![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
22 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Clinical EEC Syndrome
|
|
|
|
Synonym
|
Ectrodactyly-Ectodermal Dysplasia - Cleft lip/palate Syndrome
|
|
|
Inheritance
Prenatal |
Autosomal dominant; three gene loci identified:
EEC I on 7ql 1 21; EEC2 on chromosome 19, and EEC3, the p63 gene on 3q27 (majority of cases) DNA analysis |
|
|
Incidence
|
Rare; approximately 150 cases reported; M = F
|
|
|
Age at Presentation
|
Birth
|
|
|
Pathogenesis
|
Mutations in the p63 gene, a tumor suppressor gene required for normal limb, craniofacial, and epidermal morphogenesis, are responsible for the majority of cases; gene on chromosome 19 may be a modifying gene that modulates the phenotypic expression of p63 mutations
|
|
|
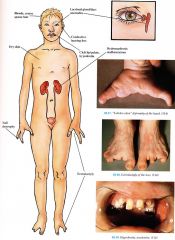
Clinical
|
Skin
Dry, scaling; thickening of palms, soles; normal sweat Hair Coarse, blonde, dry, can be sparse; axillary, pubic hair sparse Nails Dystrophic (even on unaffected fingers) Teeth Hypoclontia, premature loss of permanent teeth, problems related to cleft Musculoskeletal Ectroclactyly (80% to 1 00%) abnormal development of the median rays of feet > hands " lobster claw deformity"; cleft palate with/or without lip (70% to 100%) Ear Nose Throat Chronic otitis media, secondary conductive hearing loss (50%) Genitourinary Hydronephrosis, structural malformations (approximately 30%) Ophthalmologic Lacrimal gland/duct abnormalities |
|
|
D/Dx
|
AEC syndrome
Aplasia cutis congenita with Iimb defects Limb mammary syndrome |
|
|
Lab
|
Films to evaluate cleft, limbs
Renal ultrasound |
|
|
Management
|
Referral to plastic surgeon cleft repair team
Referral to orthopedist limb repair Referral to ENT antibiotics, follow for hearing loss Referral to dentist after cleft repair Referral to ophthalmologist, urologist based on signs, symptoms |
|
|
Prognosis
|
Early intervention will improve overall outcome
|
|
Clinical AEC Syndrome
|
|
|
|
Synonym
|
Ankyloblepharon filiforme adenatum Ectodermal dysplasia Cleft palate-Hay Wells syndrome
|
|
|
Inheritance
|
Autosomal dominant; p63 gene on 3q27
|
|
|
Preanatal
|
DNA analysis
Ultrasound |
|
|
Incidence
|
Rare; M=F
|
|
|
Age at Presentation
|
Birth
|
|
|
Pathogenesis
|
Heterozygous missense mutations in the sterile alpha motif (SAM) domain of the p63 tumor suppressor gene contribute to phenotype in many cases
|
|
|
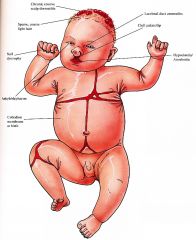
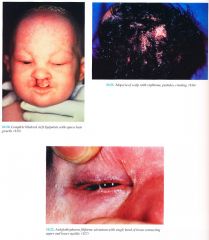
Clinical
|
Skin
Birth Collodion membrane like with erythroderma, scale, erosions; sheds to reveal dry, thin skin scalp Chronic erosive dermatitis with granulation tissue, crusting, bacterial superinfection Hair Scalp hair is sparse, wiry, light color, scarring alopecia Sparse body hair, eyelashes, eyebrows Nails Dystrophic, absent Eyes Ankyloblepharon (fusion of eyelids with strands of skin) (70%); lacrimal duct atre¬sia/obstruction with secondary conjunctivitis, blepharitis Head/Neck Cleft palate with/or without lip (80%), anodontia/hypodontia, malformed ears, chronic otitis with secondary hearing loss |
|
|
D/Dx
|
EEC syndrome (p. 288)
Rapp Hodgkin syndrome CIE (p. 12) Epidermolysis bullosa (p. 200) |
|
|
Lab
|
Bacterial cultures of skin
Head films DNA analysis |
|
|
Management
Prognosis |
Referral to plastic surgeon cleft repair team Referral to ophthalmology surgical lysis of ankyloblepharon, general ophthalmo¬logic care Referral to dermatologist emolliation, infection surveillance, gentle scalp care
Early intervention will lead to improved outcome |

