderate physical activity on most days of the week. |
|
|
|
Chronic diseases include : |
CVD Coronary heart/artery disease Congestive heart failure Hypertension (high BP) High cholesterol/other blood lipid disorders Stroke/peripheral artery disease Lungs/breathing problems Obesity Diabetes mellitus Cancer |
|
|
|
Many seeking fitness exercise training advise from personal trainers will currently be under the care of |
A physician/medical professional & maybe taking one or more prescribed medications. |
|
|
|
What is a PDR? |
Physician’s desk reference |
|
|
|
Beta blockers (B-blockers) |
Anti-hypertensive (high BP), prescribed for arrhythmias (irregular HR). |
|
|
|
Calcium-channel blockers |
Prescribed for hypertension & angina (chest pain) |
|
|
|
Ankle sprains have been shown to decrease the |
Neural control to the gluteus medius/maximus muscles, leading support control of the lower extremities during functional activities. |
|
|
|
Knee injuries can cause a decrease in the number control to the muscles that |
Stabilize the patella and lead to further injury. |
|
|
|
Noncontact Knee injuries Are often the resultIf the ankle hip begins to function properly, this results in of |
Ankle/hip dysfunctions, such as the result of an ankle sprain. |
|
|
|
If the ankle/hip begins to function improperly, this results in |
Altered movement & force distribution of the knee. |
|
|
|
Low back injuries can cause decreased neural control to stabilizing muscles of the |
Core, resulting in poor stabilization of the spine, leading to dysfunction in the upper/lower extremities. |
|
|
|
Shoulder injuries cause altered neural control of the |
Rotator cuff muscles, leading to instability of the shoulder joint during functional activities. |
|
|
|
Entries that result from HMS and balances include repetitive |
Hamstring strain & groin strain, patella tendinitis (jumpers knee), plantar fasciitis (pain in heel/bottom of foot), posterior Tibialis tendinitis (shin splints), biceps tendinitis (shoulder pain), & headaches. |
There are 7 |
|
|
Beta blockers (B-blockers) |
Anti-hypertensive (high BP), prescribed for arrhythmias (irregular HR). |
Decreased HR Decreased BP |
|
|
Calcium-channel blockers |
Prescribed for hypertension & angina (chest pain) |
Increased/no change/decreased HR Decreased BP |
|
|
Nitrates |
Hypertension, congestive heart failure. |
Increased/no change HR Increased/no change BP |
|
|
Dieuretics |
Hypertension, congestive heart failure, & peripheral edema. |
No change in HR Decreased/no change in BP |
|
|
Broncodilators |
Corrects/prevents bronchial smooth muscle constriction in individuals with asthma & other pulmonary diseases. |
No change in HR No change in BP |
|
|
Vasodilators |
Hypertension & congestive heart failure. |
Increase/no change/decrease in HR Decrease in BP |
|
|
Antidepressants |
Various psychiatric & emotional disorders. |
Increase/no change in HR Decrease/no change in BP |
|
|
Objective information collected during a fitness assessment includes |
Resting exercise physiological measurement (BP & heart rate), resting Anthrometric measurements (ht, et, BFP, circumference measurements), in specific measures of fitness (muscular durance, flexibility, cardiorespiratory). |
|
|
|
Objective information collected un the fitness assessment can be used to |
Compare beginning baseline measures of fitness with measurements taken weeks, months, or even years later. |
|
|
|
Categories of objective information include |
Physiological measurements Buddy comp assess Cardiorespiratory assess Static posture assess Movement assess (dynamic posture) Performance assess |
There are 6 |
|
|
When checking the radial pulse consider |
Being gentle Taking it when calm Take all three test at the same time for accuracy |
|
|
|
To find the I’m checking the carotid pulse considercarotid pulse |
Look on the neck just to the side of the larynx. |
|
|
|
When checking the carotid pulse considerThe typical resting heart rate is between |
Being gentle Excessive pressure can decrease HR/BPleading to an accurate reading, possible dizziness, & fainting. Taken when calm |
|
|
|
The typical resting heart rate is between |
70-80 beats/min 70 bpm for males 75 bpm for females |
|
|
|
