![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
13 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Clinical Menke's Syndrome
|
|
|
|
Synonym
|
Menkes Kinky hair syndrome
Occipital Horn Syndrome |
|
|
Inheritance
|
X linked recessive; MKN or ATP7A gene on Xq 13
|
|
|
Prenatal
|
DNA analysis
Amniocentesis/ (CVS) increased incorporation of copper in cultured amniotic fluid cells |
|
|
Incidence
|
1:35,000 in Australia, 1:300,000 in Europe; males only; approximately 90% with classic, severe form, 10% with milder OHS
|
|
|
Age at Presentation
|
First few months of life
|
|
|
Pathogenesis
|
Mutations in MKN or ATP7A, a gene encoding the copper binding enzyme adenosine triphosphatase (ATPase), leads to defective copper transport and metabolism with subsequent low levels of serum copper; phenotype reflects deficiency of copper-dependent enzyme activity in various systems
|
|
|
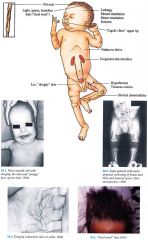
Clinical
|
Hair
Pili torti most common; trichorrhexis nodosa, monilethrix described; hypopigmented, sparse, short, brittle, "steel wool" quality; sparse, broken horizontal eyebrows; sparse eyelashes Skin Hypopigmented, "doughy" consistency with laxity, pudgy cheeks, Cupid's bow upper lip Central Nervous System Progressive deterioration with lethargy, seizures, mental and motor retardation, hyp.ertonia, hypothermia |
|
|
Clinical
|
Musculoskeletal
Failure to thrive, frontal bossing, wormian bones in sagittal and lambdoid sutures, metaphyseal widening with spurs in long bones, fractures OHS: occipital horns (exostosis at insertion of trapezius and sternocleidomastoid muscles), abnormal facies, short flat clavicles, elbow deformities secondary to radial subluxation Cardiovascular Tortuous arteries (especially brain) Genitourinary Variety of anomalies |
|
|
D/Dx
|
Battered child syndrome
Argininosuccinic aciduria (p. 278) Bjbrnstad syndrome (p. 276) |
|
|
Lab
|
Serum copper, ceruloplasmin levels
DNA analysis |
|
|
Management
|
Parenteral copper histidine if initiated first 8 weeks of life may be of benefit
Antiseizure medications, pamidronate has been helpful in preventing fractures in one study |
|
|
Prognosis
|
Progressive deterioration with death by 2 3 years of age associated with pneumonia
|

