![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
17 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Amino acids that form pyruvate
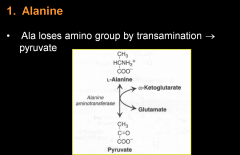
1 Alanine |
Ala loses amino group by transamination pyruvate
|
|
|
|
Amino acids that form pyruvate
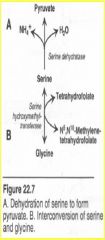
Serine |
Ser pyruvate by serine dehydratase
Ser glycine and N5, N10-methylenetetrahydrofolic acid by serine hydroxymethyltransferase |
|
|
|
Amino acids that form pyruvate
3 Glycine |
Glycine Ser by addition of methylene group from N5, N10-methylenetetrahydrofolic acid
Glycine CO2 + NH4+ by the glycine cleavage complex |
|
|
|
Nonketogenic
deficiency of = |
glycine cleavage complex
info: Glycine is a major inhibitory neurotransmitter |
|
|
|
Amino acids that form pyruvate
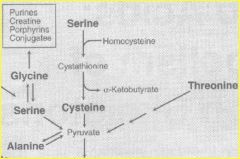
4 Cystine |
Cystine reduced to cysteine using NADH + H+
Cysteine -- desulfuration --- pyruvate |
|
|
|
Amino acids that form pyruvate
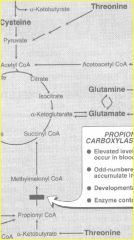
5 Threonine |
converted to pyruvate or a-ketobutyrate, which forms succinyl CoA
|
|
|
|
Amino acids that form fumarate
Phenylalanine and Tyrosine Degradation thereof = |
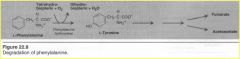
|
|
|
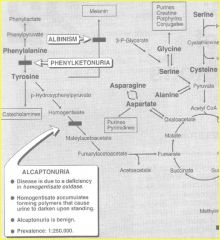
Diseases associated with tyrosine metabolism
Albinism deficiency of tyrosinase |
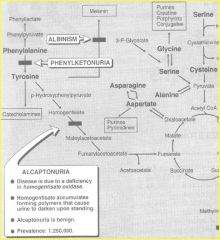
PKU
deficiency of phenylalanine hydroxylase (classic PKU) or tetrahydrobiobterin reductase (malignant PKU |
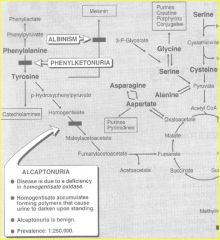
Alkaptonuria
deficiency of homogentisate oxidase |
|
|
Amino acids that form Succinyl CoA
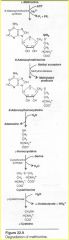
1Methionine |
Met S-adenosylmethionine (SAM)
SAM is a major methyl-group donor in 1-C metabolism |
|
|
|
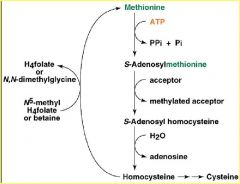
Resynthesis of methionine
requires vitamin B12 |
|
|
|
|
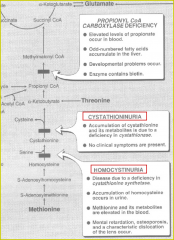
Hyperhomocysteinemia
|
homocystinuria occurs due to deficiency of cystathione synthase
|
|
|
|
Hyperhomocysteinemia
4 dz s/s |
- lens dislocation after age 3 as well as other ocular abnormalities
- osteoporosis develops during childhood, mental retardation - lipid deposits form atheromas - homocysteine can have other effects: lipid oxidation and platelet aggregation leads to fibrosis and calcification of atherosclerotic plaques |
|
|
|
Diseases associated with methionine metabolism
|
|
|
|
|
Amino acids that form Succinyl CoA
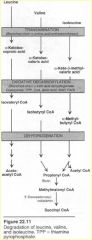
Valine and isoleucine |
branched chain amino acids
methylmalonyl CoA mutase requires B12 Maple Syrup Urine Disease (MSUD) due to a deficiency in branched chain a-keto acid dehydrogenase |
|
|
|
Diseases associated with threonine metabolism
|
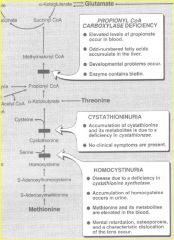
|
|
|
|
Amino acids that form Succinyl CoA
Threonine |
can also be converted to pyruvate
|
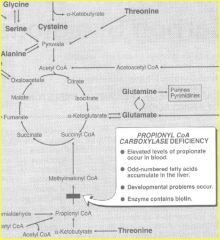
|
|
|
Amino acids that form Acetyl CoA or Acetoacetyl CoA
4 amino acids form acetyl CoA or acetoacetyl CoA directly without forming pyruvate: |
leucine
isoleucine lysine phenylalanine and tyrosine also give rise to |
acetoacetate
acetyl CoA (also propionyl CoA) acetyl CoA acetoacetate during their catabolism |

