![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
12 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
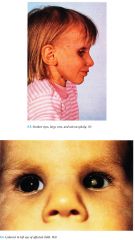
Clinical Cockayne Syndrome
|
|
|
|
Inheritance
|
Autosomal recessive; Cockayne syndrome group A (CSA): ERCC8 gene on chromosome 5
Cockayne syndrome group B (CSB): ERCC6 gene on 10q11 |
|
|
prenatal
|
Amniocentesis/amniotic fluid cell culture deficient RNA synthesis and increased c death after UV irradiation
DNA analysis |
|
|
Incidence
|
Very rare; M=F;
CSB most common (80% of cases) |
|
|
Age at Presentation
|
Birth to 2 years old; some later, into teens
|
|
|
Pathogenesis
|
Mutations in ERCC8 and ERCC6 impairs DNA repair in active genes specifically, rendering the patient hypersensitive to UV and leads to progressive neurodegeneration;
overlap of XPB, XPD, XPG with Cockayne exists in small number of patients |
|
|
Clinical
|
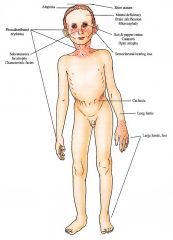
Skin
Photosensitive eruption with erythema and scale in "butterfly" distribution on face may resolve with hyperpigmentation and atrophy; Subcutaneous fat loss on face with resultant sunken eyes, aged appearance Craniofacial/Body Habitus Cachectic dwarf with microcephaly, thin nose, large ears ("Mickey Mouse" appear ance); disproportionately long limbs with joint contractures; large, cold hands and feet |
|
|
Clinical
|
Nervous System
Diffuse clemyelination of the (CNS) and peripheral nerves with progressive neurologic deterioration; mental retardation; intracranial calcifications Ear Nose Throat Sensorineural deafness Eyes: "Salt and pepper" retinal pigment, miotic pupils may be difficult to dilate, cataracts, optic atrophy Teeth Dental caries |
|
|
DDx
|
Bloom syndrome (p. 234)
Roth m u nd Thomson syndrome (p. 238) Hartnup syndrome (p. 250) XP (p. 174) Progeria (p. 156) |
|
|
Lab
|
DNA analysis
Blood serum UV irradiated cells with decreased DNA, RNA synthesis Brain computed tomography (CT) calcifications; cortical atrophy |
|
|
Management
|
Photoprotection with sunscreens, clothing, avoidance of sun
Referral to neurologist, ophthalmologist, ear nose throat (ENT) specialist, dentist |
|
|
Prognosis
|
Progressive, unremitting neurologic degeneration with death by second to third decade
|