Resting heart rate can be used to calculate |
Target heart rate (THR) zones in which a client should perform cardio respiratory exercise. |
|
|
|
What are the 2 most common ways to calculate THR? |
Use a percentage of estimated maximal heart rate (straight percentage method) Use a percentage of heart rate reserve (Karvonen method) |
|
|
|
Straight percentage method (peak maximal heart rate) Is found by |
220-Age = HR max HR max X appropriate intensity (65-95%) at which the client should work while performing cardio respiratory exercise to calculate THR. |
|
|
|
There are how many training zones for THR? |
3 |
|
|
|
Resting HR and VP is a sensitive indicator of the client’s |
Overall cardio respiratory health & fitness status. |
|
|
|
Initial assess/reassess of a client’s HR & BP helps to gather valuable information that helps in the |
Design, monitoring, & progression of the clients exercise program. |
|
|
|
Resting HR is a fairly good indicator of overall cardiorespiratory fitness, where as exercise HR is a strong indicator of |
How a client’s cardiorespiratory system is responding/adapting to exercise. |
|
|
|
A pulse is created by |
Blood moving/pulsating through arteries each time the heart contracts. |
|
|
|
Heart rate |
Heart rate |
|
|
|
The two most common sites to record a pulse are the |
Radial (wrist) & carotid (neck) arteries. |
Use the carotid with caution |
|
|
The best time to record an accurate resting heart rate is |
Rising in the morning. |
|
|
|
The radio pulse can be found |
Along the right side of the arm in the line just above the thumb. |
|
|
|
When the pulse is felt count it for |
60 seconds |
Record the 60 second pulse rate average over the course of 3 days |
|
|
Target heart rate training zone 1 builds |
Aerobic base & aids in recovery. HR max X .65 HR max X .75 |
|
|
|
Target heart rate training zone 2 increases |
Aerobic & anaerobic endurance. HR max X .76 HR max X .85 |
|
|
|
Target heart rate training zone 3 builds |
High end work capacity HR max .86 HR max .95 |
|
|
|
Exercise intensity levels may need to be lower than |
66% depending on the clients initial physical condition. (40-55%) |
|
|
|
Heart rate reserve (HRR) method (Karvonen method) Establishes The most common and university accepted method of establishing exercise training intensity is |
Training intensity on the basis of the difference between the clients predicted HR max & they’re resting heart rate. |
|
|
|
The most common and university accepted method of establishing exercise training intensity is |
Selecting a predetermined training/THR based on a given percentage of oxygen consumption. |
|
|
|
Blood pressure |
The pressure of the circulating blood against the walls of the blood vessels after the blood is ejected from the heart. |
|
|
|
There are two parts to a blood pressure measurement what are they? |
Systolic (the top number) diastolic (the bottom number) |
|
|
|
Systolic represents the pressure within |
The arterial system after the heart contracts. |
|
|
|
Diastolic represents the pressure within |
The pressure within the arterial system of the heart is resting & filling with blood. |
|
|
|
According to the American Heart Association (AHA) an acceptable systolic blood pressure measurement for health is |
= 120 mm Hg of mercury (Hg)
|
|
|
|
An acceptable diastolic blood pressure is |
= 80mm Hg |
|
|
|
Fat free mass can be defined as |
Body weight except stored fat, this includes muscles, bones, water, connective/organ tissues, teeth. |
|
|
|
Fat mass includes |
Both essential fat (crucial for normal body functioning) & non-essential fat (storage fat/adipose tissue). |
|
|
|
Benefits of body composition assessment include |
Identifying clients health risk for excessive high/low levels of body fat. Promotes clients understanding. monitoring changes in body comp itself/associated with chronic disease. Helps estimate health bodyweight. Assists in exercise program design. Use as a motivational tool. Assess his effectiveness of nutrition/exercise choices. |
There are 7 |
|
|
Body fat typically ranges from ___ to ___ for men? |
10-20% |
|
|
|
Body fat typically ranges from ___ to ___ for women? |
20-30% |
|
|
|
Body fat recommendations for men and women are |
