![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
36 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Carbohydrates are compounds containing |
Hydrogen, oxygen, & carbon. They are classified as sugars (complex)(cellulose), starches (complex), & fiber. |
|
|
|
The definition of sugar, as it would appear on a food label, is |
Any monosaccharide or disaccharide. |
|
|
|
A monosaccharide is a |
Single sugar unit, many of which are connected to make: starch (the storage form of carbohydrates in plants) Glycogen (the storage form of carbohydrates in humans) |
|
|
|
Monosaccharides include |
Glucose (blood sugar) Fructose (fruit sugar) Galactose |
There are 3 |
|
|
Disaccharides are |
2 sugar units including : Sucrose (common sugar) Lactose (milk sugar) Maltose |
There are 3 |
|
|
Polysaccharides are |
Long chains of monosaccharide units linked together, found in foods containing starch & fiber. |
|
|
|
Polysaccharides are often called |
Complex carbohydrates , Including starch found in plants, seeds, & roots. |
|
|
|
Complex carbohydrates are primarily |
Starch & fiber, & the starch is digested to glucose. |
|
|
|
What is a part of the plants that cannot be digested by human got enzymes? |
Dietary fiber |
|
|
|
Dietary fiber passes through what? How is it expelled? |
The small intestine & colon Fecal material/fermented & used as food by the good bacteria. |
|
|
|
Carbohydrates help to regulate what? |
Digestion & utilization of protein & fat. |
|
|
|
Simple sugars can be easily___ & are found in ___. |
Digested Honey & fruits |
|
|
|
Double sugars, such as table sugar, require what? |
Some digestive action. |
|
|
|
Starches, such as those found in whole grain, require what type of digestion? |
Prolonged enzymatic action to be broken down into simple sugars (glucose) for utilization. |
|
|
|
Cellulose is commonly found in what? How is it digested? |
The skins of fruits & vegetables They are largely in digestible by humans, contributing little energy value to the diet. |
|
|
|
What provides the bulk necessary for intestinal motility & aids in elimination? |
Cellulose |
|
|
|
Glycemic index G.I. is the rate at which |
Ingested carbohydrates raise blood sugar & it’s accompanying effect on insulin. |
|
|
|
How is the G.I. for food determined? |
When the particular food is consumed by itself on an empty stomach. |
|
|
|
What can alter the glycemic affect of single foods? |
Mixed meals of proteins Other carbohydrates Fat |
There are 3 ways |
|
|
Foods lower on the glycemic index are good sources of |
Complex carbohydrates High in fiber & there are two overall nutritional value |
There are 2 |
|
|
Glycemic index (G.I.) : |

Back (Definition) |
|
|
|
Glycemic index (GI) for assorted foods : |
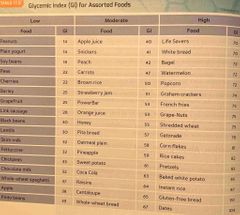
Back (Definition) |
|
|
|
Through the process of digestion and absorption, all disaccharides & polysaccharides are ultimately converted into what? |
Simple sugars such as fructose or glucose. |
|
|
|
Gradual breakdown of large starch molecules by enzymes in digestion : |
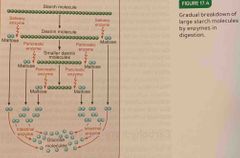
Back (Definition) |
|
|
|
Fructose must be converted into what before it can be used for energy? |
Into glucose in the liver. |
|
|
|
Some of the glucose blood sugar is used as fuel by tissues of the |
Brain Nervous system Muscles |
|
|
|
Because humans are periodic eaters, a small portion of glucose is converted into what? Where is it stored? |
Glycogen after a meals Within the liver & muscles. |
|
|
|
Any excess glycogen gets converted into what? Where is the store? |
Converted into fat Stored throughout the body as a reserve source of energy. |
|
|
|
When total caloric intake exceeds output, any excess carbohydrate, dietary fat, or protein may be stored as what? |
Body fat until the energy expenditure once again exceeds energy input. |
|
|
|
What is one of the greatest contributions made by dietary complex carbohydrate? |
Fiber |
|
|
|
Higher intakes of dietary fiber are associated with what? |
Lower incidence of heart disease & certain types of cancers. |
|
|
|
Fiber is what type of carbohydrate? |
Indigestible |
|
|
|
What are the 2 types of dietary fiber? |
Soluble Insoluble |
|
|
|
Soluble fiber is |
Dissolved by water & forms a gel like substance in the digestive tract. |
|
|
|
What are the benefits of soluble fiber? |
Moderating blood glucose levels Lowering cholesterol |
|
|
|
What are some good sources of soluble fiber? |
Oatmeal Oats Legumes (peas, beans, lentils) Barley Many uncooked fruits & vegetables (oranges, apples, carrots) |
There are 4 |

