![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
11 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Clinical Klinefelter Syndrome
|
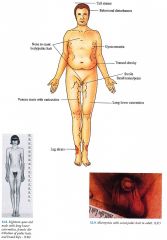
|
|
|
Inheritance
|
Not inherited
|
|
|
Prenatal
|
Amniocentesis (second trimester): chromosome analysis
|
|
|
Incidence
|
Approximately 1:500 males; increased frequency with advanced maternal age
|
|
|
Age at Presentation
|
Childhood to puberty
|
|
|
Pathogenesis
|
Several X aneuploicly variants (80% 47, XXY) secondary to nonclisjunction in maternal or paternal meiosis producing phenotype
|
|
|
Clinical
|
Skin
Varicose veins, arterial and venous leg ulcers Hair Scant body and pubic hair Musculoskeletal Tall stature, low upper to lower body ratio with long legs, obesity, gynecomastia Genitourinary Small testes with/without small penis, hyalinization and fibrosis of serniniferous tubules, infertility with lack of spermatogenesis Endocrine Markedly decreased levels of testosterone Central Nervous System Delayed speech as child, dull mentality, antisocial behavioral disturbances |
|
|
D/Dx
|
Homocystinuria
|
|
|
Lab
|
Chromosome analysis Decreased serum testosterone level; increased urinary gonaclotropins
|
|
|
Management
|
Referral to enclocrinologist testosterone replacement at puberty
Referral to psychologist psychiatrist therapy, behavioral modification Referral to vascular surgeon/dermatologist leg ulcer care |
|
|
Prognosis
|
Normal life span with improved secondary sexual characteristics with testosterone; infertile, many lead married lives
|