15% men 25% women |
|
|
|
Skinfold measurements |
Uses a caliper to estimate the amount of subcutaneous fat beneath the skin. |
|
|
|
Percent fat recommendations for men and women pictured |
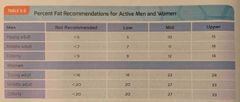
Back (Definition) |
|
|
|
Blood pressure is measured using an |
Aneroid sphygmomanometer, and inflatable cuff, a pressure dial, a bulb with a valve, & a stethoscope. |
|
|
|
When recording blood pressure instruct the client to |
Get in a comfortable see the position placing the appropriate size cuff on the clients arm just above the elbow. |
|
|
|
Have the client rest the alarm on |
A supported chair/own arm, placing the stethoscope over the brachial artery using minimal pressure. |
|
|
|
Rapidly inflate the cuff to |
20-30 mm Hg above the point at which the pulse can no longer be felt at the wrist. |
|
|
|
Release the pressure of the sphygmomanometer at a rate of about |
2 mm Hg/sec listening for a pulse |
|
|
|
To determine the systolic pressure listen for |
The first observation of the pulse. |
|
|
|
Diastolic pressure is determined when |
The pulse fades away. |
|
|
|
For greater reliability on the blood pressure assessment |
Repeat the procedure on the opposite arm. |
|
|
|
The relative percentage of body weight. Fat vs fat free tissue = Percent body fat |
The relative percentage of body weight. Fat vs fat free tissue = Percent body fat |
|
|
|
An acceptable diastolic blood pressure is |
= 80mm Hg |
|
|
|
Fat free mass can be defined as |
Body weight except stored fat, this includes muscles, bones, water, connective/organ tissues, teeth. |
|
|
|
Fat mass includes |
Both essential fat (crucial for normal body functioning) & non-essential fat (storage fat/adipose tissue). |
|
|
|
Benefits of body composition assessment include |
Identifying clients health risk for excessive high/low levels of body fat. Promotes clients understanding. monitoring changes in body comp itself/associated with chronic disease. Helps estimate health bodyweight. Assists in exercise program design. Use as a motivational tool. Assess his effectiveness of nutrition/exercise choices. |
There are 7 |
|
|
Body fat typically ranges from ___ to ___ for men? |
10-20% |
|
|
|
Body fat typically ranges from ___ to ___ for women? |
20-30% |
|
|
|
Body fat recommendations for men and women are |
15% men 25% women |
|
|
|
Skinfold measurements |
Uses a caliper to estimate the amount of subcutaneous fat beneath the skin. |
|
|
|
Percent fat recommendations for men and women pictured |

Back (Definition) |
|
|
|
Blood pressure is measured using an |
Aneroid sphygmomanometer, and inflatable cuff, a pressure dial, a bulb with a valve, & a stethoscope. |
|
|
|
When recording blood pressure instruct the client to |
Get in a comfortable see the position placing the appropriate size cuff on the clients arm just above the elbow. |
|
|
|
Have the client rest the alarm on |
A supported chair/own arm, placing the stethoscope over the brachial artery using minimal pressure. |
|
|
|
Rapidly inflate the cuff to |
20-30 mm Hg above the point at which the pulse can no longer be felt at the wrist. |
|
|
|
Release the pressure of the sphygmomanometer at a rate of about |
2 mm Hg/sec listening for a pulse |
|
|
|
To determine the systolic pressure listen for |
The first observation of the pulse. |
|
|
|
Diastolic pressure is determined when |
The pulse fades away. |
|
|
|
For greater reliability on the blood pressure assessment |
Repeat the procedure on the opposite arm. |
|
|
|
Percent fat recommendations for men and women pictured |

Back (Definition) |
|
|
|
Percent fat recommendations for active men & women |
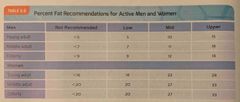
Back (Definition) |
|
|
|
Bioelectrical impedance |
Uses a portable instrument to conduct an electrical current through the body to estimate fat. |
|
|
|
Bioelectric impedance is based on |
Hypothesis that tissues that are high in water content conduct electrical currents with less resistance than those with Little water (adipose tissue). |
|
|
|
Underwater weighing (Hydrostatic weighing) is the |
Most common technique used for body comp. |
|
|
|
Bone, muscle, connective tissue (lean mass) do what during hydrostatic weighing |
Sink. |
|
|
|
Body fat does what during hydrostatic weighing? |
Float. |
|
|
|
Bone, muscle, connective tissue (lean mass) do what during hydrostatic weighing? |
Sink. |
|
|
|
A person with a larger percentage of lean body mass will weigh |
More in the water, ultimately having a lower body fat percentage. |
|
|
|
Formula on how to calculate ones fat mass & lean body mass : |
Body fat % X scale wt = fat mass Scale wt - fat mass = lean mass |
|
|
|
Calculate the fat mass in lean body mass of a 40-year-old woman weighing 130 lbs |
Fat Mass : .28 (bf%) X 130 (swt) = 36lbs of BF
Lean Body Mass : 130(swt) - 36(lbs of wt) = 94lbs of LBM |
|
|
|
A circumference measurement is a measure of the |
Girth of body segments (arm, thigh, waist, & hip) |
|
|
|
Circumference methods are affected by both |
Fat & muscle, therefore I do not provide accurate estimates of fatness. |
|
|
|
Some of the uses & benefits of circumference measurements include : |
Can be used on obese clients. Good for comparisons/progressions. Good for assessing fat pattern & distribution. Inexpensive. Little technician error. Easy to record. used for waist concert conference. Used for waist to hip ratio (WHR). |
|
|
|
The most important factor to consider when taking circumference measurements is |
Consistency, make sure that the tape is taut & level around the area being measured. |
|
|
|
A person with more body fat will have a |
Lighter body of water & higher percentage of body fat. |
|
|
|
Skinfolds (SKF) tests has the assumption that the amount of fat present in the subcutaneous regions of the body is |
Proportional to overall body fitness. |
|
|
|
Recommendations for assessing body copies in skin folds is :In a SM uses the |
Train with those skilled in SKF & frequently compare results. Take a minimum of 2 measurements at each site, each site must be within 1-2 mm to take average at each site. Open jaw of caliper before removing from site. Be meticulous when locating anatomic landmarks. Don’t measure SKF immediately after exercise. Instruct clients ahead of time regarding test protocol. Avoid performing SKFs on extremely obese clients. |
|
|
|
In a SM uses the Durnin (Durnin-Womersley) formula To calculate a client’s |
Percentage of body fat. |
|
|
|
Durban formula’s 4 sites of skinfold measurements are as follows : |
Biceps Triceps Subscapular Iliac crest |
|
|
|
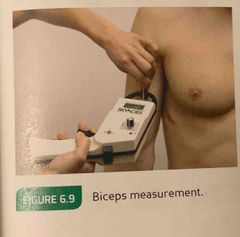
Durnin bicep measurement is |
A vertical fold on the front of the arm over the biceps muscle, halfway between the shoulder and the elbow. |
|
|
|
A vertical fold on the back of the upper arm, with the arm relaxed and held really at the side. Taken halfway between the shoulder right now though. |
A vertical fold on the back of the upper arm, with the arm relaxed and held really at the side. Taken halfway between the shoulder right now though. |
|
|
|
Durnin subscapular measurement is |
A 45° angle fold of 1-2 cm, below the inferior angle of the scapula. |
|
|
|
Durnin iliac crest measurement is |
A 45° angle fold, taken just above the iliac crest & medial to the axillary line. |
|
|
|
A person with a larger percentage of lean body mass will weigh |
More in the water, ultimately having a lower body fat percentage. |
|
|
|
Formula on how to calculate ones fat mass & lean body mass : |
Body fat % X scale wt = fat mass Scale wt - fat mass = lean mass |
|
|
|
Calculate the fat mass in lean body mass of a 40-year-old woman weighing 130 lbs |
Fat Mass : .28 (bf%) X 130 (swt) = 36lbs of BF
Lean Body Mass : 130(swt) - 36(lbs of wt) = 94lbs of LBM |
|
|
|
A circumference measurement is a measure of the |
Girth of body segments (arm, thigh, waist, & hip) |
|
|
|
Circumference methods are affected by both |
Fat & muscle, therefore I do not provide accurate estimates of fatness. |
|
|
|
Some of the uses & benefits of circumference measurements include : |
Can be used on obese clients. Good for comparisons/progressions. Good for assessing fat pattern & distribution. Inexpensive. Little technician error. Easy to record. used for waist concert conference. Used for waist to hip ratio (WHR). |
|
|
|
Durnin bicep measurement is |
A vertical fold on the front of the arm over the biceps muscle, halfway between the shoulder and the elbow. |
|
|
|
A vertical fold on the back of the upper arm, with the arm relaxed and held really at the side. Taken halfway between the shoulder right now though. |
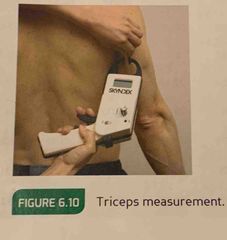
A vertical fold on the back of the upper arm, with the arm relaxed and held really at the side. Taken halfway between the shoulder right now though. |
|
|
|
Durnin subscapular measurement is |
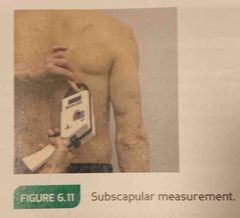
A 45° angle fold of 1-2 cm, below the inferior angle of the scapula. |
|
|
|
Durnin iliac crest measurement is |
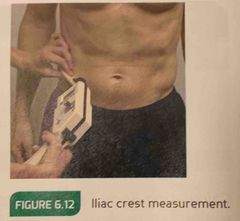
A 45° angle fold, taken just above the iliac crest & medial to the axillary line. |
|
|
|
In a SM uses the Durnin (Durnin-Womersley) formula To calculate a client’s |
Percentage of body fat. |
|
|
|
Durban formula’s 4 sites of skinfold measurements are as follows : |
Biceps Triceps Subscapular Iliac crest |
|
|
|
Durnin bicep measurement is |
A vertical fold on the front of the arm over the biceps muscle, halfway between the shoulder and the elbow. |
|
|
|
A vertical fold on the back of the upper arm, with the arm relaxed and held really at the side. Taken halfway between the shoulder right now though. |
A vertical fold on the back of the upper arm, with the arm relaxed and held really at the side. Taken halfway between the shoulder right now though. |
|
|
|
Durnin subscapular measurement is |
A 45° angle fold of 1-2 cm, below the inferior angle of the scapula. |
|
|
|
Durnin iliac crest measurement is |
A 45° angle fold, taken just above the iliac crest & medial to the axillary line. |
|
|
|
Across the Adam’s apple. |
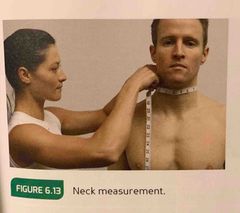
Across the Adam’s apple. |
|
|
|
Chest circumference measurement |
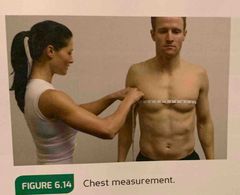
Across the nipple line. |
|
|
|
Waist circumference measurement |
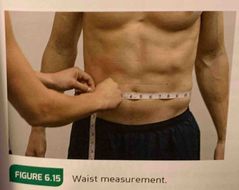
The narrowest point of the waist, below the rib cage & just above the top of the hip bones. If there is no apparent narrowing of the waste, measure at the naval. |
|
|
|
Hips circumference measurement |
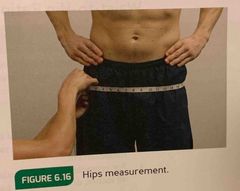
Feet together, measure circumference at the widest portion of the buttocks. |
|
|
|
Thigh circumference measurement |
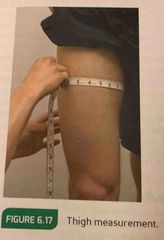
Measure 10 inches above the top of the patella for standardization. |
|
|
|
Calf circumference measurement |
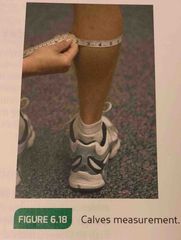
The maximal circumference between the ankle and the knee, measure the calves. |
|
|
|
Bicep circumference measurement |
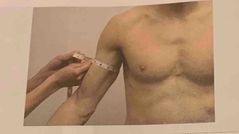
At the maximal circumference of the biceps, measure with arm extended, palm facing forward. |
|
|
|
Risk for disease increases with a BMI of |
25 or more. |
|
|
|
Individuals who are underweight are also |
At risk for premature death or illness. |
|
|
|
Most to use clinical application of girth measurements. |
Most to use clinical application of girth measurements. |
|
|
|
The waist to hip ratio assessment is important becauseThe waist to hip ratio can be computed by dividing the |
There is correlation between chronic diseases & fat stored in the midsection. |
|
|
|
The waist to hip ratio can be computed by dividing the |
Waist measurement by the hip measurement. |
|
|
|
What are the 3 steps to compute the waist measurement? |
1. Measure the smallest part of the clients waist, without instructing the clients draw in the stomach. 2. Measure the largest part of the clients hips. 3. Compute the waist to hip ratio by : waist/hip |
|
|
|
If a clients waist measures 30in & hips Measure 40in what is the waist to hip ratio? |
30/40=.75 |
|
|
|
Body mass index (BMI) is a roof assessment based on the concept that |
A persons weight should be proportional to their height. |
|
|
|
An elevated BMI is linked to |
Increased risk of disease, especially if associated with a larger waist circumference. |
|
|
|
What are the two ways to calculate BMI? |
1. BMI = Wt (kg)/Ht (m^2) 2. BMI = [Wt (lbs)/Ht (in^2)] X 703 |
|
|
|
The lowest risk for disease lies within a BMI range of |
22-24.9 |
|
|
|
Body mass index classification chart |
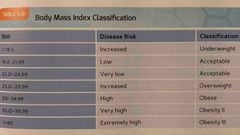
Back (Definition) |
|

